Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Despite the drive toward centralization of surgery in high-volume centers, the majority of colectomies are still performed by low- or medium-volume surgeons.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
A modification of the technique of laparoscopic right colectomy (LRC) originally described by Young-Fadok and Nelson was developed. The key points of that technique were maintained, but a different port-site layout and a counterclockwise approach were adopted, to warrant better trocar triangulation, to reduce the need of right colon manipulation and to avoid dissection along false planes. This modified technique was applied in 82 patients by 16 surgeons with no previous experience in LRC.
RESULTS:
Average operative time was 125 ± 35 min. Conversion occurred in 10 cases (12.2%). Grade III postoperative complications occurred in 3 patients (3.6%). No postoperative mortality was observed. Average number of lymph nodes retrieved was 19 ± 6. Average length of stay was 7 ± 4 days.
CONCLUSION:
Providing low-volume surgeons with simplified and easy-to-learn surgical techniques could improve outcomes and lead to an increased use of laparoscopy.
Keywords: Colon cancer, laparoscopic right colectomy, learning, right colon, surgeon volume, surgical education
INTRODUCTION
Laparoscopic right colectomy (LRC) requires advanced skills and a specific training is recommended in order to perform this operation safely and effectively. Differences in training protocols exist among surgical teams and the need for a consensus on the key steps of LRC has been stressed by many authors.[1]
The perceived difficulties in performing LRC are further enhanced by the introduction of the concept of complete mesocolic excision (CME) in the surgical treatment of colon cancer.[2,3] Several techniques have been proposed for LRC with CME and good oncologic results are reported in experienced hands.[4,5,6,7,8]
Despite the drive for centralization of surgery in high-volume centers, the majority of colectomies are still performed by low- or medium-volume surgeons[9,10] and the amount of partial colectomies performed laparoscopically in nonteaching hospitals is increased in the recent years.[11] The development and teaching of easy-to-learn and easy-to-perform surgical techniques could help to further increase the diffusion of laparoscopy among surgeons and to achieve better results, offering good surgery to patients without forcing them to move toward reference centers.
In 2000, Young-Fadok and Nelson described a simplified technique of LRC consisting in laparoscopic mobilization of the right colon followed by extracorporeal vascular ligation and ileocolic anastomosis.[12] The key point of their technique is that the right colon, once mobilized, may be exteriorized through a small supraumbilical incision that directly overlies the root of the ileocolic vessels.
We introduced some changes to further simplify the exposure of the correct planes according to the concept of CME, to reduce the need to manipulate the colon and to improve ergonomics of surgery.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Since July 2010, when the following technique was developed, all patients with cancer of the cecum and ascending colon and patients with active Crohn's disease (CD) of the terminal ileum and right colon were candidates for this procedure. Preoperative evaluation was done with colonoscopy and abdominal computed tomography scan. Laparoscopic procedure was contraindicated in case of fistulizing CD, cancer infiltrating adjacent organs or perforated cancer. Cancer with suspected infiltration of the right paracolic peritoneum and previous abdominal surgery were considered relative contraindications and a laparoscopic procedure was usually attempted.
The procedure was performed by surgeons with no previous experience on LRC, who were trained by an expert surgeon for their first three cases with the eventual supervision of the main Author. An expert surgeon was always on call.
Data on operative time, conversion, postoperative complications (occurring within 30 days after surgery), length of stay and number of harvested lymph nodes were collected retrospectively. Postoperative complications were classified according to the Clavien-Dindo grading system.
Technique
The patient is placed supine, with both arms at the side.
The surgeon is on the patient's left side; the assistant stays on the surgeon's left side; the nurse is on the patient's right, close to the legs; the monitor stays on the patient's right side.
Port Site Placement
A 10-mm Hasson trocar is placed via a cut-down procedure on the left side of the umbilicus, pneumoperitoneum is established and the laparoscope is inserted.
A 5-mm trocar is then placed in the epigastric midline (EPI), 4 cm above the first trocar. Then, a 5-mm trocar is placed in the McBurney point (MB) [Figure 1].
