Abstract
In vivo, ectopic accumulation of fatty acids in muscles leads to alterations in insulin signaling at both the IRS1 and Akt steps. However, in vitro treatments with saturated fatty acids or their derivative ceramide demonstrate an effect only at the Akt step. In this study, we adapted our experimental procedures to mimic the in vivo situation and show that the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) is involved in the long-term effects of saturated fatty acids on IRS1. C2C12 or human muscle cells were incubated with palmitate or directly with ceramide for short or long periods, and insulin signaling pathway activity was evaluated. PKR involvement was assessed through pharmacological and genetic studies. Short-term treatments of myotubes with palmitate, a ceramide precursor, or directly with ceramide induce an inhibition of Akt, whereas prolonged periods of treatment show an additive inhibition of insulin signaling through increased IRS1 serine 307 phosphorylation. PKR mRNA, protein, and phosphorylation are increased in insulin-resistant muscles. When PKR activity is reduced (siRNA or a pharmacological inhibitor), serine phosphorylation of IRS1 is reduced, and insulin-induced phosphorylation of Akt is improved. Finally, we show that JNK mediates ceramide-activated PKR inhibitory action on IRS1. Together, in the long term, our results show that ceramide acts at two distinct levels of the insulin signaling pathway (IRS1 and Akt). PKR, which is induced by both inflammation signals and ceramide, could play a major role in the development of insulin resistance in muscle cells.
Keywords: Akt PKB, ceramide, protein kinase RNA-activated (PKR), skeletal muscle, type 2 diabetes, insulin signaling
Introduction
In healthy subjects, the balance between glucose production and utilization is controlled carefully. When circulating glucose reaches a critical threshold, pancreatic β cells secrete insulin, which increases glucose uptake by skeletal muscles and inhibits hepatic glucose production. Under conditions of lipid oversupply from the diet, the capacity of adipose tissue to store fatty acids is overwhelmed, and fatty acids accumulate in peripheral tissues such as skeletal muscles or liver. Strong evidence indicates that lipid accumulation in peripheral tissues is linked to the development of insulin resistance observed during obesity or type 2 diabetes. In rodents fed a high-fat diet (HFD),3 insulin resistance is observed in skeletal muscle because of alteration of the insulin signaling pathway both at the IRS1 and Akt steps (1–3).
Among lipids, ceramide is involved in the onset of muscle insulin resistance (4). Ceramide is distributed widely in cell membranes where, beyond a structural function, it has a key role in intracellular signaling, regulation of growth, proliferation, migration, apoptosis, and differentiation (5, 6). Under conditions of fatty acid overload, ceramide is mainly synthetized by de novo synthesis from saturated fatty acids such as palmitate (4).
The key role of ceramide in diet-induced insulin resistance has been demonstrated in studies using genetic or pharmacological inhibition. For example, inhibition of serine palmitoyl transferase, the first enzyme that regulates de novo synthesis of ceramide from palmitate (7), is sufficient to restore muscle and whole-body insulin sensitivity in animals fed a HFD (8–10). The mechanisms by which ceramide inhibits insulin signaling have been elucidated in vitro, but they only partially recapitulate what is observed in vivo in muscles of HFD-fed animals. We and others have shown in muscle cell lines that ceramide does not target the insulin signaling pathway through an inhibition of IRS1 activity but, rather, by specifically inhibiting Akt by two alternative mechanisms involving atypical protein kinase Cζ (PKCζ) (11–15) or protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) (16). We have demonstrated recently that the ceramide-activated PKCζ pathway prevails in human myotubes (17). Although the mechanisms by which ceramide inhibits Akt are now well documented, those involved in the inhibition of IRS1 remain unknown.
The double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) could play a role in this process. PKR is an interferon-induced protein that is part of the innate immune response and inhibits viral replication. During viral infection, PKR is activated by double-stranded RNAs produced by viruses. The PKR main target is the eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (eiF2α), phosphorylation of which leads to translation inhibition and enables the cell to block viral protein translation (18). PKR also plays an important role in modulating insulin signaling (19–21). Mice with a global PKR invalidation display improved insulin sensitivity when fed an HFD (20). Chronic administration of PKR inhibitors to obese and diabetic mice improves both their insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance (21). In fibroblasts, PKR interferes directly with insulin signaling by phosphorylating IRS1 on serine residues or indirectly by activating stress proteins such as JNK (22).
Because both palmitate and ceramide are PKR activators (19), we hypothesize that PKR could be the missing link between ceramide and its deleterious effects on insulin signaling at the IRS1 level in muscle cells. In this study, we provide evidence that palmitate and ceramide inhibit insulin signaling acutely at the Akt level and chronically at the IRS1 level through a PKR/JNK pathway.
Experimental Procedures
Reagents
Reagent-grade chemicals, insulin, palmitate, BSA, and the JNK inhibitor SP600125 were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. C2-ceramide and imoxin were obtained from Calbiochem. Complete protein phosphatase inhibitor tablets were obtained from Boehringer-Roche Diagnostics. Antibodies against native Akt, Ser473 Akt, Thr308 Akt, Thr183/Tyr185 JNK, β-actin, and native IRS1 were from Cell Signaling Technology (New England Biolabs). Thr451 PKR and native PKR were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Ser307 IRS1 and Tyr612 IRS1 were from Upstate. Horseradish peroxidase anti-rabbit and anti-mouse IgGs were from Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, and the enhanced chemiluminescent substrate was from Pierce-Perbio Biotechnology. 2-Deoxy-[3H]d-glucose was from PerkinElmer Life Sciences. PKR siRNA sequences and non-target siRNA were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, and DharmaFECT transfection reagent was from Thermo Scientific.
Animals
Ten male C57/BL6 mice (Charles River Laboratories) were housed in a temperature-controlled room and maintained on a 12/12-h light-dark cycle and had free access to food and water. Mice were assigned randomly to a low-fat diet (10% calories from fat, Research Diets Inc.) or an HFD (60% calories from fat, Research Diets Inc.) and fed their respective diet for 8 weeks before being sacrificed. Gastrocnemius muscle was collected, snap-frozen, and stored at −80 °C. All procedures were approved by the Regional Ethics Committee in Animal Experiments no. 3 of Ile-de-France.
Cell Culture
C2C12 myoblasts were grown and differentiated as myotubes as described previously (23).
Human Skeletal Muscle Cells
Biopsies from healthy adult lean volunteers were obtained in the context of approved preclinical and clinical trials (24) and via the Tissue Bank for Research (Myobank) of the French Association against Myopathies in agreement with the French bioethical law (law no. 94-654, July 29, 1994, modified January22, 2002) regarding informed consent. Muscle samples from adult diabetic patients were obtained from healthy tissue after leg amputation. Donors had no clinical signs of muscular disease, and sampled tissues had no bacterial contamination. Fresh muscle samples were minced and dissociated enzymatically with collagenase. Satellite cells were purified, grown, and differentiated as myotubes as described previously (23).
Immunoblotting
Frozen tissues or cells were homogenized in an appropriate volume of lysis buffer, and cell lysates were subjected to SDS/PAGE and immunoblotted as described previously (25).
