Figure 2. Ameliorating effects of cpKimchi in H. pylori-infected chronic atrophic gastritis (24 weeks after H. pylori infection).
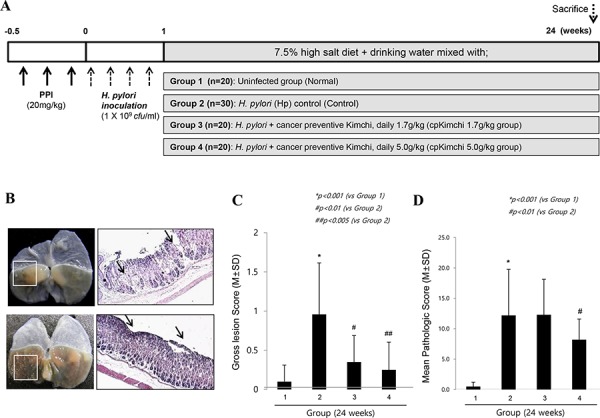
A. Protocol for H. pylori-associated gastritis model, 24 weeks. 90 mice were grouped into four, uninfected normal group (n = 20), H. pylori-infected control group (n = 30), 1.7 g/kg cpKimchi administered group (n = 20), and 5.0 g/kg cpKimchi administered group (n = 20) to document the efficacy of 24 weeks cpKimchi administration in H. pylori-initiated, high salt diet-promoted gastric damages model. B. Gross and pathological morphology and index according to group Administration of high salt diet after H. pylori infection led to accentuation of chronic atrophic gastritis. In detail, H. pylori infection followed with high salt diet led to some erosions, erythematous gastric mucosa, nodular mucosal changes, and protuberant foci of gastric mucosa at fore-stomach-glandular stomach area (box indicated). X100 C. Gross lesion scores according to group Gross lesion scores were significantly attenuated with cpKimchi administration (p < 0.01). D. Pathological scores according to group H. pylori infection for 24 weeks led to chronic atrophic gastritis presenting with loss of parietal cells, inflammatory cells such as monocytes, lymphocytes, and macrophages replacing gastric glands, and erosive mucosal changes. These changes were significantly decreased in group treated with cpKimchi 5 mg/kg (p < 0.05). The scoring system was described in “Materials and Methods”