Figure 1.
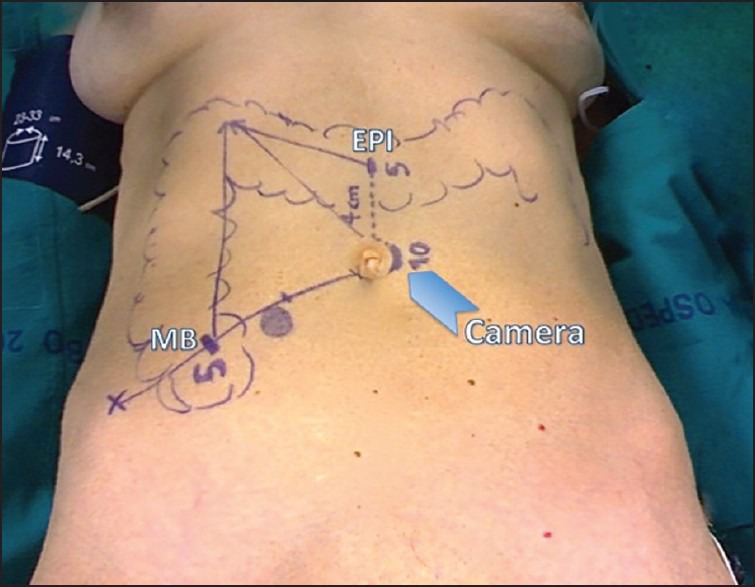
Port site placement
Step 1: Gastrocolic ligament division
The patient is positioned in reverse Trendelenburg with the right side inclined upward. This allows the small bowel, transverse colon and omentum to fall toward the left lower quadrant, tensing the gastrocolic ligament and assisting in retraction.
Using the MB trocar, the gastrocolic ligament is grasped near the transverse colon and elevated both toward the anterior abdominal wall and the feet to identify the correct plane between the gastrocolic ligament and the underlying mesentery of the transverse colon. Starting from the level of the antropyloric region and proceeding close to the colon, the ligament is then sectioned using a dissecting instrument introduced in the EPI trocar. Step 1 is completed after visualization of the second portion of the duodenum [Figure 2a].
Figure 2.
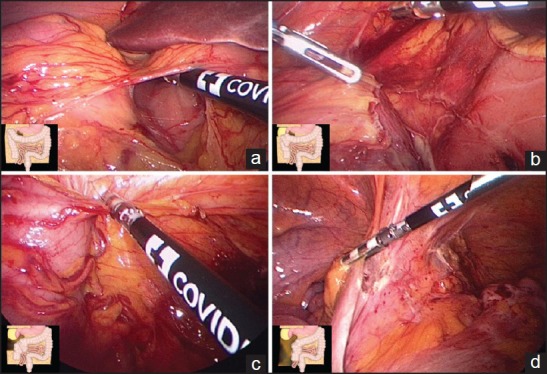
Surgical steps
Step 2: Hepatic Flexure Mobilization
The peritoneum overlying the hepatic flexure and the right phrenocolic ligament is sectioned, easily identifying the profile of the kidney without entering a wrong plane behind it.
The hepatic flexure and the proximal transverse colon are separated from the anterior surface of the kidney and the duodenum by blunt dissection, as the colon is brought by its own weight toward the pelvis and the left, without any traction.
Step 2 is completed when the third portion of the duodenum is visualized [Figure 2b].
Step 3: Right paracolic peritoneal division and cecal mobilization
Working from the free lateral peritoneal edge of the mobilized hepatic flexure, the right paracolic gutter is opened along the ascending colon toward the cecum [Figure 2c]. Once the peritoneal division around the cecum is completed, the right colon spontaneously falls toward the midline and is easy to detach from Toldt's fascia by blunt dissection, without any traction.
Step 4: Identification of the right ureter
The patient is moved to Trendelenburg, with the right side still banked up: this allows the small bowel and the mobilized cecum to fall toward the midline.