Fatty Acid Treatment
Cells were treated with palmitate conjugated with fatty acid-free BSA as described previously (23).
Analysis of Sphingolipid Content
Sphingolipids were extracted and assessed as described previously (26).
Real-time Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
Total RNA was isolated as described previously (23). Real-time quantitative RT-PCR analyses were performed as described previously (23). Primer sequences for PKR expression analysis were as follows: 5′-CCTGTCCTCTGGTTCTTTTGCT-3′ and 5′-GATGATTCAGAAGCGAGTGTGC-3′ (human) (27) and 5′-AAAACAAGGTGGATTGTCACACG-3′ and 5′-GTTGGGCTCACACTGTTCATAAT-3′ (mouse).
IRS1 Immunoprecipitation from C2C12 Lysates
C2C12 myotubes were lysed and IRS1 as described previously (28).
Transfection of Cells with PKR siRNA
25 nmol/liter of PKR siRNA or the same amount of non-target siRNA were transfected into C2C12 myotubes using DharmaFECT transfection reagent according to the instructions of the manufacturer, and the cells were sampled 96 h later.
Glucose Transport
C2C12 myotubes were washed rapidly with HEPES-buffered saline, and glucose uptake was assayed as described previously (29).
Statistics
Results are expressed as mean ± S.E. Statistical significance was assessed using one way analysis of variance. p value < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Chronic Fatty Acid Treatment Inhibits IRS1 Function in Muscle and in Cultured Myotubes
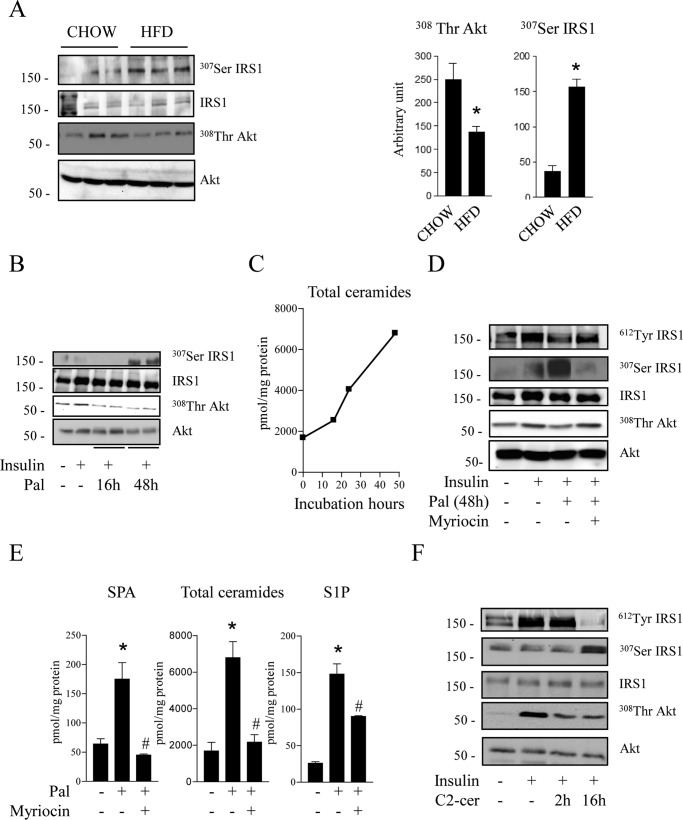
In skeletal muscle of mice fed an HFD, we observed a 3-fold increase in IRS1 serine 307 phosphorylation (Fig. 1A). Phosphorylation of this specific residue has been associated extensively with a loss of the insulin signal (30–32). Concomitantly, a 40% decrease in Akt threonine 308 phosphorylation was also observed in muscle lysates of HFD-treated mice compared with control mice (Fig. 1A), confirming impaired activation of the insulin signaling pathway in muscles of HFD-treated mice.
FIGURE 1.
Effects of palmitate and ceramide on the insulin signaling pathway in muscle and cultured myotubes. A, gastrocnemius muscles from mice fed a control diet (CHOW) or HFD were extracted and lysed. Scanning densitometry was performed to quantify changes in Thr308 Akt and Ser307 IRS1. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. from three mice. *, p < 0.05 compared with chow diet. B, C2C12 myotubes were treated for 16 or 48 h with 0.25 mmol/liter palmitate (Pal), followed by 100 nmol/liter insulin 10 min before cell lysis. C, cells were incubated with 0.25 mmol/liter palmitate for 16–48 h, and intracellular sphingolipids species were assessed. D, C2C12 myotubes were treated for 48 h with 0.25 mmol/liter palmitate in the presence or absence of 10 μmol/liter myriocin, followed by 100 nmol/liter insulin 10 min before cell lysis. E, cells were incubated with 0.25 mmol/liter palmitate for 48 h in the presence or absence of 10 μmol/liter myriocin, and intracellular sphingolipids species sphinganine (SPA), total ceramides, sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) were assessed. Results are mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 compared with untreated cells. #, p < 0.05 compared with palmitate-treated cells. F, C2C12 myotubes were treated with 50 μmol/liter C2-ceramide (C2-cer) for 2 or 16 h, followed by 100 nmol/liter insulin for the last 10 min. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Representative immunoblots of at least three independent experiments are shown.
Until now, these results obtained in vivo could not be reproduced in vitro. Indeed, treatment of C2C12 myotubes with an excess of palmitate for up to 16 h prevented insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation without any serine phosphorylation of IRS1 (Fig. 1B). We tried to mimic the in vivo situation by treating C2C12 myotubes for longer periods (48 h) with lower concentrations of palmitate (0.25 mmol/liter) to avoid cell death (33). Fig. 1C shows that ceramide concentrations increased 3-fold in cells incubated with palmitate for 16 and 48 h. Figs. 1B shows that, as observed in vivo, 48-h palmitate treatment induced an increase in IRS1 serine 307 phosphorylation. Concomitantly, we observed a decrease in IRS1 tyrosine 612 phosphorylation (Fig. 1D). In parallel, phosphorylation of Akt was impaired in response to insulin (Fig. 1D).
We have shown previously that ceramide is responsible for the acute deleterious effect of palmitate on insulin signaling in muscle (4, 34). We therefore inhibited sphingolipid synthesis with myriocin, an inhibitor of serine palmitoyl transferase. Fig. 1E shows that exposure of C2C12 myotubes to palmitate for 48 h induced an increase of sphinganine (ceramide precursor), total ceramide, and sphingosine-1-phosphate (a ceramide derivative). As expected, sphingolipid metabolism was inhibited after pretreatment of cells with myriocin (Fig. 1E). As shown in Fig. 1D, the deleterious effect of 48-h palmitate treatment was totally abolished for IRS1 and Akt after pretreatment of cells with myriocin, demonstrating that chronic palmitate action on insulin signaling occurred through ceramide.
