Abstract
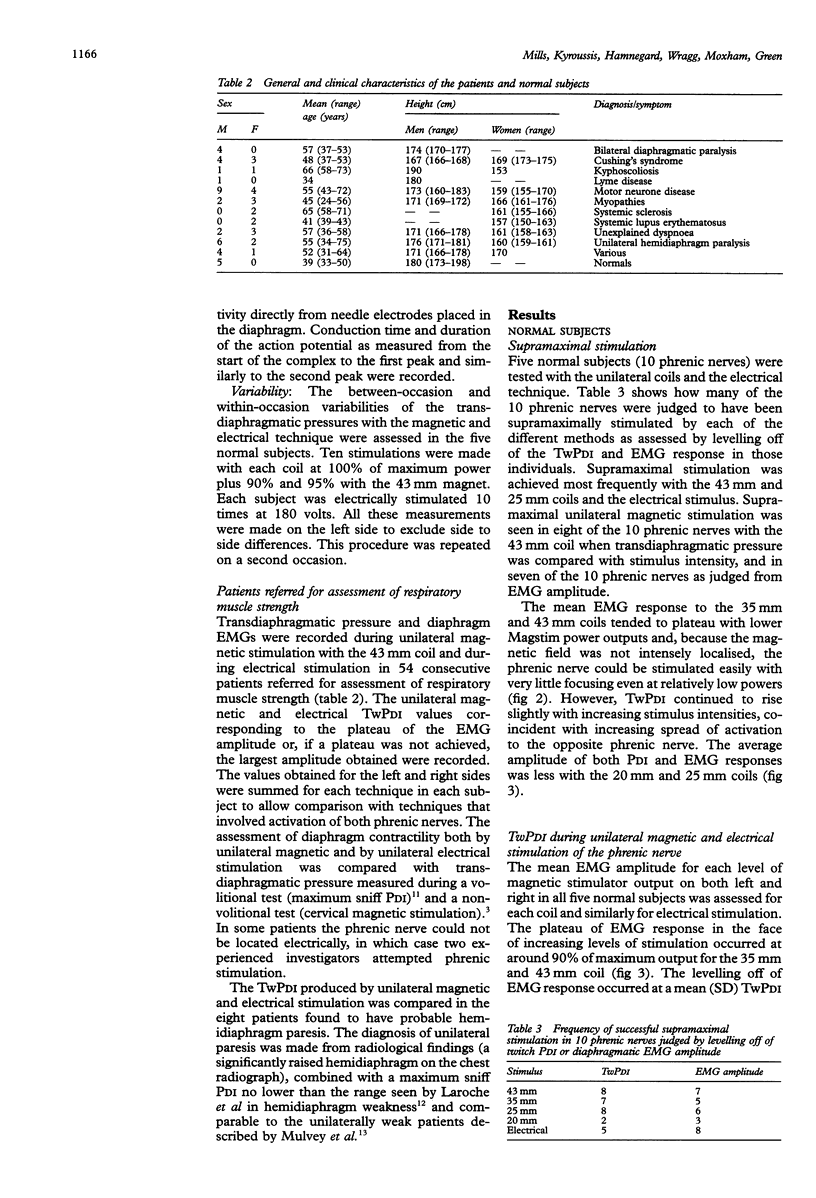
