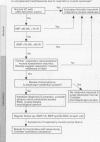
Full text
PDF


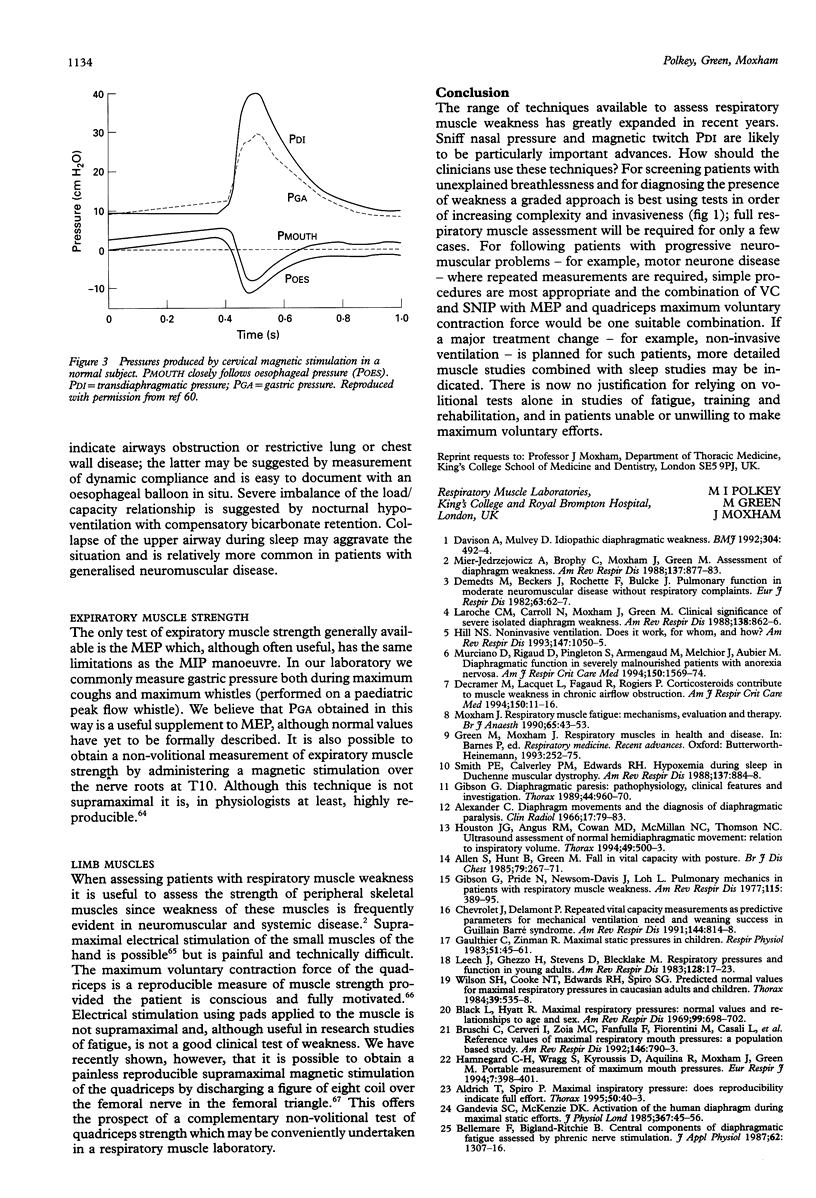

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldrich T. K., Spiro P. Maximal inspiratory pressure: does reproducibility indicate full effort? Thorax. 1995 Jan;50(1):40–43. doi: 10.1136/thx.50.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander C. Diaphragm movements and the diagnosis of diaphragmatic paralysis. Clin Radiol. 1966 Jan;17(1):79–83. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(66)80128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen G. M., McKenzie D. K., Gandevia S. C., Bass S. Reduced voluntary drive to breathe in asthmatic subjects. Respir Physiol. 1993 Jul;93(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(93)90065-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. M., Hunt B., Green M. Fall in vital capacity with posture. Br J Dis Chest. 1985 Jul;79(3):267–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker A. T., Freeston I. L., Jalinous R., Jarratt J. A. Magnetic stimulation of the human brain and peripheral nervous system: an introduction and the results of an initial clinical evaluation. Neurosurgery. 1987 Jan;20(1):100–109. doi: 10.1097/00006123-198701000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Bigland-Ritchie B. Assessment of human diaphragm strength and activation using phrenic nerve stimulation. Respir Physiol. 1984 Dec;58(3):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Bigland-Ritchie B. Central components of diaphragmatic fatigue assessed by phrenic nerve stimulation. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Mar;62(3):1307–1316. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.3.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Bigland-Ritchie B. Central components of diaphragmatic fatigue assessed by phrenic nerve stimulation. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Mar;62(3):1307–1316. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.3.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black L. F., Hyatt R. E. Maximal respiratory pressures: normal values and relationship to age and sex. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 May;99(5):696–702. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.5.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi C., Cerveri I., Zoia M. C., Fanfulla F., Fiorentini M., Casali L., Grassi M., Grassi C. Reference values of maximal respiratory mouth pressures: a population-based study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Sep;146(3):790–793. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.3.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Collins S., Remtulla H., Parkes A., Bolton C. F. Phrenic nerve conduction study in normal subjects. Muscle Nerve. 1995 Mar;18(3):330–335. doi: 10.1002/mus.880180311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevrolet J. C., Deléamont P. Repeated vital capacity measurements as predictive parameters for mechanical ventilation need and weaning success in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Oct;144(4):814–818. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.4.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N. Phrenic nerve conduction in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967 Oct;30(5):420–426. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.30.5.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A., Mulvey D. Idiopathic diaphragmatic weakness. BMJ. 1992 Feb 22;304(6825):492–494. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6825.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decramer M., Lacquet L. M., Fagard R., Rogiers P. Corticosteroids contribute to muscle weakness in chronic airflow obstruction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Jul;150(1):11–16. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.1.8025735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demedts M., Beckers J., Rochette F., Bulcke J. Pulmonary function in moderate neuromuscular disease without respiratory complaints. Eur J Respir Dis. 1982 Jan;63(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Young A., Hosking G. P., Jones D. A. Human skeletal muscle function: description of tests and normal values. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Mar;52(3):283–290. doi: 10.1042/cs0520283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., McKenzie D. K. Activation of the human diaphragm during maximal static efforts. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:45–56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaultier C., Zinman R. Maximal static pressures in healthy children. Respir Physiol. 1983 Jan;51(1):45–61. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(83)90101-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. J. Diaphragmatic paresis: pathophysiology, clinical features, and investigation. Thorax. 1989 Nov;44(11):960–970. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.11.