Abstract
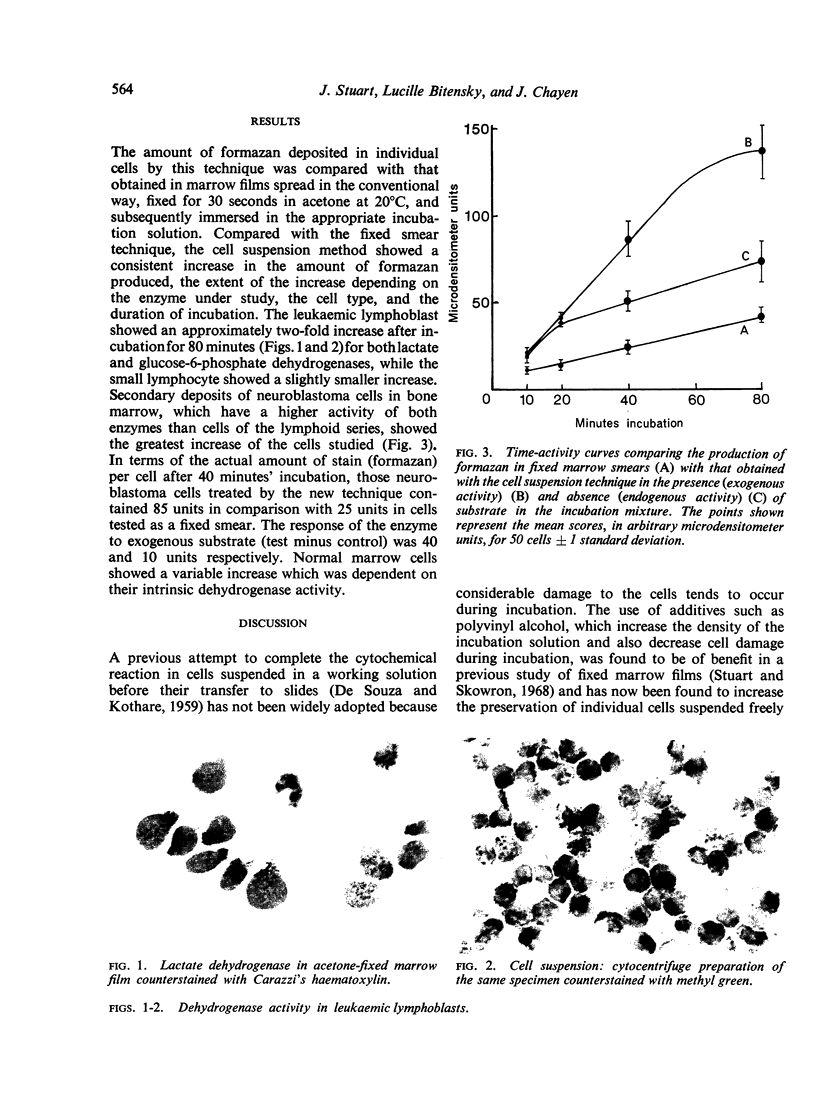
A new technique for the quantitative estimation of glycolytic and respiratory enzyme activity in intact and unfixed bone marrow and peripheral blood cells is described. The method gives a two- to three-fold increase in demonstrable enzyme activity per cell compared with existing techniques using fixed marrow film preparations, and is particularly applicable to the study of relatively fragile cells such as the leukaemic lymphoblast.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DE SOUZA E. J., KOTHARE S. N. A method for the cytochemical demonstration of succinic dehydrogenase in human leucocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1959 Mar;7(2):77–79. doi: 10.1177/7.2.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J., Elves M. W. Studies of lymphocytes and their derivative cells in vitro. II. Enzyme cytochemistry. Acta Haematol. 1967;37(1):42–52. doi: 10.1159/000209051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAGLINO D., HAYHOE F. G. Acetone fixation for the cytochemical demonstration of dehydrogenases in blood and bone marrow cells. Nature. 1960 Jul 2;187:85–86. doi: 10.1038/187085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACKTOR B., DICK A. R. Alpha-glycerophosphate and lactic dehydrogenases of hematopoietic cells from leukemic mice. Cancer Res. 1960 Oct;20:1408–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J., Skowron P. N. A cytochemical study of marrow enzymes in megaloblastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1968 Nov;15(5):443–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]