Figure 3. Suppression of NDRG1 by siRNA prevented β-catenin nuclear accumulation in HCC cells.
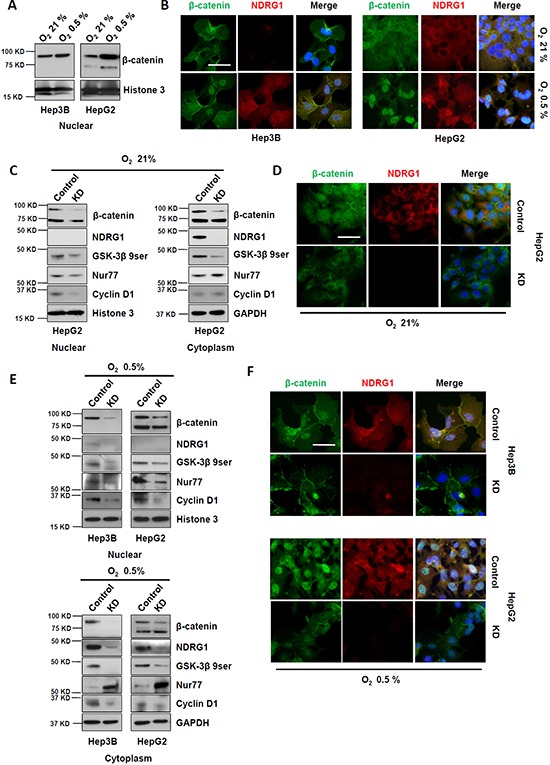
A. Western blot and B. immunofluorescence showing expression and localization of NDRG1 and β-catenin in Hep3B and HepG2 cells, under normoxia and hypoxia (400× magnification; scale bars: 5 μm). C. Western blot showing that suppression of NDRG1 decreased cytoplasmic and nuclear β-catenin levels, with corresponding changes in GSK-3β 9ser, Nur77, and Cyclin D1. GAPDH and Histone3 are used as loading controls. D. The changes in NDRG1 and β-catenin protein levels and their cellular localizations (after NDRG1 suppression) were confirmed by immunofluorescence staining (400× magnification; scale bars: 5 μm). E. The changes in protein levels of NDRG1, β-catenin, GSK-3β 9ser, Nur77, and Cyclin D1 caused by suppression of NDRG1 under hypoxia were detected by Western blot. GAPDH and Histone3 are used as loading controls. F. The changes in NDRG1 and β-catenin protein levels and their cellular localizations (after NDRG1 suppression) were confirmed by immunofluorescence staining of HCC cells cultured under hypoxia (400× magnification; scale bars: 5 μm).