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. J., Pride N. B., Davis J. N., Loh L. C. Pulmonary mechanics in patients with respiratory muscle weakness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Mar;115(3):389–395. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamnegåard C. H., Wragg S., Kyroussis D., Mills G., Bake B., Green M., Moxham J. Mouth pressure in response to magnetic stimulation of the phrenic nerves. Thorax. 1995 Jun;50(6):620–624. doi: 10.1136/thx.50.6.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamnegård C. H., Wragg S., Kyroussis D., Aquilina R., Moxham J., Green M. Portable measurement of maximum mouth pressures. Eur Respir J. 1994 Feb;7(2):398–401. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07020398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill N. S. Noninvasive ventilation. Does it work, for whom, and how? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Apr;147(4):1050–1055. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.4.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston J. G., Angus R. M., Cowan M. D., McMillan N. C., Thomson N. C. Ultrasound assessment of normal hemidiaphragmatic movement: relation to inspiratory volume. Thorax. 1994 May;49(5):500–503. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.5.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Héritier F., Rahm F., Pasche P., Fitting J. W. Sniff nasal inspiratory pressure. A noninvasive assessment of inspiratory muscle strength. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Dec;150(6 Pt 1):1678–1683. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.6.7952632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koulouris N., Mulvey D. A., Laroche C. M., Green M., Moxham J. Comparison of two different mouthpieces for the measurement of Pimax and Pemax in normal and weak subjects. Eur Respir J. 1988 Oct;1(9):863–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koulouris N., Mulvey D. A., Laroche C. M., Sawicka E. H., Green M., Moxham J. The measurement of inspiratory muscle strength by sniff esophageal, nasopharyngeal, and mouth pressures. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):641–646. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyroussis D., Mills G., Hamnegard C. H., Wragg S., Road J., Green M., Moxham J. Inspiratory muscle relaxation rate assessed from sniff nasal pressure. Thorax. 1994 Nov;49(11):1127–1133. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.11.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laroche C. M., Carroll N., Moxham J., Green M. Clinical significance of severe isolated diaphragm weakness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):862–866. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laroche C. M., Mier A. K., Moxham J., Green M. Diaphragm strength in patients with recent hemidiaphragm paralysis. Thorax. 1988 Mar;43(3):170–174. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.3.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laroche C. M., Mier A. K., Moxham J., Green M. The value of sniff esophageal pressures in the assessment of global inspiratory muscle strength. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Sep;138(3):598–603. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.3.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laroche C. M., Mier A. K., Spiro S. G., Newsom-Davis J., Moxham J., Green M. Respiratory muscle weakness in the Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. Thorax. 1989 Nov;44(11):913–918. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.11.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech J. A., Ghezzo H., Stevens D., Becklake M. R. Respiratory pressures and function in young adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jul;128(1):17–23. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. Voluntary strength and fatigue. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):553–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machetanz J., Bischoff C., Pichlmeier R., Riescher H., Meyer B. U., Sader A., Conrad B. Magnetically induced muscle contraction is caused by motor nerve stimulation and not by direct muscle activation. Muscle Nerve. 1994 Oct;17(10):1170–1175. doi: 10.1002/mus.880171007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mador M. J., Magalang U. J., Kufel T. J. Twitch potentiation following voluntary diaphragmatic contraction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Mar;149(3 Pt 1):739–743. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.3.8118645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier-Jedrzejowicz A., Brophy C., Moxham J., Green M. Assessment of diaphragm weakness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):877–883. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier A., Brophy C., Moxham J., Green M. Phrenic nerve stimulation in normal subjects and in patients with diaphragmatic weakness. Thorax. 