We reproduced the long-term action of palmitate by treating C2C12 myotubes directly with a cell-permeable, short-chain C2-ceramide analogue. When added to cells, C2-ceramide is elongated rapidly to give endogenous and long-chain ceramide (35). Fig. 1F shows that, as described previously (12), 2-h treatment with ceramide inhibits Akt phosphorylation in response to insulin without any negative effect on IRS1. However, treatment of C2C12 myotubes with C2-ceramide for 16 h (at 50 μm, half the concentration we usually use in short-term experiments) decreased insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation and concomitantly increased IRS1 serine 307 phosphorylation (Fig. 1F). A loss of tyrosine 612 phosphorylation of IRS1 was also observed, indicating an inhibition of insulin-induced IRS1 activation (Fig. 1F). These results demonstrate that, in the long term, palmitate-produced ceramide acts negatively on IRS1.
PKR Is Activated in Insulin-resistant Muscle Cells
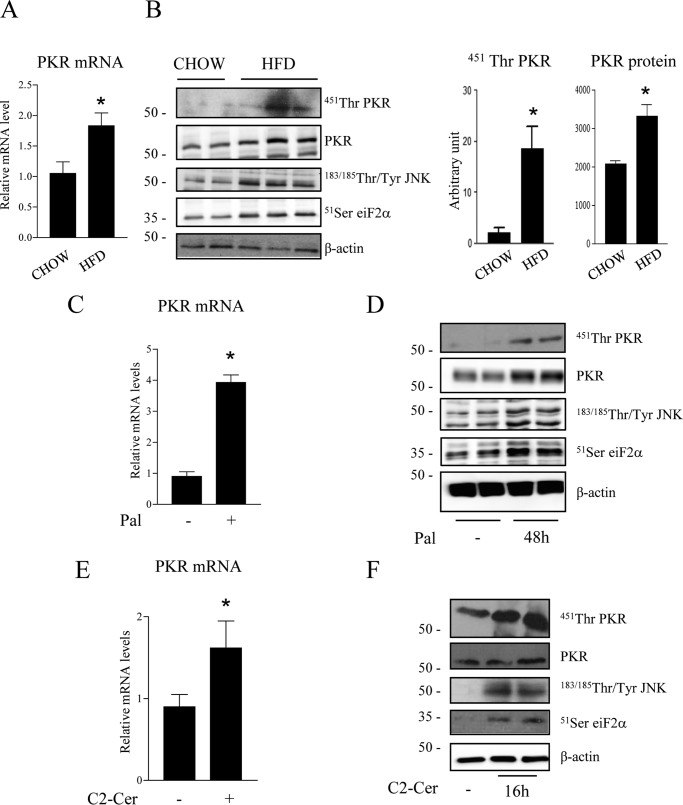
Although the mechanisms involved in the inhibition of Akt by ceramide are now well documented (4, 12–14, 36), no genuine mechanism has been described to explain how ceramide prevents insulin-induced IRS1 activation in myotubes. We hypothesized that PKR could be a potential candidate to mediate ceramide effects on IRS1. PKR is mainly activated by dimerization and autophosphorylation on at least 15 different sites, but phosphorylation on threonine 451 is critical for its kinase activity (37). In addition, activated PKR regulates its own expression through increased transcription (38, 39). We show here that PKR mRNA (Fig. 2A), PKR phosphorylation on threonine 451, and protein expression (Fig. 2B) were all increased in muscles of HFD mice compared with control mice. In parallel, an increase in phosphorylation of both JNK and eiF2α, two PKR direct targets, was observed in muscle of HFD mice (Fig. 2B). As observed in HFD-fed animals, an increase in PKR mRNA (Fig. 2C), phosphorylation, and expression (Fig. 2D) was observed when C2C12 myotubes were treated with palmitate for 48 h. A 16-h ceramide treatment of C2C12 myotubes induced PKR mRNA expression (Fig. 2E) and phosphorylation on threonine 541 but did not significantly modify total PKR expression (Fig. 2F). We hypothesized that cells had to be exposed to ceramide for a longer period of time to observe an effect on protein expression. Indeed, PKR expression was increased when cells were incubated for at least 24 h with ceramide (data not shown). As a consequence of PKR activation, both JNK and eiF2α were also phosphorylated in response to palmitate or ceramide (Fig. 2, D–F).
FIGURE 2.
Effect of lipid load on PKR phosphorylation state. A, RNA from muscles of mice fed a chow diet or HFD were extracted. PKR mRNA levels were assessed by quantitative RT-PCR. Results are mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 compared with chow diet. B, gastrocnemius muscles from mice fed a chow diet or HFD were extracted and lysed. Scanning densitometry was performed to quantify changes in total and phosphorylated PKR in cell lysates. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.05 compared with chow diet. C–F, C2C12 myotubes were treated with 0.25 mmol/liter palmitate (Pal) for 48 h (C and D) or with 50 μmol/liter ceramide (C2-Cer) for 16 h (E and F). PKR mRNA levels were assessed by quantitative RT-PCR. Results are mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 compared with control cells. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The blots shown are representative of three to six separate experiments.
PKR Mediates Long-term Effects of Palmitate on IRS1 in C2C12 Myotubes
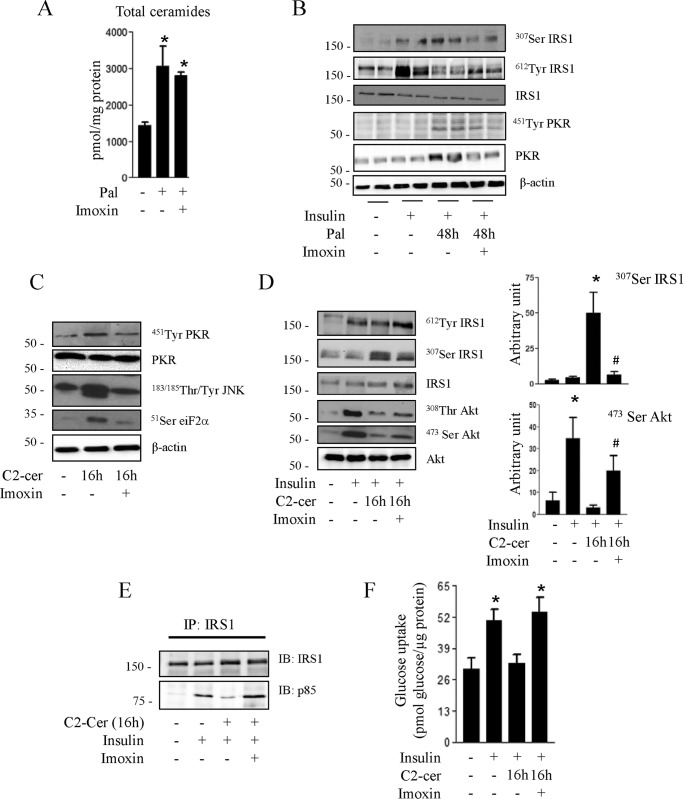
To study the role of PKR in mediating the long-term effects of ceramide on insulin signaling, we used a well characterized chemical inhibitor of PKR (imoxin), an imidazolo-oxindole derivative that acts as an inhibitor of the PKR ATP-binding site (21, 40). We verified first that imoxin does not affect ceramide biosynthesis by measuring the total ceramide concentration in the presence of palmitate (Fig. 3A).
FIGURE 3.
