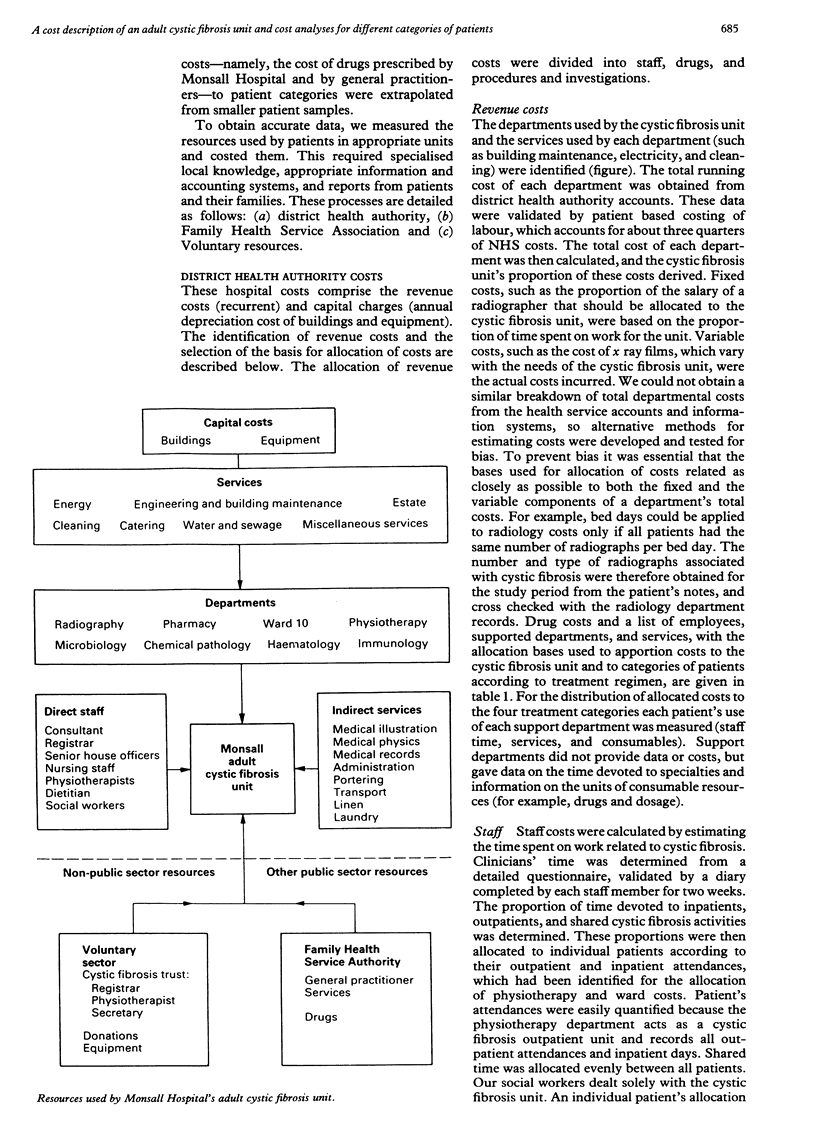
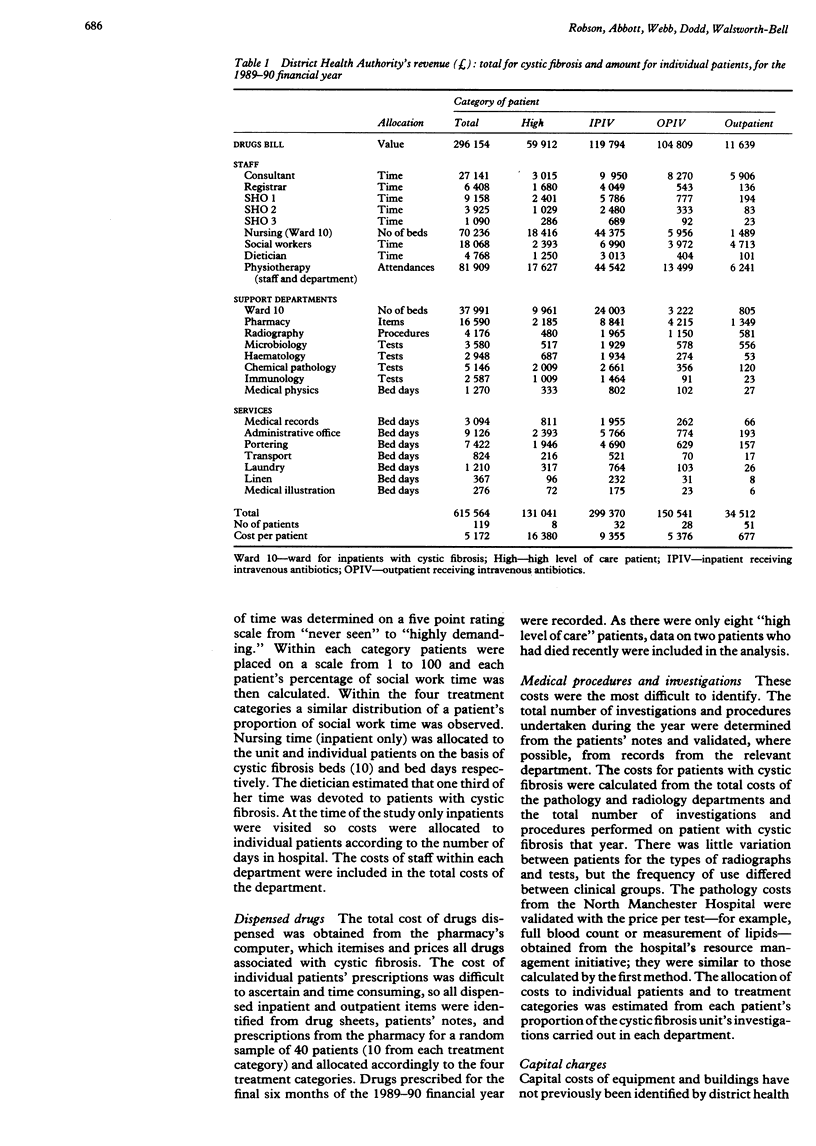
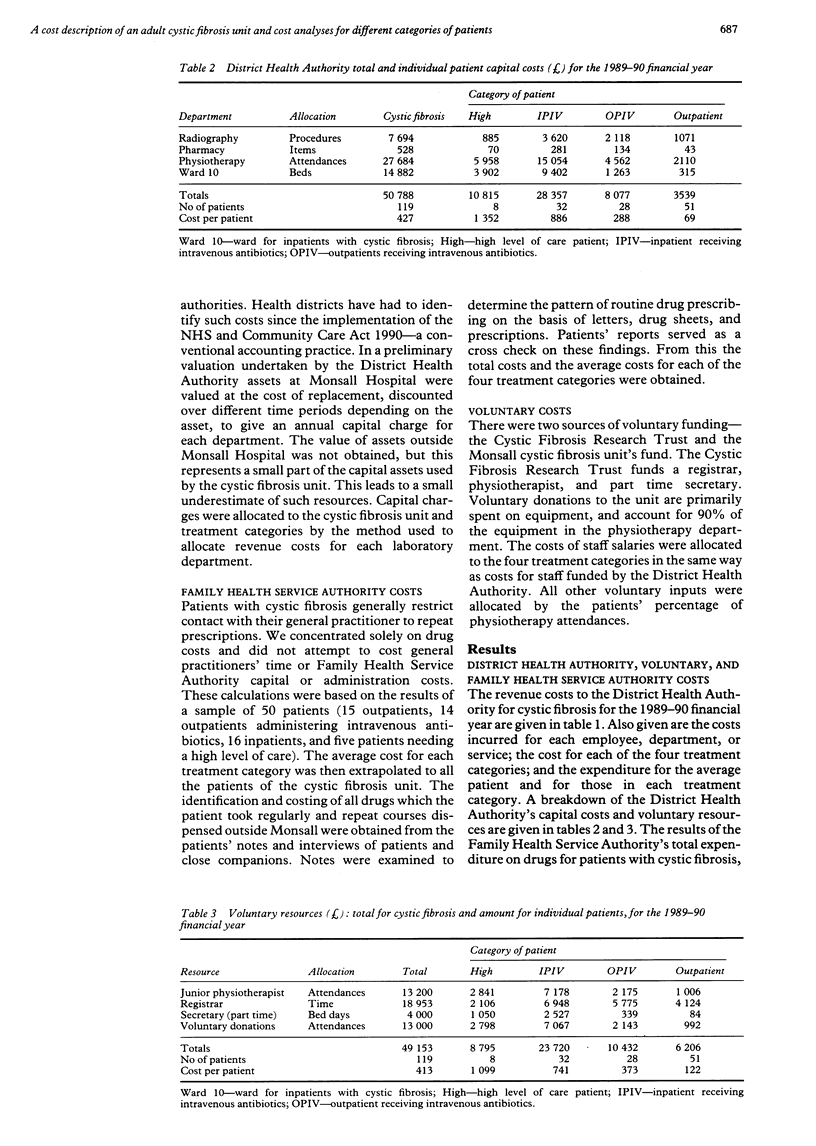
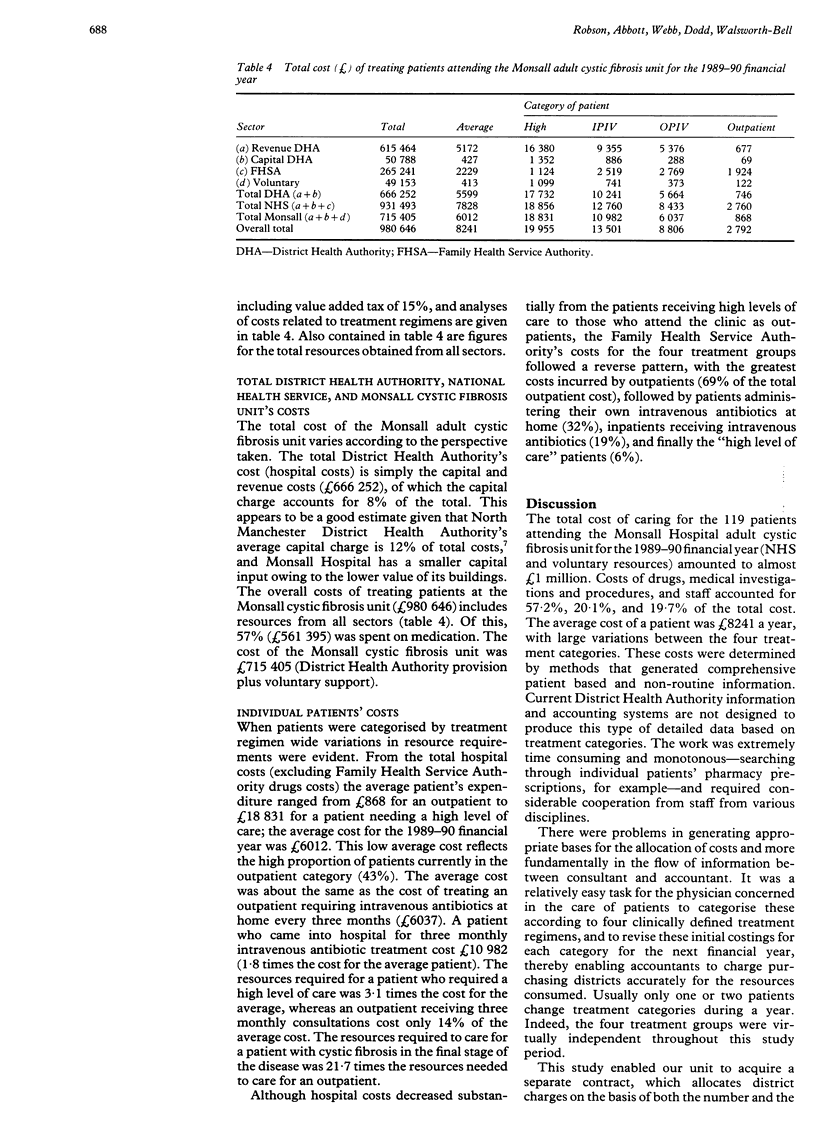
Abstract
BACKGROUND: There is little information on the costs of running an adult cystic fibrosis centre. The aim of this study was to provide detailed costs to assist funding and planning for these patients. METHODS: The cost of a regional adult cystic fibrosis centre serving 119 cystic fibrosis patients, categorised according to four treatment regimens, was determined. District health authority, family health service authority, and voluntary resources used from April 1989 to March 1990 were determined, with appropriate bases for allocation of costs and patient based costs from local information. RESULTS: The total annual cost of treating the 119 patients was 980,646 pounds, with an average cost 8241 pounds per patient. An outpatient reviewed at three monthly intervals cost 2792 pounds a year; an outpatient receiving intravenous antibiotics cost 8606 pounds; an inpatient receiving intravenous antibiotics cost 13,501 pounds; and a patient needing a high level of care cost 19,955 pounds. Medication accounted for 57% (561,395 pounds) of the total cost. CONCLUSIONS: This analysis has helped us to secure funding for patients with cystic fibrosis and it facilitates the prediction of future requirements. The study also indicates the limitations of using average patient costs and difficulties as a result of the poorly structured British National Health Service accounting and information systems.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hodson M. E. Managing adults with cystic fibrosis. BMJ. 1989 Feb 25;298(6672):471–472. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6672.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan P., Hey E. Cystic fibrosis mortality in England and Wales and in Victoria, Australia 1976-80. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Jan;59(1):71–73. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb A. K. The difficulties of treating cystic fibrosis in adults. J R Soc Med. 1987;80 (Suppl 15):47–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


