Abstract
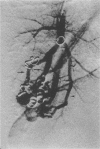
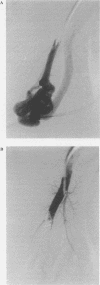
BACKGROUND--Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations may cause a number of complications when left untreated. Embolisation of the feeding vessels is a relatively new approach and information concerning its efficacy and long term results is scarce. METHODS--Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations with feeding arteries of > 3 mm were treated by embolisation. Right to left shunt fraction and arterial oxygen pressure breathing air (PaO2) were measured before and after treatment. Six monthly measurement of shunt fraction was used for follow up. RESULTS--In 32 patients 92 pulmonary arteriovenous malformations were treated by coil embolisation. Mean shunt fraction decreased from 16.6% to 7.4% and PaO2 increased from 9.6 kPa to 11.5 kPa. Treatment was incomplete in two patients, one of whom was subsequently treated surgically. Serious complications occurred in one patient. Recanalisation of embolised vessels occurred in two cases after 22 and 28 months, respectively. Mean period of follow up was 25 months. CONCLUSIONS--Embolisation is a safe and efficacious treatment for most pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Long term studies are necessary to determine the risk of recanalisation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke C. M., Safai C., Nelson D. P., Raffin T. A. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: a critical update. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;134(2):334–339. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers E. R., Whyte M. K., Jackson J. E., Allison D. J., Hughes J. M. Effect of percutaneous transcatheter embolization on pulmonary function, right-to-left shunt, and arterial oxygenation in patients with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Aug;142(2):420–425. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.2.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dines D. E., Arms R. A., Bernatz P. E., Gomes M. R. Pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Jul;49(7):460–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dines D. E., Seward J. B., Bernatz P. E. Pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas. Mayo Clin Proc. 1983 Mar;58(3):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. Digital subtraction angiography of the chest. Clin Chest Med. 1984 Jun;5(2):313–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianturco C., Anderson J. H., Wallace S. Mechanical devices for arterial occlusion. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975 Jul;124(3):428–435. doi: 10.2214/ajr.124.3.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goergen S. K., Sacharias N. R. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: pathology, clinical features and treatment with balloon and coil occlusion. Australas Radiol. 1992 Aug;36(3):222–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1673.1992.tb03156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartnell G. G., Allison D. J. Coil embolization in the treatment of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. J Thorac Imaging. 1989 Jan;4(1):81–85. doi: 10.1097/00005382-198901000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartnell G. G., Jackson J. E., Allison D. J. Coil embolization of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1990 Dec;13(6):347–350. doi: 10.1007/BF02578672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewes R. C., Auster M., White R. I., Jr Cerebral embolism--first manifestation of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1985;8(3):151–155. doi: 10.1007/BF02552883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. E., Whyte M. K., Allison D. J., Hughes J. M. Coil embolization of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Cor Vasa. 1990;32(3):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour K. A., Hatcher C. R., Jr, Logan W. D., Jr, Abbott O. A. Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula. Am Surg. 1971 Apr;37(4):203–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press O. W., Ramsey P. G. Central nervous system infections associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am J Med. 1984 Jul;77(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puskas J. D., Allen M. S., Moncure A. C., Wain J. C., Jr, Hilgenberg A. D., Wright C., Grillo H. C., Mathisen D. J. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: therapeutic options. Ann Thorac Surg. 1993 Aug;56(2):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(93)91156-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remy-Jardin M., Wattinne L., Remy J. Transcatheter occlusion of pulmonary arterial circulation and collateral supply: failures, incidents, and complications. Radiology. 1991 Sep;180(3):699–705. doi: 10.1148/radiology.180.3.1871280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remy J., Remy-Jardin M., Wattinne L., Deffontaines C. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: evaluation with CT of the chest before and after treatment. Radiology. 1992 Mar;182(3):809–816. doi: 10.1148/radiology.182.3.1535899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román G., Fisher M., Perl D. P., Poser C. M. Neurological manifestations of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber disease): report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Ann Neurol. 1978 Aug;4(2):130–144. doi: 10.1002/ana.410040207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter-Eringa H., Orie N. G., Sluiter H. J. Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula. Diagnosis and prognosis in noncomplainant patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Aug;100(2):177–188. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.100.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. G., Cockerill E. M., Manfredi F., Klatte E. C. Therapeutic embolization of the pulmonary artery in pulmonary arteriovenous fistula. Am J Med. 1978 Feb;64(2):360–365. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry P. B., White R. I., Jr, Barth K. H., Kaufman S. L., Mitchell S. E. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Physiologic observations and results of therapeutic balloon embolization. N Engl J Med. 1983 May 19;308(20):1197–1200. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198305193082005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler H. R. Brain abscess and pulmonary arteriovenous fistulae. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1973;98:314–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vase P., Holm M., Arendrup H. Pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Acta Med Scand. 1985;218(1):105–109. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1985.tb08832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. I., Jr, Barth K. H., Kaufman S. L., Terry P. B. Detachable silicone balloons: results of experimental study and clinical investigations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Ann Radiol (Paris) 1980 Apr-May;23(4):338–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. I., Jr, Lynch-Nyhan A., Terry P., Buescher P. C., Farmlett E. J., Charnas L., Shuman K., Kim W., Kinnison M., Mitchell S. E. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: techniques and long-term outcome of embolotherapy. Radiology. 1988 Dec;169(3):663–669. doi: 10.1148/radiology.169.3.3186989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. I., Jr, Pollak J. S. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: diagnosis with three-dimensional helical CT--a breakthrough without contrast media. Radiology. 1994 Jun;191(3):613–614. doi: 10.1148/radiology.191.3.8184034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]