If present, the appendix is grasped to hold the cecum upwards and straighten the terminal ileum; otherwise, the peritoneal edge around the cecum is grasped.
The ureter is pursued via blunt dissection along the Toldt's fascia, medially to the gonadal vessels.
Step 5: Terminal ileum mobilization and medialization of the right colon
After clear identification of the right ureter, the terminal ileum is mobilized dissecting the peritoneum along the base of the small-bowel mesentery [Figure 2d] until the right colon spontaneously falls toward the midline, disappearing from the monitor: this sign indicates that the dissection is sufficient for exteriorization.
In few cases, little further blunt dissection along the Toldt's fascia is needed to complete the medialization of the right colon.
Step 6: Exteriorization, vascular ligation, resection and anastomosis
The appendix (or the terminal ileus) is firmly grasped through the MB trocar: this helps to retrieve the right colon.
The periumbilical port-site incision is extended cephalad to join the epigastric port-site incision, and the right colon is exteriorized [Figure 3].
Figure 3.
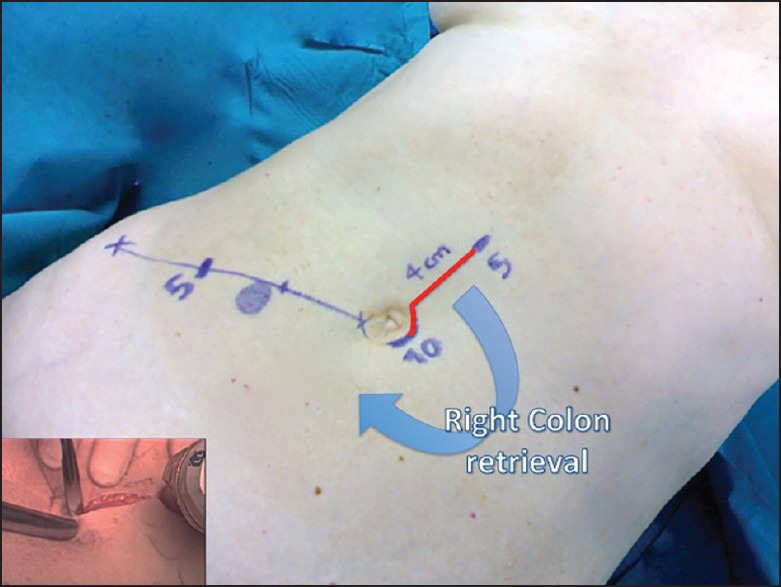
The final incision joins the epigastric and periumbilical port sites
After the terminal ileum and transverse colon are divided at the chosen level, the mesocolon is severed in a V-shape-like fashion toward the supplying vessels using a sealing-dissecting device. The ileocolic vessels and if present the right colic vessels are prepared and divided at their origin [Figure 4]. The anastomosis is performed according to the surgeon's preference. Before closing the midline incision, if desired, a drain is placed through the MB port site.
Figure 4.