1987 Nov;42(11):885–888. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.11.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier A., Brophy C., Moxham J., Green M. Repetitive stimulation of phrenic nerves in myasthenia gravis. Thorax. 1992 Aug;47(8):640–644. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.8.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier A., Brophy C., Moxham J., Green M. Twitch pressures in the assessment of diaphragm weakness. Thorax. 1989 Dec;44(12):990–996. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.12.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Moxham J., Green M. The maximal sniff in the assessment of diaphragm function in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Jul;69(1):91–96. doi: 10.1042/cs0690091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham J. Respiratory muscle fatigue: mechanisms, evaluation and therapy. Br J Anaesth. 1990 Jul;65(1):43–53. doi: 10.1093/bja/65.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murciano D., Aubier M., Bussi S., Derenne J. P., Pariente R., Milic-Emili J. Comparison of esophageal, tracheal, and mouth occlusion pressure in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease during acute respiratory failure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):837–841. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murciano D., Rigaud D., Pingleton S., Armengaud M. H., Melchior J. C., Aubier M. Diaphragmatic function in severely malnourished patients with anorexia nervosa. Effects of renutrition. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Dec;150(6 Pt 1):1569–1574. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.6.7952616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitjean M., Bellemare F. Phonomyogram of the diaphragm during unilateral and bilateral phrenic nerve stimulation and changes with fatigue. Muscle Nerve. 1994 Oct;17(10):1201–1209. doi: 10.1002/mus.880171011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Similowski T., Fleury B., Launois S., Cathala H. P., Bouche P., Derenne J. P. Cervical magnetic stimulation: a new painless method for bilateral phrenic nerve stimulation in conscious humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Oct;67(4):1311–1318. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.4.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Similowski T., Gauthier A. P., Yan S., Macklem P. T., Bellemare F. Assessment of diaphragm function using mouth pressure twitches in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Apr;147(4):850–856. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.4.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Similowski T., Yan S., Gauthier A. P., Macklem P. T., Bellemare F. Contractile properties of the human diaphragm during chronic hyperinflation. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 26;325(13):917–923. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109263251304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. E., Calverley P. M., Edwards R. H. Hypoxemia during sleep in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):884–888. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uldry C., Fitting J. W. Maximal values of sniff nasal inspiratory pressure in healthy subjects. Thorax. 1995 Apr;50(4):371–375. doi: 10.1136/thx.50.4.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. E., Drinnan M. J., Smithson A. J., Griffiths C. J., Gibson G. J. Respiratory muscle activity and oxygenation during sleep in patients with muscle weakness. Eur Respir J. 1995 May;8(5):807–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. H., Cooke N. T., Edwards R. H., Spiro S. G. Predicted normal values for maximal respiratory pressures in caucasian adults and children. Thorax. 1984 Jul;39(7):535–538. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.7.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wragg S., Aquilina R., Moran J., Ridding M., Hamnegard C., Fearn T., Green M., Moxham J. Comparison of cervical magnetic stimulation and bilateral percutaneous electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves in normal subjects. Eur Respir J. 1994 Oct;7(10):1788–1792. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07101788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wragg S., Hamnegard C., Road J., Kyroussis D., Moran J., Green M., Moxham J. Potentiation of diaphragmatic twitch after voluntary contraction in normal subjects. Thorax. 1994 Dec;49(12):1234–1237. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.12.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan S., Gauthier A. P., Similowski T., Macklem P. T., Bellemare F. Evaluation of human diaphragm contractility using mouth pressure twitches. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 May;145(5):1064–1069. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.5.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]