Effect of imoxin on palmitate and ceramide-induced inhibition of insulin signaling in C2C12 myotubes. A, C2C12 myotubes were treated with 0.25 mmol/liter palmitate (Pal) with or without imoxin (1 μmol/liter) for 48 h, and the total intracellular ceramide amount was quantified. Results are mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 relative to untreated control. B, C2C12 myotubes were incubated with 0.25 mmol/liter palmitate for 48 h in the presence or absence of imoxin, followed by insulin in the last 10 min before being lysed and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Representative immunoblots of at least three independent experiments are shown. C2C12 myotubes were pretreated with imoxin (1 μmol/liter) for 1 h prior to incubation with C2-ceramide (50 μmol/liter) for 16 h. C, cells were lysed, and the lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. C2-cer, C2-ceramide. D, cells were incubated with 100 nmol/liter insulin for 10 min prior to being lysed. The histograms show densitometric quantification of Ser473 Akt and Ser307 IRS1. *, p < 0.05 relative to untreated control; #, p < 0.05 relative to cells only incubated with C2-ceramide. The representative immunoblots are from three different experiments. E, cells were lysed, and lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-IRS1 antibody. Immunoprecipitated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and blotted with anti-p85 or IRS1 antibodies. The blots are representative of three separate experiments. IB, immunoblot. F, glucose transport was assessed after 30 min of 100 nm insulin incubation. Results are mean ± S.E. (n = 4). *, p < 0.05 relative to untreated control.
Then we analyzed the consequences of PKR inhibition on the IRS1 phosphorylation state in response to palmitate. Palmitate-induced IRS1 serine 307 phosphorylation as well as PKR phosphorylation and expression were prevented when PKR was inhibited (Fig. 3B). Concomitantly, the inhibitory effect of palmitate on IRS1 tyrosine 312 phosphorylation was partially restored (Fig. 3B).
We then treated cells directly with C2-ceramide to delineate the mechanism by which PKR acts on insulin signaling. Treatment of C2C12 myotubes with imoxin prevents ceramide-induced phosphorylation of PKR, JNK, and eiF2α (Fig. 3C), confirming the blockade of PKR signaling in C2C12 myotubes.
Inhibition of PKR prevents ceramide-induced inhibition of IRS1 tyrosine phosphorylation and up-regulation of IRS1 serine phosphorylation (Fig. 3D). Analyses of IRS1 precipitates with an antibody against the regulatory 85-kDa (p85) regulatory subunit of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, a downstream target of IRS1, revealed that p85 was associated with IRS1 in response to insulin but not when cells were incubated with ceramide for 16 h (Fig. 3E). Preincubation of cells with imoxin, however, prevented the inhibitory action of ceramide on insulin-induced IRS1/p85 association (Fig. 3E). Interestingly, inhibition of PKR activity by imoxin also counteracted, at least partially, the inhibitory action of ceramide on Akt (Fig. 3D). We then assessed the effect of preventing ceramide-induced PKR activation on insulin-induced glucose uptake, an end point of insulin action in muscle. As shown in Fig. 3F, the inhibition of glucose uptake observed in the presence of ceramide was reversed when PKR activity was blunted.
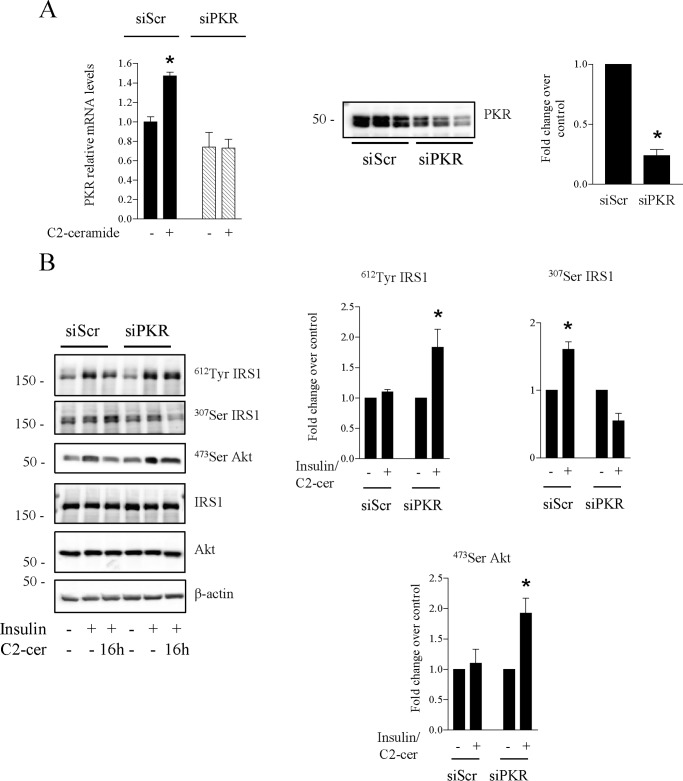
We confirmed these results by silencing PKR using a siRNA strategy in cultured C2C12 myotubes. siRNA mediated-silencing of PKR successfully abrogated PKR protein levels and ceramide response on PKR mRNA expression (Fig. 4A). As observed with imoxin, PKR silencing prevented the inhibition of insulin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1 and IRS1 serine phosphorylation induced by ceramide (Fig. 4B,). In addition, silencing of PKR also partially alleviated ceramide inhibition of insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation (Fig. 4B).
FIGURE 4.
Effect of PKR knockdown on ceramide-induced inhibition of insulin signaling in C2C12 myotubes. C2C12 muscle cells were transfected with a PKR siRNA before being treated with C2-ceramide (50 μm, 16 h). A, quantification of PKR mRNA was performed by quantitative RT-PCR. Results are mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 compared with cells transfected with scramble siRNA (siScr) (left panel). C2C12 lysates were immunoblotted with a PKR antibody. Scanning densitometry was performed to quantify changes in total PKR (right panel). B, C2C12-transfected myotubes were treated with C2-ceramide (C2-cer, 50 μmol/liter) for 16 h, followed by 10-min treatment with 100 nmol/liter insulin. Cells were lysed, and lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Scanning densitometry was performed to quantify changes in phosphorylated IRS1 and PKB in siRNA-transfected cell lysates. Results are mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 compared with control cells.
PKR Inhibition of IRS1 in Myotubes Is Mediated by JNK
Then we analyzed how PKR could induce IRS1 phosphorylation on serine residues. A study has shown that PKR binds and phosphorylates IRS1 directly on its serine 307 residue (22). However, we could not reproduce this data in our model (data not shown). Studies have also demonstrated the role of JNK in impairing insulin signaling by phosphorylating IRS1 on the serine 307 residue. Because JNK is a target of PKR (20, 22), we inhibited JNK phosphorylation using the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (41) and studied the consequences on the insulin signaling pathway. Incubation of C2C12 myotubes with SP600125 prevented ceramide-induced phosphorylation of JNK and its downstream target c-Jun (Fig. 5A). Consequently, SP600125 prevented ceramide-induced IRS1 serine phosphorylation and induced insulin-induced IRS1 tyrosine phosphorylation (Fig. 5B), demonstrating that the effects of PKR on IRS1 occur through JNK. However, no improvement of the insulin-induced stimulation of Akt was observed after treatment of cells with the JNK inhibitor (Fig. 5B).