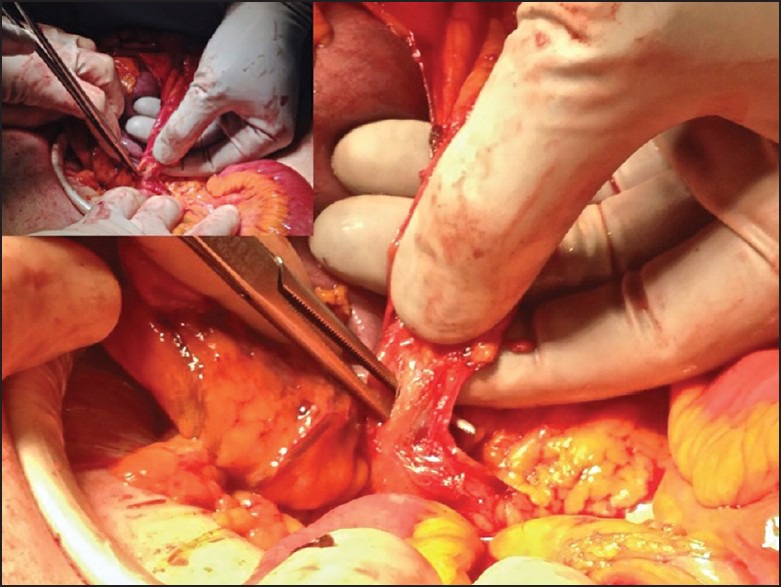
Central vascular ligation through the midline incision
RESULTS
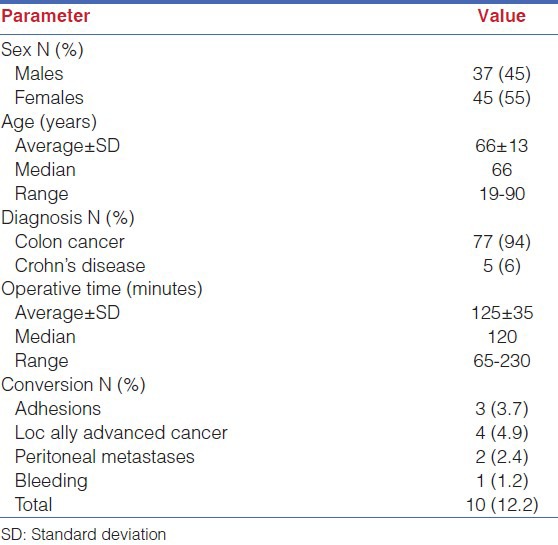
Between July 2010 and July 2014 the above-described technique was applied in 82 consecutive patients by 16 surgeons (10 residents and 6 fellows). Average number of operations per surgeon was 5 ± 3 (median 5, range 1-10). Average operative time was 125 ± 35 min. Conversion occurred in 10 cases (12.2%): 3 for adhesions, 6 for unsuspected peritoneal metastases or locally advanced tumor and 1 for bleeding due to tearing of the Henle's gastrocolic trunk occurred in the extracorporeal phase of the operation [Table 1].
Table 1.
Patient's characteristics and intraoperative data
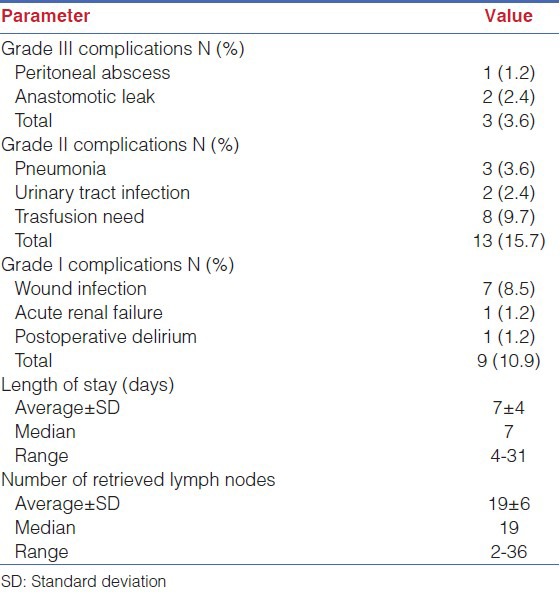
Grade III postoperative complications occurred in three patients (3.6%):
1. Peritoneal abscess (requiring drainage), 2. Anastomotic leaks (2.4%, requiring reoperation). No postoperative mortality was observed.
Average length of stay was 7 ± 4 days. Average number of lymph nodes retrieved was 19 ± 6 [Table 2].
Table 2.
Postoperative outcomes
DISCUSSION
In the recent years an advice toward centralization of colorectal surgery to high-volume centers has been given by many authors.[13] Nevertheless, the association between caseload and outcomes is still questionable[14] and the majority of colorectal operations are still not performed by high-volume surgeons.[9,10,11,15] There is a growing agreement that providing local services with adequate surgical education and training could be a more effective strategy to improve outcomes and global health.[16] Arming the growing surgeon with simplified and easy-to-learn surgical techniques could be an important step of this strategy.
