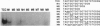Abstract
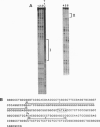
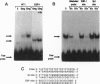
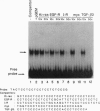
The putative Wilms tumor suppressor gene, wt1, encodes a zinc-finger protein that binds to the DNA sequence 5'-GCGGGGGCG-3'. We previously reported that WT1 has separable domains that function either to activate or suppress transcription. We now have identified a second WT1 binding sequence (5'-TCCTCCTCCTCCTCTCC-3') 3' to the transcription initiation site of the platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene by DNase I footprinting and gel mobility shift assays. WT1 requires both 5' and 3' binding sites for transcriptional suppression; however, WT1 functions as a transcriptional activator when it binds to either the 5' or 3' site alone. This second WT1 binding sequence functions equally well as the previously identified 5'-GCGGGGGCG-3' sequence when analyzed in transient transfection assays. A core DNA sequence recognized by WT1 was defined by using related synthetic oligonucleotides. We also identified sequences similar to the WT1 binding site within the promoter regions of five other growth-related genes and demonstrated that each of these sequences also binds WT1 in gel mobility shift assays. These results thus identify a second WT1 binding site and suggest that additional growth-related genes may be transcriptionally influenced by WT1.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bickmore W. A., Oghene K., Little M. H., Seawright A., van Heyningen V., Hastie N. D. Modulation of DNA binding specificity by alternative splicing of the Wilms tumor wt1 gene transcript. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):235–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1321494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call K. M., Glaser T., Ito C. Y., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Rose E. A., Kral A., Yeger H., Lewis W. H. Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at the human chromosome 11 Wilms' tumor locus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90601-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F. Polypeptide growth factors: roles in normal and abnormal cell growth. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:443–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond I. A., Madden S. L., Rohwer-Nutter P., Bell G. I., Sukhatme V. P., Rauscher F. J., 3rd Repression of the insulin-like growth factor II gene by the Wilms tumor suppressor WT1. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):674–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1323141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraizer G. E., Bowen-Pope D. F., Vogel A. M. Production of platelet-derived growth factor by cultured Wilms' tumor cells and fetal kidney cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Oct;133(1):169–174. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessler M., Poustka A., Cavenee W., Neve R. L., Orkin S. H., Bruns G. A. Homozygous deletion in Wilms tumours of a zinc-finger gene identified by chromosome jumping. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):774–778. doi: 10.1038/343774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber D. A., Sohn R. L., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Call K. M., Housman D. E. Alternative splicing and genomic structure of the Wilms tumor gene WT1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9618–9622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. K., Trusko S. P., Murphy M., George D. L. An S1 nuclease-sensitive homopurine/homopyrimidine domain in the c-Ki-ras promoter interacts with a nuclear factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2705–2709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. C., Jinno Y., Merlino G. T. Modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor proto-oncogene transcription by a promoter site sensitive to S1 nuclease. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4174–4184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinniburgh A. J. A cis-acting transcription element of the c-myc gene can assume an H-DNA conformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7771–7778. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafyatis R., Denhez F., Williams T., Sporn M., Roberts A. Sequence specific protein binding to and activation of the TGF-beta 3 promoter through a repeated TCCC motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6419–6425. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X., Wang Z., Gu L., Deuel T. F. Functional analysis of the human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain promoter region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25614–25619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden S. L., Cook D. M., Morris J. F., Gashler A., Sukhatme V. P., Rauscher F. J., 3rd Transcriptional repression mediated by the WT1 Wilms tumor gene product. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1550–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.1654597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maheswaran S., Park S., Bernard A., Morris J. F., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Hill D. E., Haber D. A. Physical and functional interaction between WT1 and p53 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5100–5104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morris J. F., Tournay O. E., Cook D. M., Curran T. Binding of the Wilms' tumor locus zinc finger protein to the EGR-1 consensus sequence. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1259–1262. doi: 10.1126/science.2244209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Seino M., Nishi S., Bell G. I. Structure of the human insulin receptor gene and characterization of its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):114–118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression: alpha and beta promoters are trans activated by viral functions in permissive human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.135-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P. Early transcriptional events in cell growth: the Egr family. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1990 Dec;1(6):859–866. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V16859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Y., Lin X. H., Nobyuoshi M., Qui Q. Q., Deuel T. F. Binding of single-stranded oligonucleotides to a non-B-form DNA structure results in loss of promoter activity of the platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13669–13674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Y., Madden S. L., Deuel T. F., Rauscher F. J., 3rd The Wilms' tumor gene product, WT1, represses transcription of the platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):21999–22002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Y., Qiu Q. Q., Deuel T. F. The Wilms' tumor gene product WT1 activates or suppresses transcription through separate functional domains. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9172–9175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Lin X. H., Qiu Q. Q., Deuel T. F. Modulation of transcription of the platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene by a promoter region sensitive to S1 nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17022–17031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]