Abstract
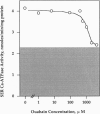
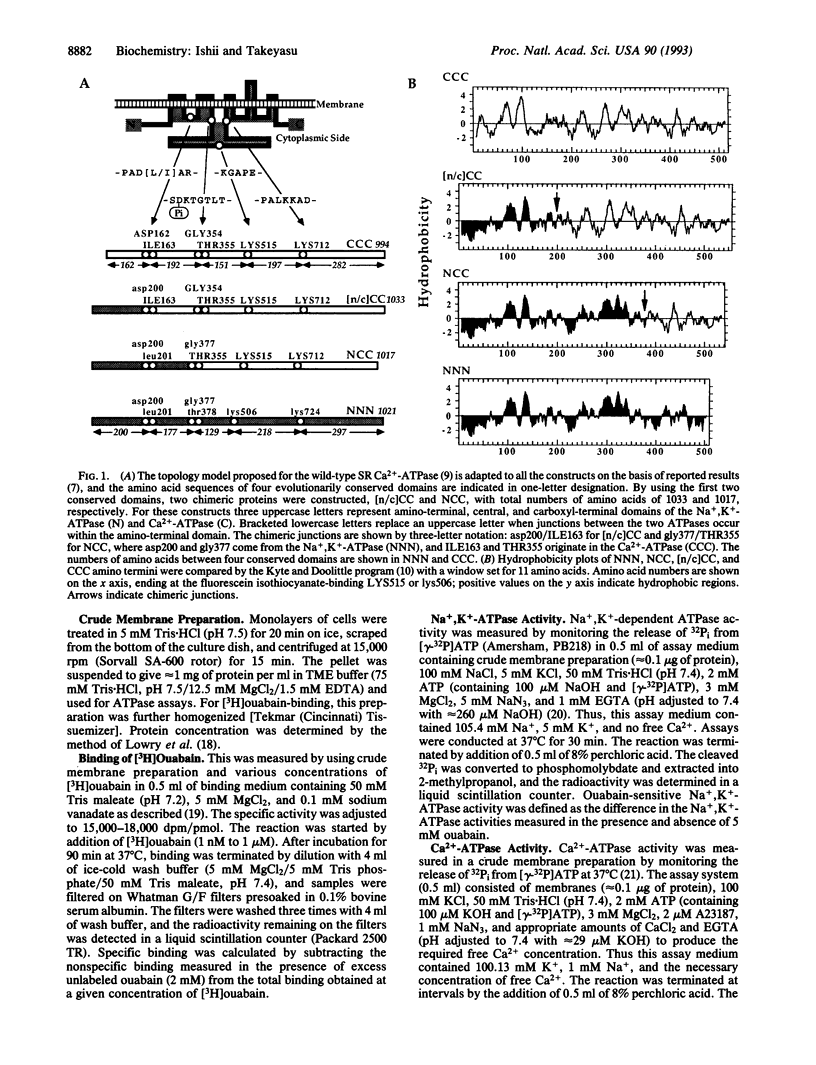
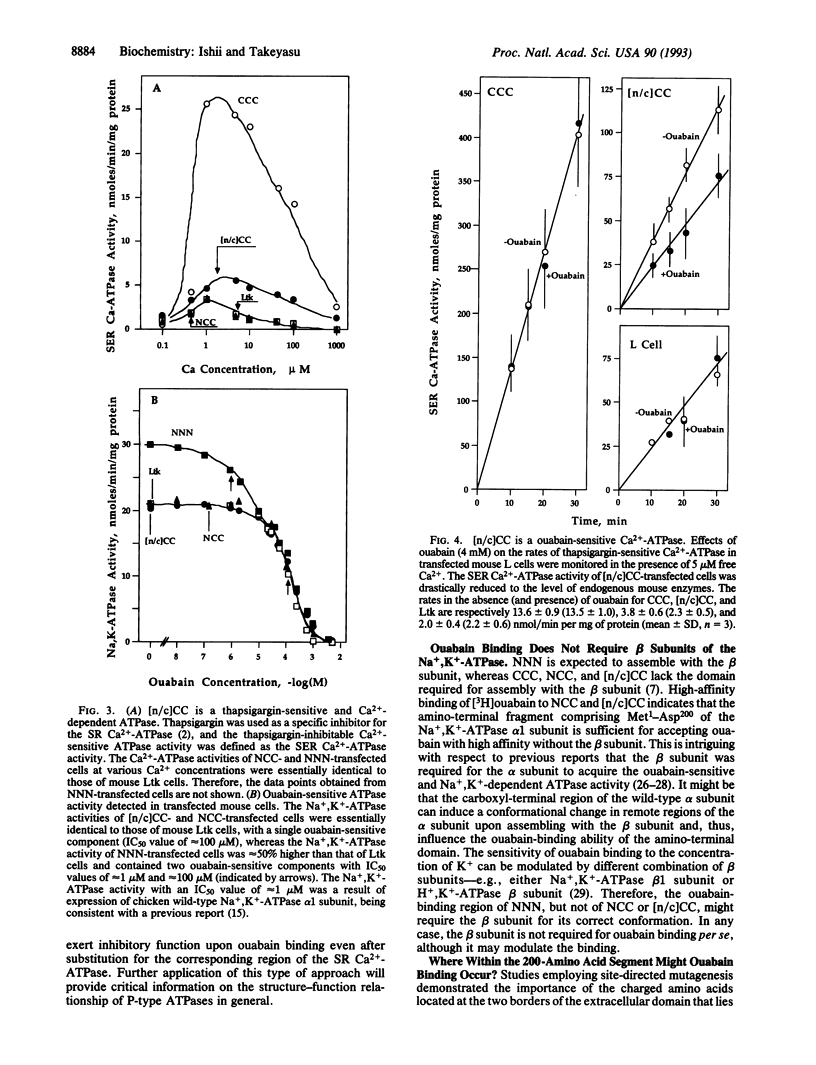
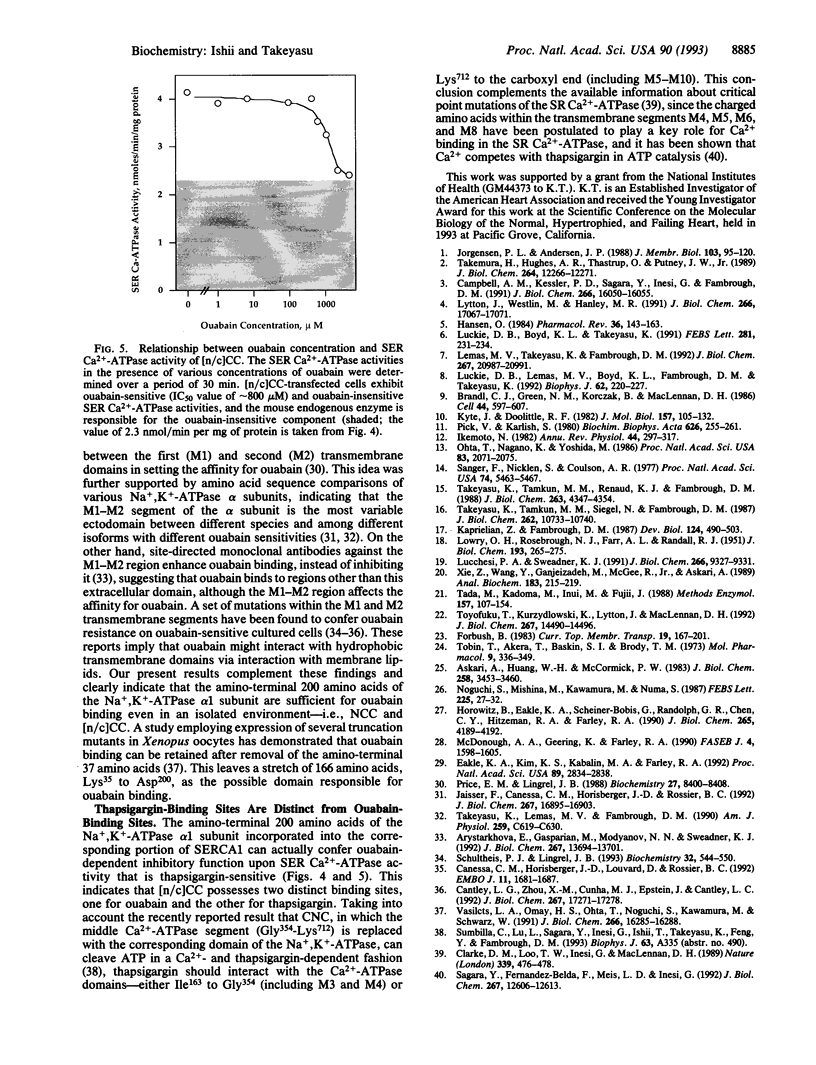
Cardiac glycosides such as G-strophanthin (ouabain) bind to and inhibit the plasma membrane Na+,K(+)-ATPase but not the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+)-ATPase, whereas thapsigargin specifically blocks the SR Ca(2+)-ATPase. The chimera [n/c]CC, in which the amino-terminal amino acids Met1 to Asp162 of the SR Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA1) were replaced with the corresponding portion of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit (Met1 to Asp200), retained thapsigargin- and Ca(2+)-sensitive ATPase activity, although the activity was lower than that of the wild-type SR Ca(2+)-ATPase. Moreover, this Ca(2+)-sensitive ATPase activity was inhibited by ouabain. The chimera NCC, in which Met1-Gly354 of the SR Ca(2+)-ATPase were replaced with the corresponding portion of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase, lost the thapsigargin-sensitive Ca(2+)-ATPase activity seen in CCC and [n/c]CC. [3H]Ouabain binding to [n/c]CC and NCC demonstrated that the affinity for this inhibitor seen in the wild-type chicken Na+,K(+)-ATPase was restored in these chimeric molecules. Thus, the ouabain-binding domains are distinct from the thapsigargin sites; ouabain binds to the amino-terminal portion (Met1 to Asp200) of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit, whereas thapsigargin interacts with the regions after Asp162 of the Ca(2+)-ATPase. Moreover, the amino-terminal 200 amino acids of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 subunit are sufficient to exert ouabain-dependent inhibition even after incorporation into the corresponding portion of the Ca(2+)-ATPase, and the segment Ile163 to Gly354 of the SR Ca(2+)-ATPase is critical for thapsigargin- and Ca(2+)-sensitive ATPase activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arystarkhova E., Gasparian M., Modyanov N. N., Sweadner K. J. Na,K-ATPase extracellular surface probed with a monoclonal antibody that enhances ouabain binding. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13694–13701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askari A., Huang W. H., McCormick P. W. (Na+ + K+)-dependent adenosine triphosphatase. Regulation of inorganic phosphate, magnesium ion, and calcium ion interactions with the enzyme by ouabain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3453–3460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Green N. M., Korczak B., MacLennan D. H. Two Ca2+ ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. M., Kessler P. D., Sagara Y., Inesi G., Fambrough D. M. Nucleotide sequences of avian cardiac and brain SR/ER Ca(2+)-ATPases and functional comparisons with fast twitch Ca(2+)-ATPase. Calcium affinities and inhibitor effects. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16050–16055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Louvard D., Rossier B. C. Mutation of a cysteine in the first transmembrane segment of Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit confers ouabain resistance. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1681–1687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. G., Zhou X. M., Cunha M. J., Epstein J., Cantley L. C. Ouabain-resistant transfectants of the murine ouabain resistance gene contain mutations in the alpha-subunit of the Na,K-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17271–17278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., Inesi G., MacLennan D. H. Location of high affinity Ca2+-binding sites within the predicted transmembrane domain of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):476–478. doi: 10.1038/339476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakle K. A., Kim K. S., Kabalin M. A., Farley R. A. High-affinity ouabain binding by yeast cells expressing Na+, K(+)-ATPase alpha subunits and the gastric H+, K(+)-ATPase beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen O. Interaction of cardiac glycosides with (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase. A biochemical link to digitalis-induced inotropy. Pharmacol Rev. 1984 Sep;36(3):143–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz B., Eakle K. A., Scheiner-Bobis G., Randolph G. R., Chen C. Y., Hitzeman R. A., Farley R. A. Synthesis and assembly of functional mammalian Na,K-ATPase in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4189–4192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemoto N. Structure and function of the calcium pump protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:297–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaisser F., Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Primary sequence and functional expression of a novel ouabain-resistant Na,K-ATPase. The beta subunit modulates potassium activation of the Na,K-pump. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16895–16903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Andersen J. P. Structural basis for E1-E2 conformational transitions in Na,K-pump and Ca-pump proteins. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(2):95–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01870942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemas M. V., Takeyasu K., Fambrough D. M. The carboxyl-terminal 161 amino acids of the Na,K-ATPase alpha-subunit are sufficient for assembly with the beta-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20987–20991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckie D. B., Boyd K. L., Takeyasu K. Ouabain- and Ca2(+)-sensitive ATPase activity of chimeric Na- and Ca-pump molecules. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80400-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckie D. B., Lemas V., Boyd K. L., Fambrough D. M., Takeyasu K. Molecular dissection of functional domains of the E1E2-ATPase using sodium and calcium pump chimeric molecules. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;62(1):220–227. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81807-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J., Westlin M., Hanley M. R. Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase family of calcium pumps. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17067–17071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough A. A., Geering K., Farley R. A. The sodium pump needs its beta subunit. FASEB J. 1990 Apr 1;4(6):1598–1605. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.6.2156741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi S., Mishina M., Kawamura M., Numa S. Expression of functional (Na+ + K+)-ATPase from cloned cDNAs. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Nagano K., Yoshida M. The active site structure of Na+/K+-transporting ATPase: location of the 5'-(p-fluorosulfonyl)benzoyladenosine binding site and soluble peptides released by trypsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price E. M., Lingrel J. B. Structure-function relationships in the Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit: site-directed mutagenesis of glutamine-111 to arginine and asparagine-122 to aspartic acid generates a ouabain-resistant enzyme. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8400–8408. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagara Y., Fernandez-Belda F., de Meis L., Inesi G. Characterization of the inhibition of intracellular Ca2+ transport ATPases by thapsigargin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12606–12613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Kadoma M., Inui M., Fujii J. Regulation of Ca2+-pump from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:107–154. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Hughes A. R., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of calcium entry by the tumor promoter thapsigargin in parotid acinar cells. Evidence that an intracellular calcium pool and not an inositol phosphate regulates calcium fluxes at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12266–12271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Lemas V., Fambrough D. M. Stability of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha-subunit isoforms in evolution. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):C619–C630. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.4.C619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Tamkun M. M., Renaud K. J., Fambrough D. M. Ouabain-sensitive (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity expressed in mouse L cells by transfection with DNA encoding the alpha-subunit of an avian sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4347–4354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Tamkun M. M., Siegel N. R., Fambrough D. M. Expression of hybrid (Na+ + K+)-ATPase molecules after transfection of mouse Ltk-cells with DNA encoding the beta-subunit of an avian brain sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10733–10740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin T., Akera T., Baskin S. I., Brody T. M. Calcium ion and sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase: its mechanism of inhibition and identification of the E 1 -P intermediate. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 May;9(3):336–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyofuku T., Kurzydlowski K., Lytton J., MacLennan D. H. The nucleotide binding/hinge domain plays a crucial role in determining isoform-specific Ca2+ dependence of organellar Ca(2+)-ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14490–14496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilets L. A., Omay H. S., Ohta T., Noguchi S., Kawamura M., Schwarz W. Stimulation of the Na+/K+ pump by external [K+] is regulated by voltage-dependent gating. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16285–16288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Z. J., Wang Y. H., Ganjeizadeh M., McGee R., Jr, Askari A. Determination of total (Na+ + K+)-ATPase activity of isolated or cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1989 Dec;183(2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90470-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]