Abstract
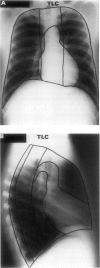
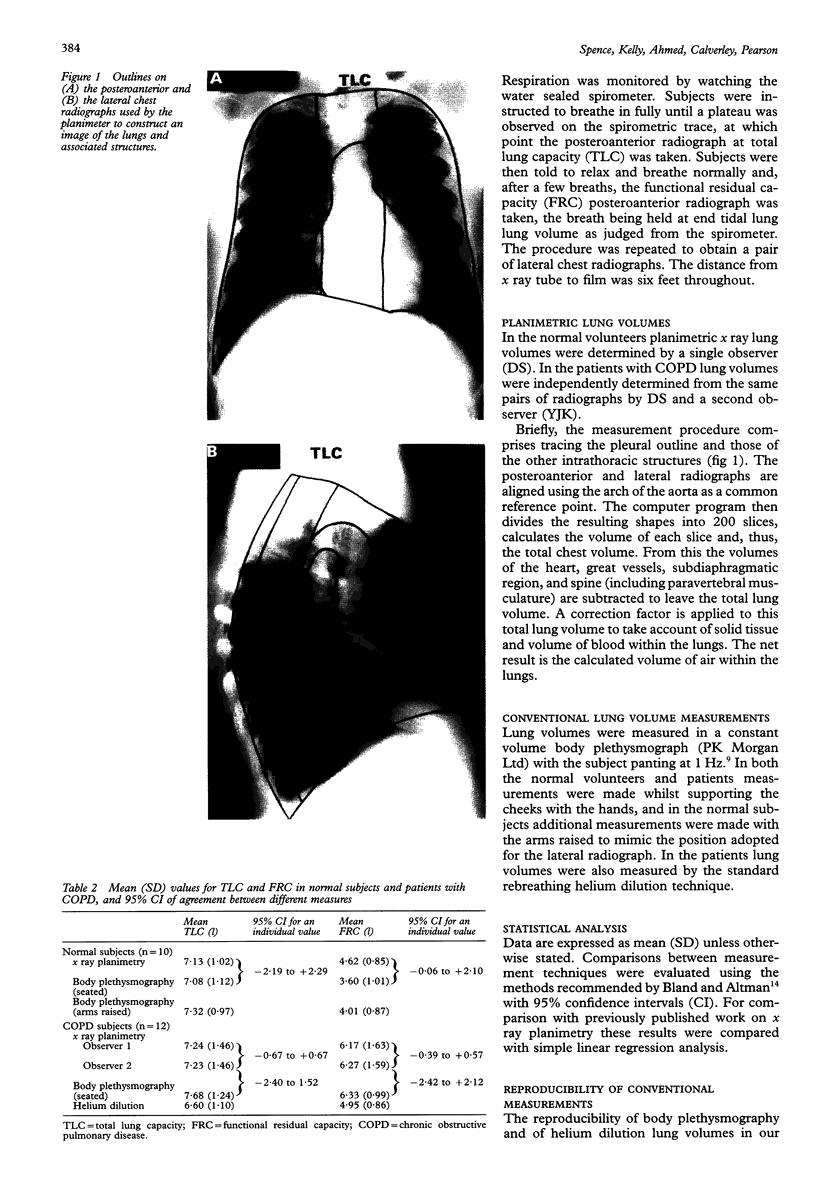
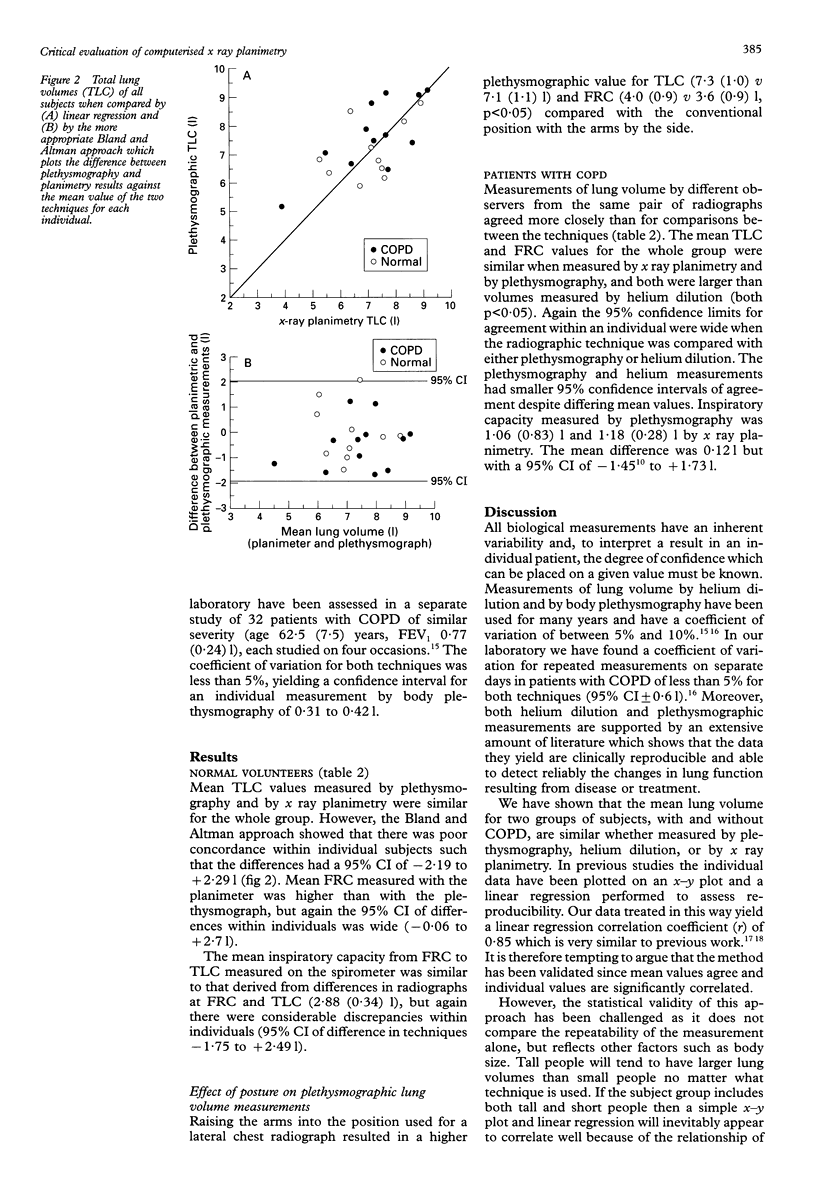
BACKGROUND--Computerised x-ray planimetry has been advocated as an alternative to body plethysmography and helium dilution for measuring static lung volumes. The accuracy and reproducibility of this method has been assessed in comparison with these standard methods. METHODS--Plethysmographic and planimetric measurements of total lung capacity (TLC) and functional residual capacity (FRC) were made in 10 normal subjects and in 12 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), with additional helium dilution measurements in the latter 12 patients. RESULTS--Mean lung volumes (TLC and FRC) for groups of subjects measured by planimetry and by plethysmography were similar in both groups and larger than the helium dilution measurement in patients with COPD. Intraindividual agreement between planimetry and plethysmography was poor, however, with a wide confidence interval (-2.2 to +2.31). The planimeter did not measure reliably changes in volume from TLC to FRC in individuals. CONCLUSIONS--Mean lung volumes measured by planimetry in a group of patients probably reflect a regression to the mean of the computer algorithm rather than accurate TLC estimation. The technique is not yet robust enough to replace the established techniques of helium dilution or plethysmography.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNHARD H. J., PIERCE J. A., JOYCE J. W., BATES J. H. Roentgenographic determination of total lung capacity. A new method evaluated in health, emphysema and congestive heart failure. Am J Med. 1960 Jan;28:51–60. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., BEDELL G. N., MARSHALL R., COMROE J. H., Jr A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):322–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI103281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtado A., Fray W. W. STUDIES OF TOTAL PULMONARY CAPACITY AND ITS SUB-DIVISIONS. II. CORRELATION WITH PHYSICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL MEASUREMENTS. J Clin Invest. 1933 Sep;12(5):807–823. doi: 10.1172/JCI100541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACH J. C., AVEDIAN V., MORALES G., POULOS P. Lung compartment determination. J Thorac Surg. 1956 Apr;31(4):452–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Warshaw R. H., Thornton J. C., Thornton K., Miller A. Predictive equations for total lung capacity and residual volume calculated from radiographs in a random sample of the Michigan population. Thorax. 