FIGURE 5.
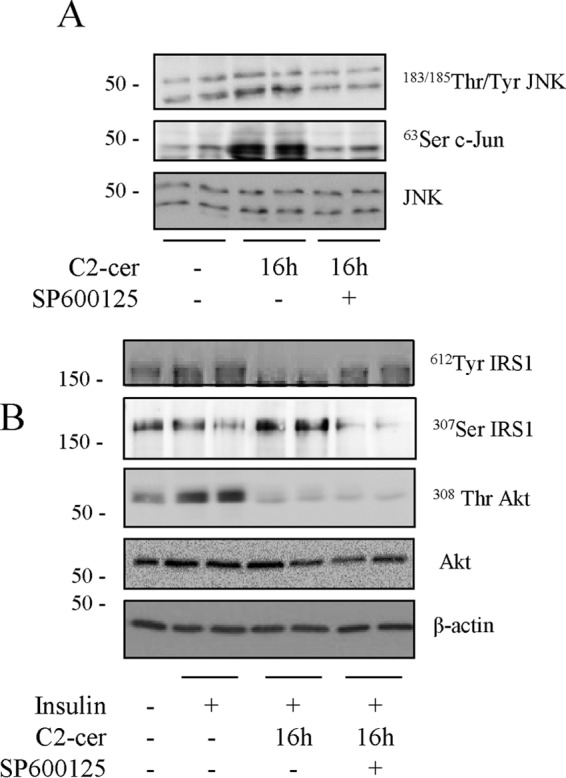
Effect of JNK inactivation on Akt phosphorylation in ceramide-treated C2C12 myotubes. A, cells were treated with 10 μmol/liter JNK inhibitor (SP600125) for 1 h prior to being incubated with 50 μmol/liter C2-ceramide (C2-cer) for 16 h. B, incubation of cells with 50 μmol/liter C2-ceramide for 16 h with or without SP6000125, followed by 100 nm insulin for 10 min. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The experiment was repeated twice in duplicates.
Short-term Inhibition of PKR Does Not Prevent Ceramide-induced Akt Inhibition
We tried to figure out whether inhibition of PKR could prevent ceramide-induced Akt inhibition in the short term (2 h). Fig. 6 shows that, like in the long term, 2-h ceramide treatment induced PKR phosphorylation. However, no ceramide-induced JNK phosphorylation was observed. Therefore, as anticipated and opposite to chronic incubation, ceramide-negative action on Akt after 2-h treatment was not mediated through PKR activation because incubation of myotubes with imoxin did not prevent ceramide-induced Akt inhibition (Fig. 6).
FIGURE 6.
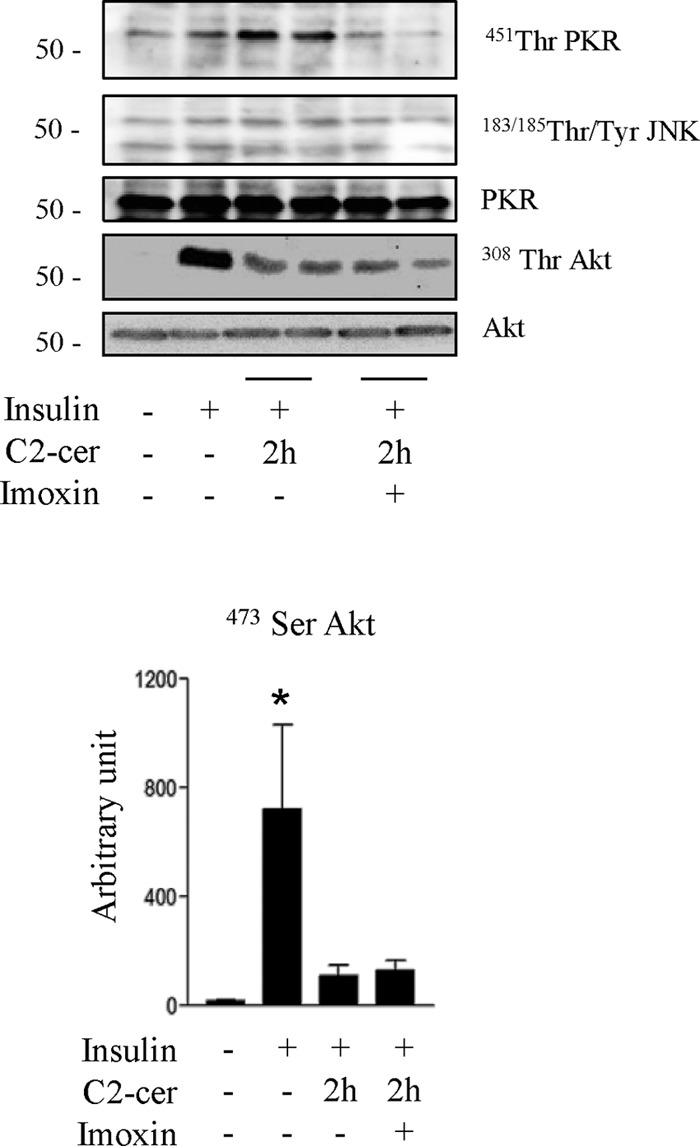
Effect of PKR inhibition on acute ceramide-induced inhibition of the insulin signaling pathway in C2C12 myotubes. C2C12 myotubes were treated with 50 μmol/liter C2-ceramide (C2-cer) for 2 h with or without imoxin (1 μmol/liter), followed by an insulin pulse before being lysed and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The histogram represents densitometric quantification of Ser473 Akt.
PKR Mediates Long-term Effects of Palmitate on Insulin Signaling in Human Myotubes
Finally, we validated these findings in human myotubes. We first compared PKR expression and phosphorylation in cultured muscle cells isolated from control or diabetic patients. PKR mRNA levels (Fig. 7A) and PKR phosphorylation and protein expression (Fig. 7B) were increased in myotubes of diabetic patients compared with human control myotubes.
FIGURE 7.
