Abstract
A 37-year-old male patient presented with right knee pain and swelling. The patient had a 6-year history of rheumatoid arthritis. Physical examination was notable for swelling and tenderness of the right knee. The diagnosis of lipoma arborescens (LA) was confirmed from the magnetic resonance imaging of the right knee. Herein, we report the use of bone scintigraphy in a case of LA treated with yttrium-90 radiosynovectomy.
Keywords: Bone scintigraphy, lipoma arborescens, radiosynovectomy, yttrium-90
A 37-year-old male patient presented with right knee pain and swelling. He had a 6-year history of rheumatoid arthritis with technetium-99m, methylene diphosphonate (MDP) bone scan showed evidence of increased perfusion, blood pool, and circular activity in suprapatellar pouch of right knee [Figure 1a]. Delayed image showed prominent right patellar and right knee joint MDP activity. Also, suprapatellar activity accumulation on the soft tissue was observed (arrow) [Figure 1b]. Radiosynovectomy (RS) was applied using 185 MBq yttrium-90 (Y-90) citrate combined with a 40 mg triamcinolone acetonide by intra-articular injection. Bremsstrahlung images revealed intense Y-90 distribution in the right knee, mainly in the suprapatellar region [Figure 1e]. Three months after therapy, distribution of activity decreased in the right knee, particularly in the central part of suprapatellar region comparing bone scintigraphy images performed at baseline [Figure 1c and d]. Sagittal fat-saturated proton density-weighted image showed irregularly shaped soft tissue lesion of fatty signal intensity within the suprapatellar pouch and joint effusion in the knee joint space and suprapatellar bursa [Figure 1f].
Figure 1.
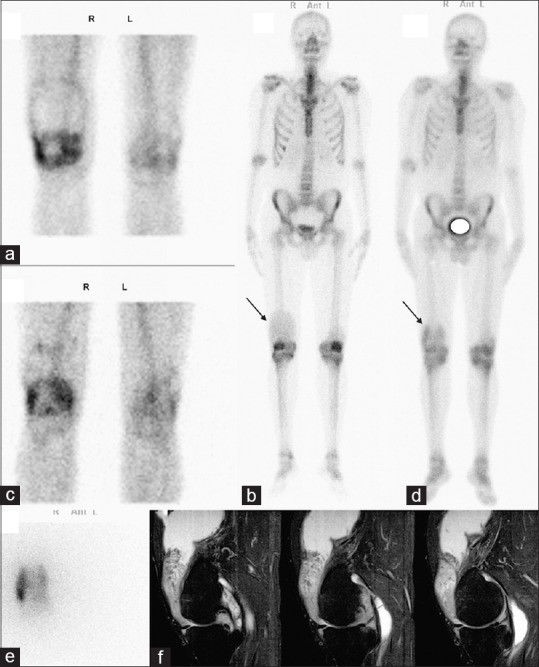
Blood pool image showing evidence of increased perfusion, circular activity in suprapatellar pouch of right knee. (a) Delayed whole body image showing prominent right patellar, right knee joint, and suprapatellar activity accumulation on soft tissue is observed (arrow). (b) In the bremsstrahlung images, the intense yttrium-90 accumulation in the right suprapatellar region. (e) After therapy, activity decreased in the right knee mainly in the central part of suprapatellar region. (c and d) Magnetic resonance imaging showing fatty signal intensity within the suprapatellar pouch and joint effusion in the knee joint space and suprapatellar bursa (f)
Lipoma arborescens (LA) is an uncommon, benign intra-articular lesion most commonly found in the knee, characterized by villous lipomatous proliferation of synovial membrane. The pathognomonic and gold standard imaging modality for diagnosis is magnetic resonance imaging.[1] To the best of our knowledge, bone scan appearance of RS treatment response was not defined in LA. RS is generally used in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, other inflammatory arthropathy, such as osteoarthritis and hemophilic arthropathy.[2] Intra-articular injection of Y-90 results in coagulation necrosis of the superficial cells of the synovium. Subsequently, synovial cells count and blood flow reduced in this area.[3] As MDP uptake is directly proportional with blood flow and osteoblastic activity, decreased MDP activity is observed in LA after Y-90 therapy. Finally, BS is not a first-line diagnostic imaging modality for LA; however, it can be used for the treatment response of Y-90 in patient with LA.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Vilanova JC, Barceló J, Villalón M, Aldomà J, Delgado E, Zapater I. MR imaging of lipoma arborescens and the associated lesions. Skeletal Radiol. 2003;32:504–9. doi: 10.1007/s00256-003-0654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Turkmen C, Kilicoglu O, Dikici F, Bezgal F, Kuyumcu S, Gorgun O, et al. Survival analysis of Y-90 radiosynovectomy in the treatment of haemophilic synovitis of the knee: A 10-year retrospective review. Haemophilia. 2014;20:e45–50. doi: 10.1111/hae.12252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fischer M, Mödder G. Radionuclide therapy of inflammatory joint diseases. Nucl Med Commun. 2002;23:829–31. doi: 10.1097/00006231-200209000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


