Abstract
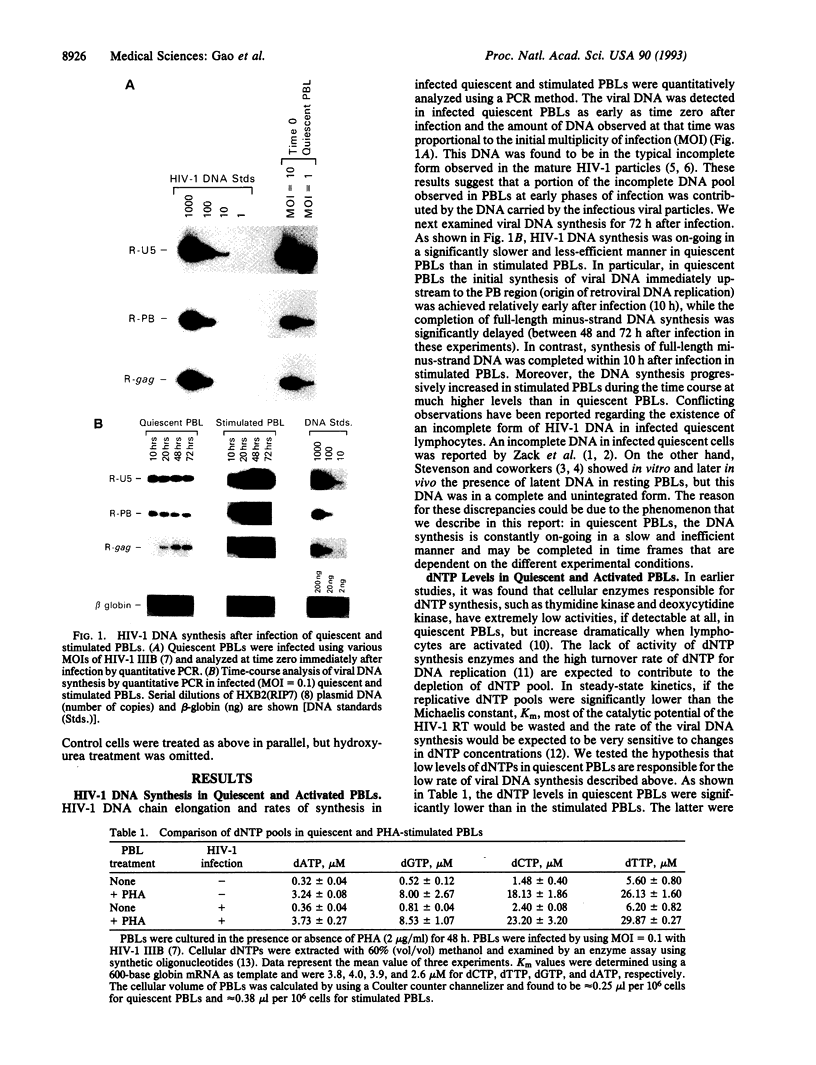
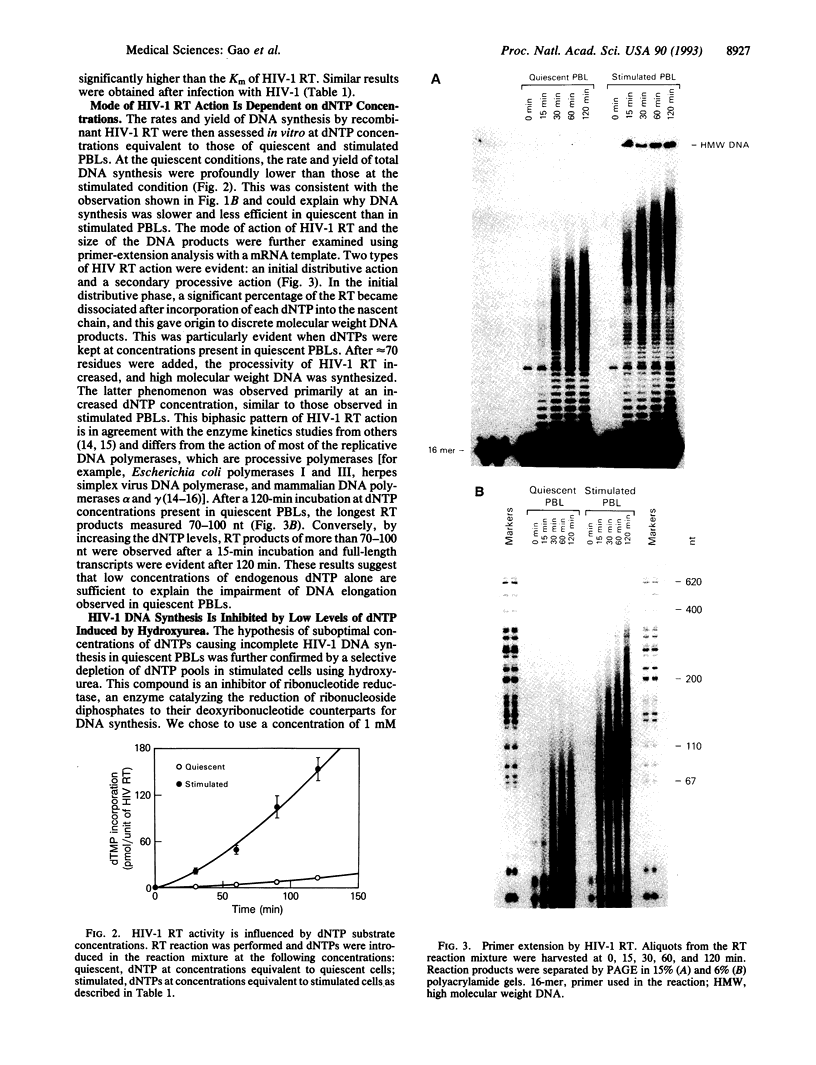
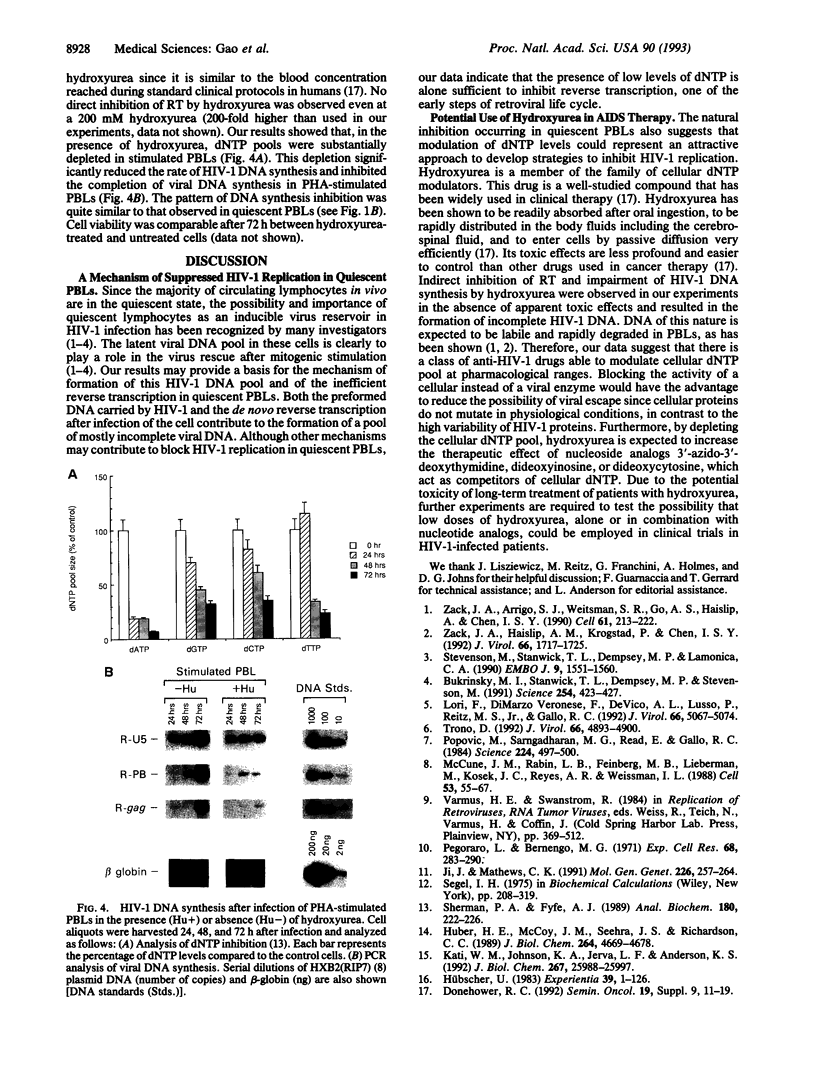
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) viral DNA synthesis in quiescent and activated peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) was studied. Incomplete viral DNA (previously demonstrated to be associated with HIV-1 virions) is carried by HIV-1 virions into quiescent and activated PBLs, contributing to the formation of an early viral DNA pool in these cells. The viral DNA is subsequently completed but only extremely slowly and inefficiently in quiescent PBLs compared to that in stimulated PBLs. We find that this correlates with significantly lower levels of dNTP substrates in quiescent compared to activated PBLs. At these low dNTP concentrations, HIV-1 reverse transcriptase acts in a partially distributive manner. Increasing dNTP concentrations from the levels of quiescent PBLs to the levels of activated PBLs increases the processive action of reverse transcriptase, which in turn stimulates rapid and efficient formation of full-length DNA. Furthermore, hydroxyurea treatment of stimulated PBLs decreases the dNTP levels and the DNA synthesis rate to levels comparable to quiescent PBLs. Our data therefore indicate that low levels of dNTP may explain why HIV-1 DNA is synthesized slowly and inefficiently in quiescent PBLs and suggest that pharmacologic induction of low dNTP levels represents a therapeutic approach for inhibition of HIV-1 replication.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bukrinsky M. I., Stanwick T. L., Dempsey M. P., Stevenson M. Quiescent T lymphocytes as an inducible virus reservoir in HIV-1 infection. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.1925601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower R. C. An overview of the clinical experience with hydroxyurea. Semin Oncol. 1992 Jun;19(3 Suppl 9):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., McCoy J. M., Seehra J. S., Richardson C. C. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 reverse transcriptase. Template binding, processivity, strand displacement synthesis, and template switching. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4669–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U. DNA polymerases in prokaryotes and eukaryotes: mode of action and biological implications. Experientia. 1983 Jan 15;39(1):1–25. doi: 10.1007/BF01960616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji J. P., Mathews C. K. Analysis of mutagenesis induced by a thermolabile T4 phage deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase suggests localized deoxyribonucleotide pool imbalance. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):257–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00273611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kati W. M., Johnson K. A., Jerva L. F., Anderson K. S. Mechanism and fidelity of HIV reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25988–25997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lori F., di Marzo Veronese F., de Vico A. L., Lusso P., Reitz M. S., Jr, Gallo R. C. Viral DNA carried by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5067–5074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5067-5074.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegoraro L., Bernengo M. G. Thymidine kinase, deoxycytidine kinase and deoxycytidylate deaminase activities in phytohaemagglutinin stimulated human lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Oct;68(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Fyfe J. A. Enzymatic assay for deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates using synthetic oligonucleotides as template primers. Anal Biochem. 1989 Aug 1;180(2):222–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Stanwick T. L., Dempsey M. P., Lamonica C. A. HIV-1 replication is controlled at the level of T cell activation and proviral integration. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1551–1560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08274.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D. Partial reverse transcripts in virions from human immunodeficiency and murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4893–4900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4893-4900.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S. R., Go A. S., Haislip A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 entry into quiescent primary lymphocytes: molecular analysis reveals a labile, latent viral structure. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90802-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Haislip A. M., Krogstad P., Chen I. S. Incompletely reverse-transcribed human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes in quiescent cells can function as intermediates in the retroviral life cycle. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1717–1725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1717-1725.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