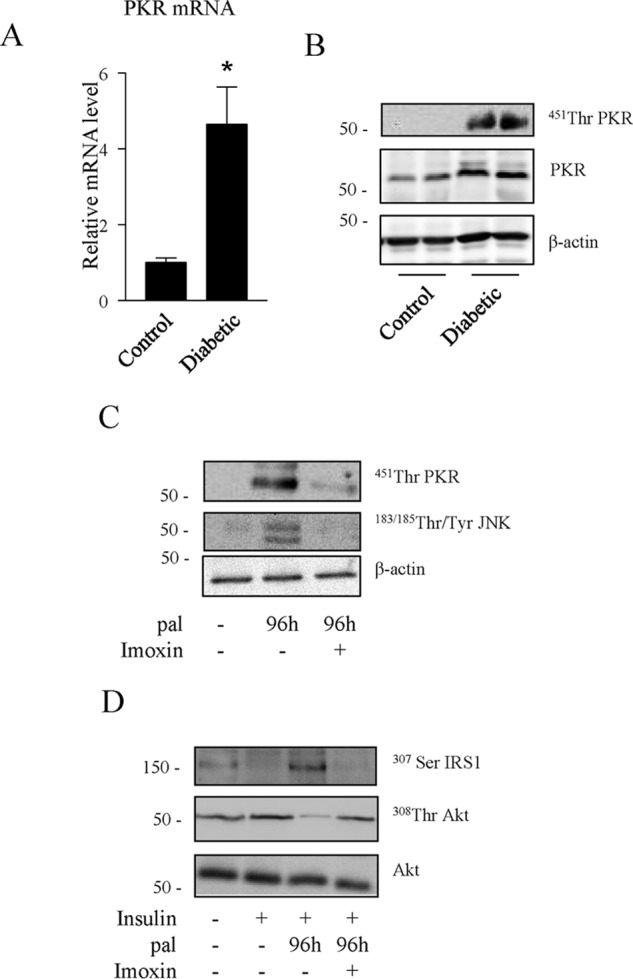
Effect of PKR inhibition on chronic palmitate-induced inhibition of the insulin signaling pathway in human myotubes. A, PKR mRNA levels in skeletal muscle obtained from three diabetic patients compared with three healthy non-diabetic subjects. *, p < 0.05 relative to non-diabetic subjects. B, PKR phosphorylation state from skeletal muscle biopsy lysates obtained from two different diabetic patients compared with healthy non-diabetic subjects. C, cultured human myotubes were incubated with 0.5 mmol/liter palmitate (pal) for 96 h before being lysed. D, cultured human myotubes were incubated with 0.5 mmol/liter palmitate in the presence or absence of imoxin for 96 h, followed by 100 nmol/liter insulin for 10 min. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
Then we studied the effect of chronic treatment with palmitate and the involvement of PKR on insulin signaling in cultured human myotubes. The de novo ceramide synthesis rate in human myotubes is very slow, as assessed by dosage of intracellular ceramide amounts after 24-h palmitate treatment (a 2.4-fold increase in C2C12 myotubes compared with a 1.3-fold increase in human myotubes). Therefore, we slightly modified our culture conditions by incubating human myotubes with 0.5 mmol/liter palmitate for 4 days (instead of the usual 2 days) in the presence or absence of imoxin. As observed in C2C12 myotubes, imoxin blocked palmitate-induced phosphorylation of PKR and JNK in human myotubes (Fig. 7C), and exposure of human myotubes to palmitate induced IRS1 serine phosphorylation (Fig. 7D) as well as the inhibition of insulin-induced phosphorylation of Akt. As observed in the mouse cell line, inhibition of PKR with imoxin completely prevented the serine phosphorylation of IRS1 and partially prevented the inhibitory effect of palmitate on Akt (Fig. 7D).
Discussion
In contrast with previous in vitro studies, we demonstrate here that the loss of insulin sensitivity observed in muscle cells during long-term saturated fatty acid or ceramide oversupply is a direct consequence of the inhibition of two critical actors of the insulin signaling pathway, IRS1 and Akt. These different results are the consequence of longer treatments with palmitate and ceramide. This allowed us to involve the activation of the JNK/PKR pathway in their deleterious effects.
We show here that PKR autophosphorylation is enhanced in several models of insulin resistance, including both palmitate- and ceramide-treated myotubes and muscle from mice fed with a high-fat diet. In primary cultured myotubes obtained from type 2 diabetes patients, both PKR mRNA levels and PKR autophosphorylation are enhanced compared with myotubes from control patients. This model is attractive because it offers enough material to study insulin signaling in vitro in cells that display several characteristics of mature human skeletal muscle. Indeed, myotubes established from patients with type 2 diabetes have been shown to maintain their metabolic phenotype in culture (42). Using this model, we show that PKR mRNA and expression levels and PKR autophosphorylation are enhanced compared with myotubes from control patients. Overall, these results are in line with in vivo data describing a potential role of PKR in the control of insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in muscle (20) and the fact that PKR activity is increased in muscles of obese patients (43).
We went further ahead and show a direct link between increased PKR activity in response to ceramide produced from excess saturated fatty acids (palmitate) and insulin resistance in muscle cells. To our knowledge, this is the first time that PKR involvement in the onset of ceramide-induced insulin resistance is demonstrated in muscle cells.
Interestingly, inhibition of PKR activity or expression not only prevents ceramide inhibition of insulin-induced IRS1 activation but also reverses ceramide-induced inhibition of Akt and, therefore, prevents the lipid inhibitory action on glucose uptake. An improvement in insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation was also observed in isolated muscles obtained from PKR−/− mice treated with palmitate (20). Together, these data suggest that, in the long term, ceramide acts negatively, preferentially through a PKR/IRS1 pathway, on insulin signaling.
When we inhibited JNK activity, we could not see the partial restoration of Akt activation in response to insulin observed when PKR activity is blunted. This result is still not clear but may be explained by the fact that, like ceramide, PKR can also activate PP2A (44) and, therefore, still inhibit Akt even when JNK activity is reduced.
Interestingly, short-term (2-h) ceramide treatment on myotubes does not involve the PKR/JNK pathway to inhibit insulin signaling in C2C12 myotubes. In this time frame, only PKR is phosphorylated in response to ceramide without any change in JNK phosphorylation state, suggesting that ceramide-induced PKR-mediated JNK phosphorylation requires more time (up to 16 h). This is not unprecedented because several studies show that incubation of myotubes from 16–24 h is necessary to see palmitate or ceramide induce JNK phosphorylation (45–48). This result confirms previous data demonstrating that, in the short term, ceramide inhibits insulin signaling through the activation of PP2A, which dephosphorylates Akt in C2C12 myotubes (16, 17).
The implication of PKR in the long-term deleterious action of ceramide on insulin signaling may not be limited to muscle because its activation has also been demonstrated in the liver and adipose tissue of obese human patients (43). Importantly, bariatric surgery is concomitant with weight loss and improvement of insulin sensitivity and a complete reduction of PKR activity in adipose tissue of obese individuals (43), demonstrating a strong correlation between PKR activity and insulin sensitivity.
In summary, our study demonstrates that ceramide produced from saturated fatty acid excess inhibits the insulin signaling pathway in muscle cells by targeting, in a time-dependent manner, two important actors, Akt and IRS1 (Fig. 8). The discovery of the involvement of PKR in the deleterious effects of ceramide strengthens the central role of this kinase as an integrator of pathogen response, inflammation, and nutrient oversupply.
FIGURE 8.
