Abstract
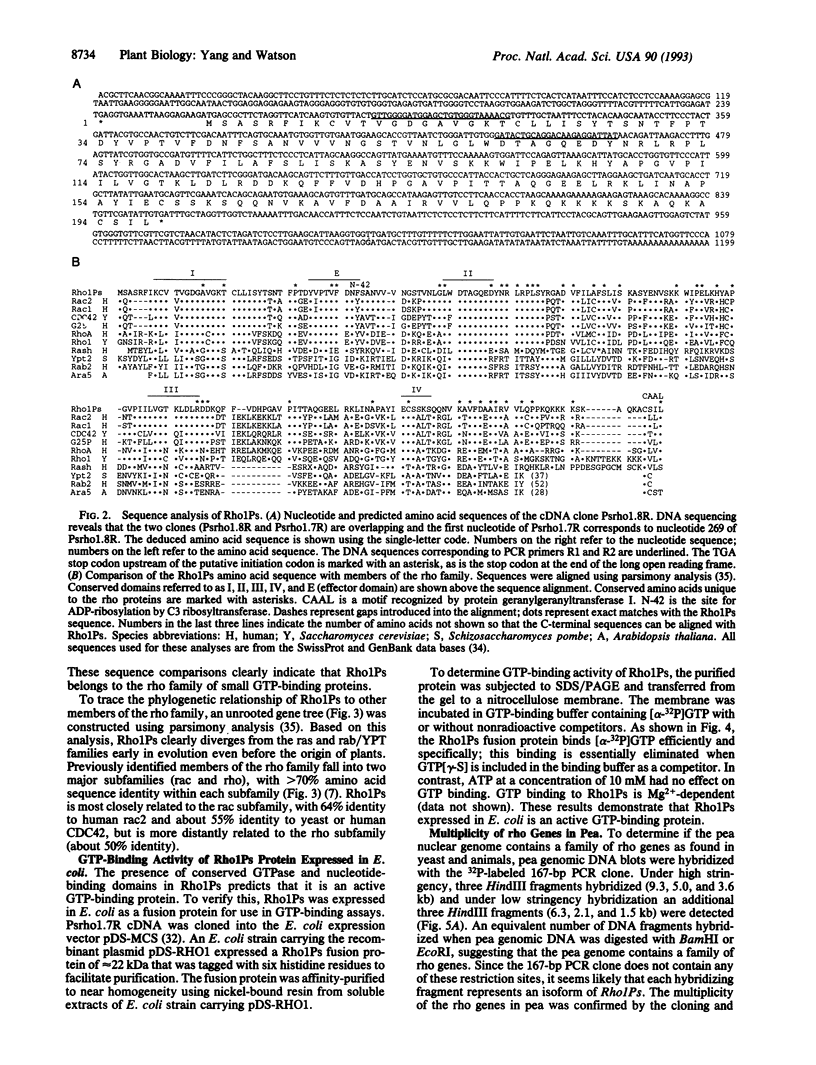
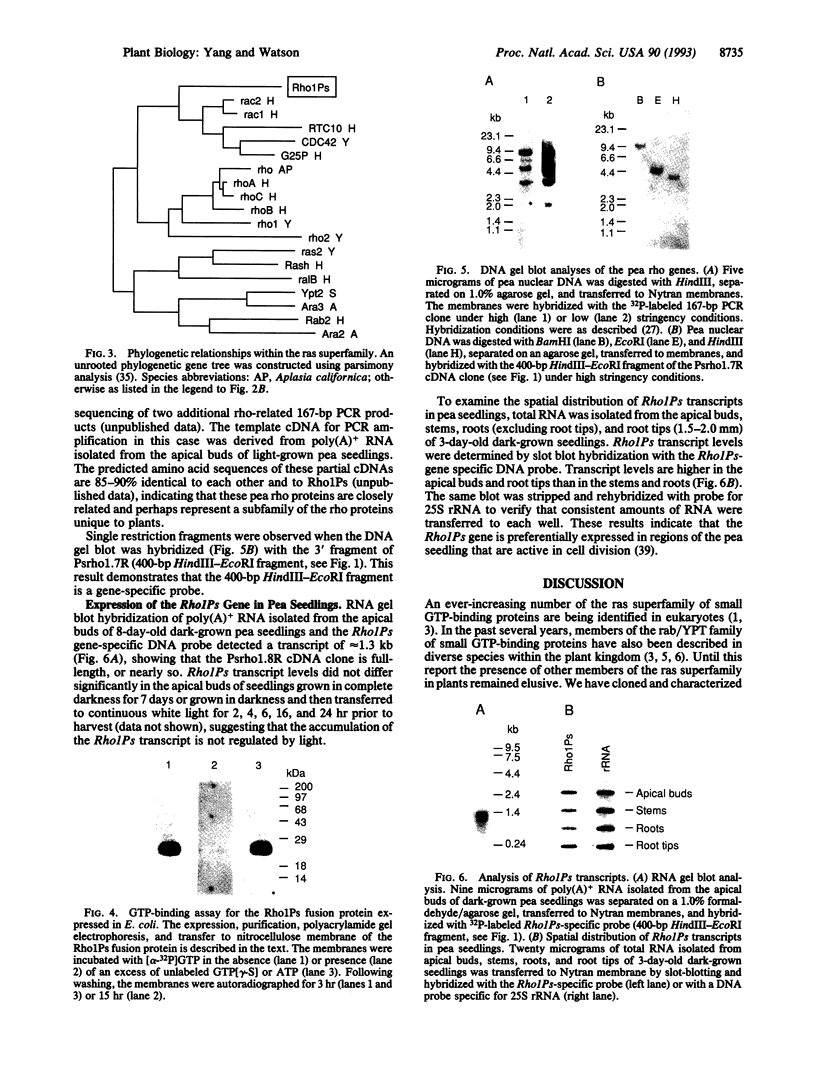
The rho proteins, members of the ras superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins, play a central role in the modulation of cellular functions involving the actin cytoskeleton such as in the establishment of cell polarity and morphology. As a first step in elucidating signal transduction pathways leading to processes mediated by the actin cytoskeleton in plants, we initiated cloning and characterization of rho proteins from pea. One rho-related, partial cDNA clone of 167 bp was isolated utilizing a polymerase chain reaction-based cloning strategy, using degenerate primers that correspond to conserved domains within the rho proteins. A full-length cDNA was isolated by screening a pea cDNA library using the 167-bp cDNA as a probe. The Rho1Ps cDNA contains an open reading frame encoding a polypeptide (Rho1Ps) of 197 amino acids that shows 45-64% sequence identity to members of the rho family and about 30% identity to other members of the ras superfamily. In addition to the nucleotide-binding and GTPase domains, Rho1Ps shares conserved residues and motifs unique to the rho proteins. Purified Rho1Ps protein expressed in Escherichia coli retains specific GTP-binding activity. These data indicate that Rho1Ps encodes a small GTP-binding protein of the rho family. The Rho1Ps transcript is expressed in all organs of pea seedlings, being more abundant in root tips and apical buds. DNA gel blot analyses show that the rho proteins in pea are encoded by a multigene family.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aktories K., Braun U., Rösener S., Just I., Hall A. The rho gene product expressed in E. coli is a substrate of botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase C3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):209–213. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag G., McCormick F. Regulators and effectors of ras proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:601–632. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Boquet P., Madaule P., Popoff M. R., Rubin E. J., Gill D. M. The mammalian G protein rhoC is ADP-ribosylated by Clostridium botulinum exoenzyme C3 and affects actin microfilaments in Vero cells. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1087–1092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet J. P., Tuana B. S. Identification of low molecular weight GTP-binding proteins and their sites of interaction in subcellular fractions from skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17613–17620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. Regulatory mechanisms for ras proteins. Bioessays. 1992 Mar;14(3):177–184. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Cadwallader K., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. A CAAX or a CAAL motif and a second signal are sufficient for plasma membrane targeting of ras proteins. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4033–4039. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. I., Pringle J. R. Molecular characterization of CDC42, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in the development of cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):143–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Der C. J., Bokoch G. M. The ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins: guidelines on nomenclature. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2512–2513. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1592203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimczak L. J., Schindler U., Cashmore A. R. DNA binding activity of the Arabidopsis G-box binding factor GBF1 is stimulated by phosphorylation by casein kinase II from broccoli. Plant Cell. 1992 Jan;4(1):87–98. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X., Feng X. H., Watson J. C. Differential accumulation of transcripts encoding protein kinase homologs in greening pea seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6951–6955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui M., Sasamoto S., Kunieda T., Nomura N., Ishizaki R. Cloning of ara, a putative Arabidopsis thaliana gene homologous to the ras-related gene family. Gene. 1989;76(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Toh-E A. Yeast RHO3 and RHO4 ras superfamily genes are necessary for bud growth, and their defect is suppressed by a high dose of bud formation genes CDC42 and BEM1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5690–5699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palme K., Diefenthal T., Vingron M., Sander C., Schell J. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of genes from Zea mays (L.) coding for members of the ras-related ypt gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):787–791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall S. K., Marshall M. S., Crowell D. N. Protein isoprenylation in suspension-cultured tobacco cells. Plant Cell. 1993 Apr;5(4):433–442. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Stradley S. J., Gierasch L. M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Sequence requirement for peptide recognition by rat brain p21ras protein farnesyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):732–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine A., Fujiwara M., Narumiya S. Asparagine residue in the rho gene product is the modification site for botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8602–8605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Kikuchi A., Kawata M. Small GTP-binding proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;133:187–230. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61861-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S., Jeanteur P., Fort P. Growth-regulated expression of rhoG, a new member of the ras homolog gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3138–3148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. C., Kaufman L. S., Thompson W. F. Developmental regulation of cytosine methylation in the nuclear ribosomal RNA genes of Pisum sativum. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):15–26. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90622-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Cramer C. L., Watson J. C. Protein farnesyltransferase in plants. Molecular cloning and expression of a homolog of the beta subunit from the garden pea. Plant Physiol. 1993 Feb;101(2):667–674. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziman M., O'Brien J. M., Ouellette L. A., Church W. R., Johnson D. I. Mutational analysis of CDC42Sc, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene that encodes a putative GTP-binding protein involved in the control of cell polarity. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3537–3544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