The original technique proposed by Young-Fadok and Nelson is intended to keep the laparoscopic procedure as close to the open procedure as possible, in order to make it easily reproducible. Their technique requires one left upper quadrant trocar for the camera and two trocars (one supraumbilical and one suprapubic) for the dissecting instruments: the laparoscopic work is to mobilize the cecum and the terminal ileum first, followed by the right colon in a clockwise fashion.
As outlined by the authors themselves, it is important to keep the right colon pulled and elevated at any stage during laparoscopy in order to identify the correct planes for dissection. This advice is particularly true during hepatic flexure mobilization, when inadvertent dissection behind the kidney, injury of the duodenum and inability to find the correct plane between the gastrocolic ligament and the underlying mesentery of the transverse colon may be causes of conversion.
The port site layout by Young-Fadok and Nelson requires placing the camera in the upper trocar, and the surgeon works with both hands coming in sight from the left side: this lateral vision could be difficult to get used to, because our brain works with central vision and expects to see our hands coming in from their own side.
Moreover, the dissecting instruments are quite coaxial during hepatic flexure mobilization and triangulation is lost.
Our modification is conceived to respect visual ergonomics (restoring central vision) and to allow for the correct triangulation of port sites, especially during hepatic flexure mobilization, which is often the most critical phase.
Starting from transverse colon mobilization and proceeding counterclockwise toward the cecum we take advantage of gravity for handling the colon: there is no need to hold the right colon elevated during hepatic flexure mobilization. Also, there is no risk of inadvertent dissection behind the kidney because the dissection proceeds above it in a plane where the Gerota's fascia is easily identifiable.
With this anterior approach to the hepatic flexure, the first target is the exposure of the second portion of the duodenum, which is easily detected: the novice surgeon is not tempted to start with the dissection into the mesocolon, where vascular structures are close and tearing could led to cancer cells seeding. Thanks to gravity, the effort to expose the mesocolon is minimal and only a gentle blunt dissection is required to detach it from the posterior planes in a cranial to caudal direction.
In a similar way, Benseler et al. found the anterior approach to be safer for mobilization of the splenic flexure during laparoscopic rectal cancer resection.[17]
According to the principles of CME, central vascular ligation is performed after complete mobilization of the right colon, as described by Hohenberger et al.[2]
Central vascular ligation is done as in open surgery: the use of a sealing-dissecting device is intended to seal the two fascial layers of the mesocolon and reduce the risk of spillage of cancer cells. The integrity of the mesocolon is violated at the end of the dissection, proceeding from the terminal ileum and the transverse colon toward the central vascular structures. The medial-to-lateral approach, in which the integrity of the mesocolon is disrupted close to the main colic vessels as the initial step of surgery, is deliberately avoided.
The above-presented technique was applied in 82 patients by 16 low-volume surgeons with a low rate of severe postoperative complications (3.6%) and reoperation (2.4%). The procedure was completed laparoscopically in 87.8% of the patients. Half of the patients had 19 or more lymph nodes removed.
Our results support the advice that even low-volume surgeons, when provided with easy-to-perform surgical techniques, adequate training and a teaching-oriented environment, can achieve good outcomes.