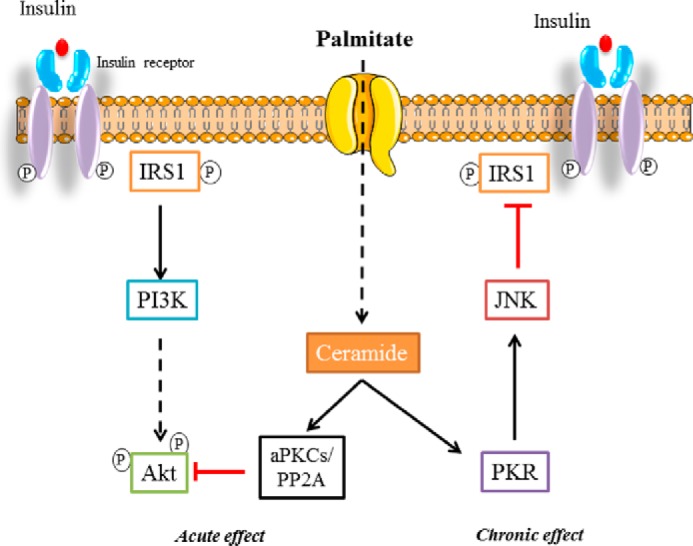
The mechanism mediating ceramide inhibitory action on insulin signaling in myotubes. Palmitate-generated ceramide alters insulin signaling through two different ways in a time frame-dependent manner in myotubes. First, ceramide inhibits Akt via PP2A or atypical PKCs (aPKCs), and, later, ceramide acts negatively on IRS1 through activation of the PKR/JNK pathway.
Author Contributions
R. H. H., A. C. P. de S., R. M., I. H., A. B. Z., and J. G. participated in data collection and generation and reviewed the manuscript. O. B. and F. K. collected human muscle samples. P. F., F. F., and E. H. designed the experiments, participated in data collection and generation, and wrote and edited the manuscript. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank J. T. Vilquin (UPMC UM76, Groupe Hospitalier Pitié-Salpêtrière, Paris, France), J. Gaudric, C. Goulfier, C. Jouhannet, and T. Khalife (Service de Chirurgie Vasculaire, AP-HP, Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, Paris, France) for providing the human muscle samples. We also thank the staff of Centre d'Exploration Fonctionnelle (Cordeliers Research Centre, Paris, France) for technical assistance and the tissue bank of the Association Française des Myopathies for human biopsies for control human biopsy samples.
This work was supported by INSERM, the Société Francophone du Diabète (an Association Nationale pour les Traitements à Domicile, les Innovations et la Recherche grant), Agence Nationale de la Recherche Project ANR 11 BSV1 03101-Crisalis, and the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (équipe FRM DEQ20140329504). The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
- HFD
- high-fat diet
- PKR
- double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase.
References
- 1.Silveira L. R., Fiamoncini J., Hirabara S. M., Procópio J., Cambiaghi T. D., Pinheiro C. H., Lopes L. R., and Curi R. (2008) Updating the effects of fatty acids on skeletal muscle. J. Cell. Physiol. 217, 1–12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Petersen K. F., and Shulman G. I. (2006) Etiology of insulin resistance. Am. J. Med. 119, S10-S16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tanti J. F., Gual P., Gremeaux T., Gonzalez T., Barres R., and Le Marchand-Brustel Y. (2004) Alteration in insulin action: role of IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in the retroregulation of insulin signalling. Ann. Endocrinol. 65, 43–48 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hage Hassan R., Bourron O., and Hajduch E. (2014) Defect of insulin signal in peripheral tissues: important role of ceramide. World J. Diabetes 5, 244–257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hannun Y. A., and Obeid L. M. (2008) Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 139–150 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bartke N., and Hannun Y. A. (2009) Bioactive sphingolipids: metabolism and function. J. Lipid Res. 50, S91-S96 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bellini L., Campana M., Mahfouz R., Carlier A., Véret J., Magnan C., Hajduch E., and Le Stunff H. (2015) Targeting sphingolipid metabolism in the treatment of obesity/type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 19, 1037–1050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Holland W. L., Brozinick J. T., Wang L. P., Hawkins E. D., Sargent K. M., Liu Y., Narra K., Hoehn K. L., Knotts T. A., Siesky A., Nelson D. H., Karathanasis S. K., Fontenot G. K., Birnbaum M. J., and Summers S. A. (2007) Inhibition of ceramide synthesis ameliorates glucocorticoid-, saturated-fat-, and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 5, 167–179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ussher J. R., Koves T. R., Cadete V. J., Zhang L., Jaswal J. S., Swyrd S. J., Lopaschuk D. G., Proctor S. D., Keung W., Muoio D. M., and Lopaschuk G. D. (2010) Inhibition of de novo ceramide synthesis reverses diet-induced insulin resistance and enhances whole-body oxygen consumption. Diabetes 59, 2453–2464 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Frangioudakis G., Garrard J., Raddatz K., Nadler J. L., Mitchell T. W., and Schmitz-Peiffer C. (2010) Saturated- and n-6 polyunsaturated-fat diets each induce ceramide accumulation in mouse skeletal muscle: reversal and improvement of glucose tolerance by lipid metabolism inhibitors. Endocrinology 151, 4187–4196 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Litherland G. J., Hajduch E., and Hundal H. S. (2001) Intracellular signalling mechanisms regulating glucose transport in insulin-sensitive tissues. Mol. Membr. Biol. 18, 195–204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hajduch E., Balendran A., Batty I. H., Litherland G. J., Blair A. S., Downes C. P., and Hundal H. S. (2001) Ceramide impairs the insulin-dependent membrane recruitment of protein kinase B leading to a loss in downstream signalling in L6 skeletal muscle cells. Diabetologia 44, 173–183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hajduch E., Turban S., Le Liepvre X., Le Lay S., Lipina C., Dimopoulos N., Dugail I., and Hundal H. S. (2008) Targeting of PKCζ and PKB to caveolin-enriched microdomains represents a crucial step underpinning the disruption in PKB-directed signalling by ceramide. Biochem. J. 410, 369–379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Blouin C. M., Prado C., Takane K. K., Lasnier F., Garcia-Ocana A., Ferré P., Dugail I., and Hajduch E. (2010) Plasma membrane subdomain compartmentalization contributes to distinct mechanisms of ceramide action on insulin signaling. Diabetes 59, 600–610 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Powell D. J., Hajduch E., Kular G., and Hundal H. S. (2003) Ceramide disables 3-phosphoinositide binding to the Pleckstrin homology domain of protein kinase B (PKB)/Akt by a PKCζ-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 7794–7808 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chavez J. A., Knotts T. A., Wang L. P., Li G., Dobrowsky R. T., Florant G. L., and Summers S. A. (2003) A role for ceramide, but not diacylglycerol, in the antagonism of insulin signal transduction by saturated fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 10297–10303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mahfouz R., Khoury R., Blachnio-Zabielska A., Turban S., Loiseau N., Lipina C., Stretton C., Bourron O., Ferré P., Foufelle F., Hundal H. S., and Hajduch E. (2014) Characterising the inhibitory actions of ceramide upon insulin signaling in different skeletal muscle cell models: a mechanistic insight. PLoS ONE 9, e101865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baird T. D., and Wek R. C. (2012) Eukaryotic initiation factor 2 phosphorylation and translational control in metabolism. Adv. Nutr. 3, 307–321 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yang X., Nath A., Opperman M. J., and Chan C. (2010) PKR differentially regulates IRS1 and IRS2 in HepG2 cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 3449–3458 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Carvalho-Filho M. A., Carvalho B. M., Oliveira A. G., Guadagnini D., Ueno M., Dias M. M., Tsukumo D. M., Hirabara S. M., Reis L. F., Curi R., Carvalheira J. B., and Saad M. J. (2012) Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase is a key modulator of insulin sensitivity in physiological conditions and in obesity in mice. Endocrinology 153, 5261–5274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nakamura T., Arduini A., Baccaro B., Furuhashi M., and Hotamisligil G. S. (2014) Small molecule inhibitors of PKR improve glucose homeostasis in obese, diabetic mice. Diabetes 63, 526–534 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nakamura T., Furuhashi M., Li P., Cao H., Tuncman G., Sonenberg N., Gorgun C. Z., and Hotamisligil G. S. (2010) Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase links pathogen sensing with stress and metabolic homeostasis. Cell 140, 338–348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hage Hassan R., Hainault I., Vilquin J. T., Samama C., Lasnier F., Ferré P., Foufelle F., and Hajduch E. (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress does not mediate palmitate-induced insulin resistance in mouse and human muscle cells. Diabetologia 55, 204–214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vilquin J. T., Marolleau J. P., Sacconi S., Garcin I., Lacassagne M. N., Robert I., Ternaux B., Bouazza B., Larghero J., and Desnuelle C. (2005) Normal growth and regenerating ability of myoblasts from unaffected muscles of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy patients. Gene Ther. 12, 1651–1662 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hajduch E., Alessi D. R., Hemmings B. A., and Hundal H. S. (1998) Constitutive activation of protein kinase B α by membrane targeting promotes glucose and system A amino acid transport, protein synthesis, and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 in L6 muscle cells. Diabetes 47, 1006–1013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Blachnio-Zabielska A. U., Persson X. M., Koutsari C., Zabielski P., and Jensen M. D. (2012) A liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for measuring the in vivo incorporation of plasma free fatty acids into intramyocellular ceramides in humans. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 26, 1134–1140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yang X., and Chan C. (2009) Repression of PKR mediates palmitate-induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells through regulation of Bcl-2. Cell Res. 19, 469–486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hajduch E., Rencurel F., Balendran A., Batty I. H., Downes C. P., and Hundal H. S. (1999) Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine), a novel regulator of glucose transport in rat skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 13563–13568 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Blair A. S., Hajduch E., Litherland G. J., and Hundal H. S. (1999) Regulation of glucose transport and glycogen synthesis in L6 muscle cells during oxidative stress: evidence for cross-talk between the insulin and SAPK2/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 36293–36299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jiang G., Dallas-Yang Q., Liu F., Moller D. E., and Zhang B. B. (2003) Salicylic acid reverses phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA)- and tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)-induced insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) serine 307 phosphorylation and insulin resistance in human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 180–186 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Danielsson A., Ost A., Nystrom F. H., and Strålfors P. (2005) Attenuation of insulin-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 serine 307 phosphorylation in insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 34389–34392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Reynoso R., Salgado L. M., and Calderón V. (2003) High levels of palmitic acid lead to insulin resistance due to changes in the level of phosphorylation of the insulin receptor and insulin receptor substrate-1. Mol. Cell Biochem. 246, 155–162 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Peterson J. M., Wang Y., Bryner R. W., Williamson D. L., and Alway S. E. (2008) Bax signaling regulates palmitate-mediated apoptosis in C(2)C(12) myotubes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 295, E1307-E1314 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Powell D. J., Turban S., Gray A., Hajduch E., and Hundal H. S. (2004) Intracellular ceramide synthesis and protein kinase Cζ activation play an essential role in palmitate-induced insulin resistance in rat L6 skeletal muscle cells. Biochem. J. 382, 619–629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ogretmen B., Pettus B. J., Rossi M. J., Wood R., Usta J., Szulc Z., Bielawska A., Obeid L. M., and Hannun Y. A. (2002) Biochemical mechanisms of the generation of endogenous long chain ceramide in response to exogenous short chain ceramide in the A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Role for endogenous ceramide in mediating the action of exogenous ceramide. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 12960–12969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Turban S., and Hajduch E. (2011) Protein kinase C isoforms: mediators of reactive lipid metabolites in the development of insulin resistance. FEBS Lett. 585, 269–274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Romano P. R., Garcia-Barrio M. T., Zhang X., Wang Q., Taylor D. R., Zhang F., Herring C., Mathews M. B., Qin J., and Hinnebusch A. G. (1998) Autophosphorylation in the activation loop is required for full kinase activity in vivo of human and yeast eukaryotic initiation factor 2α kinases PKR and GCN2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 2282–2297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Thomis D. C., and Samuel C. E. (1992) Mechanism of interferon action: autoregulation of RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 α protein kinase (PKR) expression in transfected mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 10837–10841 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gusella G. L., Musso T., Rottschafer S. E., Pulkki K., and Varesio L. (1995) Potential requirement of a functional double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) for the tumoricidal activation of macrophages by lipopolysaccharide or IFN-α β, but not IFN-γ. J. Immunol. 154, 345–354 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lin S. S., Lee D. C., Law A. H., Fang J. W., Chua D. T., and Lau A. S. (2010) A role for protein kinase PKR in the mediation of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1-induced IL-6 and IL-10 expression. Cytokine 50, 210–219 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bennett B. L., Sasaki D. T., Murray B. W., O'Leary E. C., Sakata S. T., Xu W., Leisten J. C., Motiwala A., Pierce S., Satoh Y., Bhagwat S. S., Manning A. M., and Anderson D. W. (2001) SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 13681–13686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aas V., Bakke S. S., Feng Y. Z., Kase E. T., Jensen J., Bajpeyi S., Thoresen G. H., and Rustan A. C. (2013) Are cultured human myotubes far from home? Cell Tissue Res. 354, 671–682 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Carvalho B. M., Oliveira A. G., Ueno M., Araújo T. G., Guadagnini D., Carvalho-Filho M. A., Geloneze B., Lima M. M., Pareja J. C., Carvalheira J. B., and Saad M. J. (2013) Modulation of double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase in insulin sensitive tissues of obese humans. Obesity 21, 2452–2457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Xu Z., and Williams B. R. (2000) The B56α regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A is a target for regulation by double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 5285–5299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jaiswal N., Gunaganti N., Maurya C. K., Narender T., and Tamrakar A. K. (2015) Free fatty acid induced impairment of insulin signaling is prevented by the diastereomeric mixture of calophyllic acid and isocalophyllic acid in skeletal muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 746, 70–77 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kadotani A., Tsuchiya Y., Hatakeyama H., Katagiri H., and Kanzaki M. (2009) Different impacts of saturated and unsaturated free fatty acids on COX-2 expression in C(2)C(12) myotubes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 297, E1291-E1303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Taheripak G., Bakhtiyari S., Rajabibazl M., Pasalar P., and Meshkani R. (2013) Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibition ameliorates palmitate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in skeletal muscle cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 65, 1435–1446 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yuzefovych L. V., Solodushko V. A., Wilson G. L., and Rachek L. I. (2012) Protection from palmitate-induced mitochondrial DNA damage prevents from mitochondrial oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and impaired insulin signaling in rat L6 skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology 153, 92–100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]