1992 Jul;47(7):519–523. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.7.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyd H. M., String S. T., DuBois A. B. Radiographic and plethysmographic determination of total lung capacity. Radiology. 1966 Jan;86(1):7–14. doi: 10.1148/86.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyd H. M., String S. T., DuBois A. B. Radiographic and plethysmographic determination of total lung capacity. Radiology. 1966 Jan;86(1):7–14. doi: 10.1148/86.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J., Lapp N. L., Russakoff A. D., Reger R., Morgan W. K. Determination of lung volumes from chest films. Thorax. 1970 Sep;25(5):544–549. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.5.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt P. C., Klugh G. A. A method for the determination of total lung capacity from posteroanterior and lateral chest roentgenograms. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Sep;96(3):548–552. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.3.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reger R. B., Young A., Morgan W. K. An accurate and rapid radiographic method of determining total lung capacity. Thorax. 1972 Mar;27(2):163–168. doi: 10.1136/thx.27.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenstein D. O., Stănescu D. C., Francis C. Demonstration of failure of body plethysmography in airway obstruction. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Apr;52(4):949–954. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.4.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenstein D. O., Stănescu D. C. Frequency dependence of plethysmographic volume in healthy and asthmatic subjects. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Jan;54(1):159–165. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.54.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenstein D. O., Stănescu D. C. Reassessment of lung volume measurement by helium dilution and by body plethysmography in chronic air-flow obstruction. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Dec;126(6):1040–1044. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.6.1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stănescu D. C., Rodenstein D., Cauberghs M., Van de Woestijne K. P. Failure of body plethysmography in bronchial asthma. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Apr;52(4):939–948. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]