CONCLUSION
The relationship between outcomes and the surgeon's caseload in colorectal surgery is still unclear.[18] In the ongoing effort to improve quality of surgery, education and training of the surgeon may be an alternative strategy to centralization of patients to high-volume centers. As a part of the educational strategy, improving simplicity and reproducibility of laparoscopic surgical techniques could be an effective way to increase the diffusion of laparoscopy among surgeons and to achieve good outcomes. Our proposed surgical technique could safely put LRC in the hands of the low-volume surgeon and help the growing surgeon to achieve an increased confidence in laparoscopic colorectal surgery.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Dijkstra FA, Bosker RJ, Veeger NJ, van Det MJ, Pierie JP. Procedural key steps in laparoscopic colorectal surgery, consensus through Delphi methodology. Surg Endosc. 2014 Dec 6; doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3979-7. [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 25480611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hohenberger W, Weber K, Matzel K, Papadopoulos T, Merkel S. Standardized surgery for colonic cancer: Complete mesocolic excision and central ligation — Technical notes and outcome. Colorectal Dis. 2009;11:354–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2008.01735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Søndenaa K, Quirke P, Hohenberger W, Sugihara K, Kobayashi H, Kessler H, et al. The rationale behind complete mesocolic excision (CME) and a central vascular ligation for colon cancer in open and laparoscopic surgery: Proceedings of a consensus conference. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2014;29:419–28. doi: 10.1007/s00384-013-1818-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Feng B, Sun J, Ling TL, Lu AG, Wang ML, Chen XY, et al. Laparoscopic complete mesocolic excision (CME) with medial access for right-hemi colon cancer: Feasibility and technical strategies. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:3669–75. doi: 10.1007/s00464-012-2435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Siani LM, Pulica C. Laparoscopic Complete Mesocolic Excision with Central Vascular Ligation in right colon cancer: Long-term oncologic outcome between mesocolic and non-mesocolic planes of surgery. Scand J Surg. 2014 Nov 12; doi: 10.1177/1457496914557017. pii: 1457496914557017 [Epub ahead of print] PMID: 25391978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kang J, Kim IK, Kang SI, Sohn SK, Lee KY. Laparoscopic right hemicolectomy with complete mesocolic excision. Surg Endosc. 2014;28:2747–51. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3521-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Feng B, Ling TL, Lu AG, Wang ML, Ma JJ, Li JW, et al. Completely medial versus hybrid medial approach for laparoscopic complete mesocolic excision in right hemicolon cancer. Surg Endosc. 2014;28:477–83. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-3225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mori S, Baba K, Yanagi M, Kita Y, Yanagita S, Uchikado Y, et al. Laparoscopic complete mesocolic excision with radical lymph node dissection along the surgical trunk for right colon cancer. Surg Endosc. 2015;29:34–40. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3650-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Damle RN, Macomber CW, Flahive JM, Davids JS, Sweeney WB, Sturrock PR, et al. Surgeon volume and elective resection for colon cancer: An analysis of outcomes and use of laparoscopy. J Am Coll Surg. 2014;218:1223–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2014.01.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Etzioni DA, Young-Fadok TM, Cima RR, Wasif N, Madoff RD, Naessens JM, et al. Patient survival after surgical treatment of rectal cancer: Impact of surgeon and hospital characteristics. Cancer. 2014;120:2472–81. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bardakcioglu O, Khan A, Aldridge C, Chen J. Growth of laparoscopic colectomy in the United States: Analysis of regional and socioeconomic factors over time. Ann Surg. 2013;258:270–4. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31828faa66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Young-Fadok TM, Nelson H. Laparoscopic right colectomy: Five-step procedure. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000;43:267–71. doi: 10.1007/BF02236994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Archampong D, Borowski D, Wille-Jørgensen P, Iversen LH. Workload and surgeon's specialty for outcome after colorectal cancer surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;3:CD005391. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005391.pub3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Burns EM, Bottle A, Almoudaris AM, Mamidanna R, Aylin P, Darzi A, et al. Hierarchical multilevel analysis of increased caseload volume and postoperative outcome after elective colorectal surgery. Br J Surg. 2013;100:1531–8. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kuwabara K, Matsuda S, Fushimi K, Ishikawa KB, Horiguchi H, Fujimori K. Impact of hospital case volume on the quality of laparoscopic colectomy in Japan. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009;13:1619–26. doi: 10.1007/s11605-009-0956-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hopkins MA. Surgical education and global health: Call to action. Am J Surg. 2015;209:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2014.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Benseler V, Hornung M, Iesalnieks I, von Breitenbuch P, Glockzin G, Schlitt HJ, et al. Different approaches for complete mobilization of the splenic flexure during laparoscopic rectal cancer resection. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012;27:1521–9. doi: 10.1007/s00384-012-1495-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Merlino J. Defining the volume-quality debate: Is it the surgeon, the center, or the training? Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2007;20:231–6. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-984867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