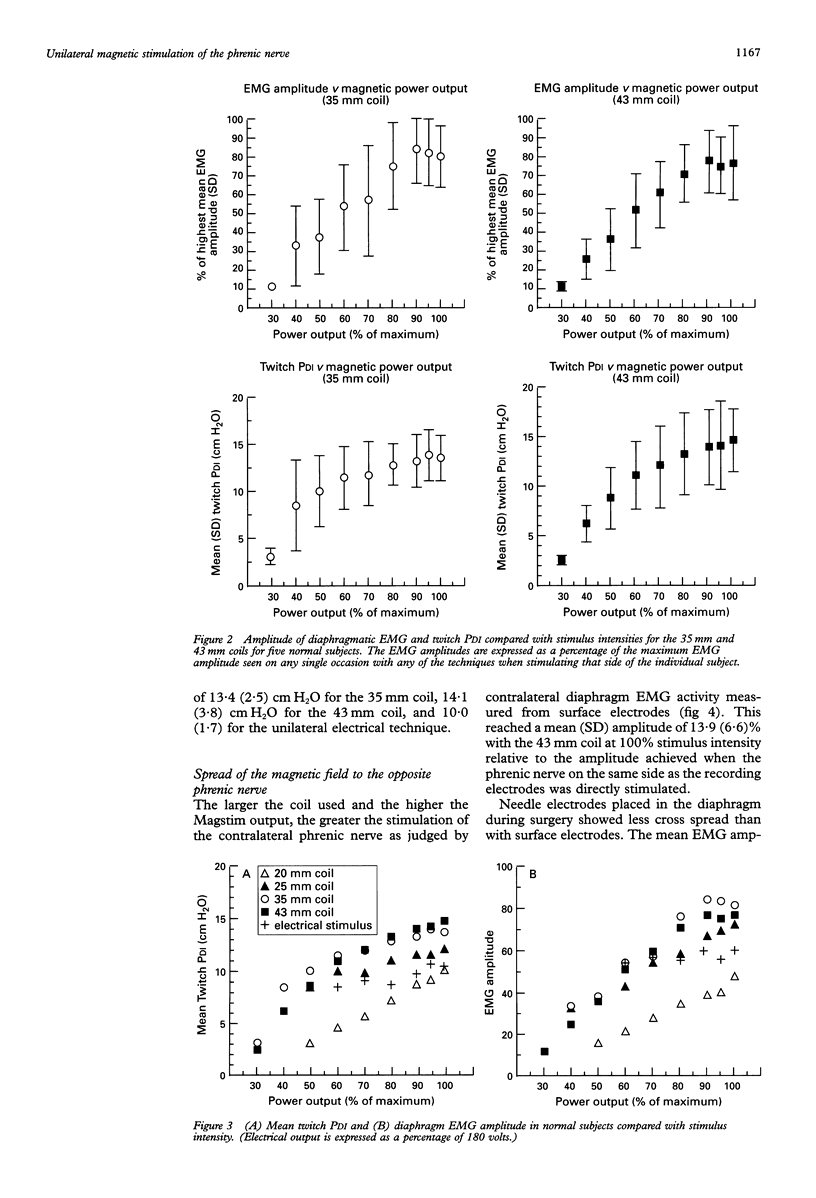
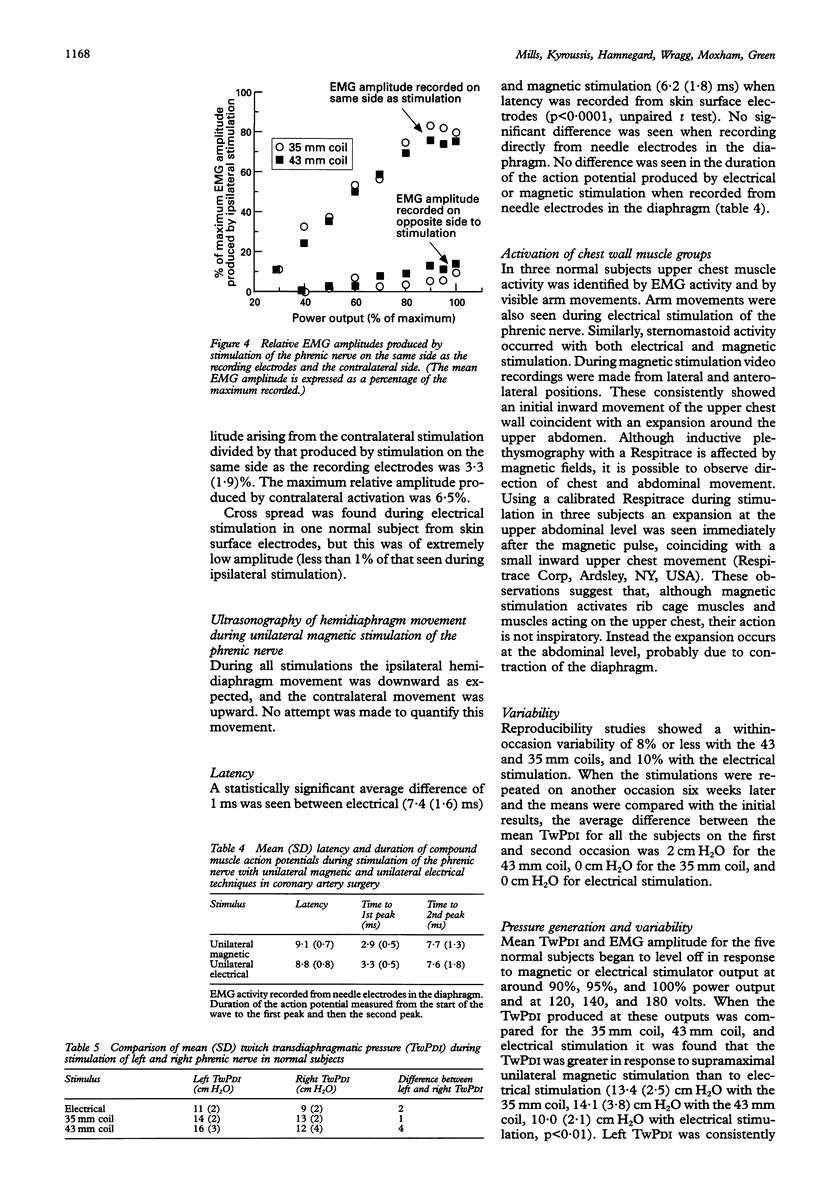
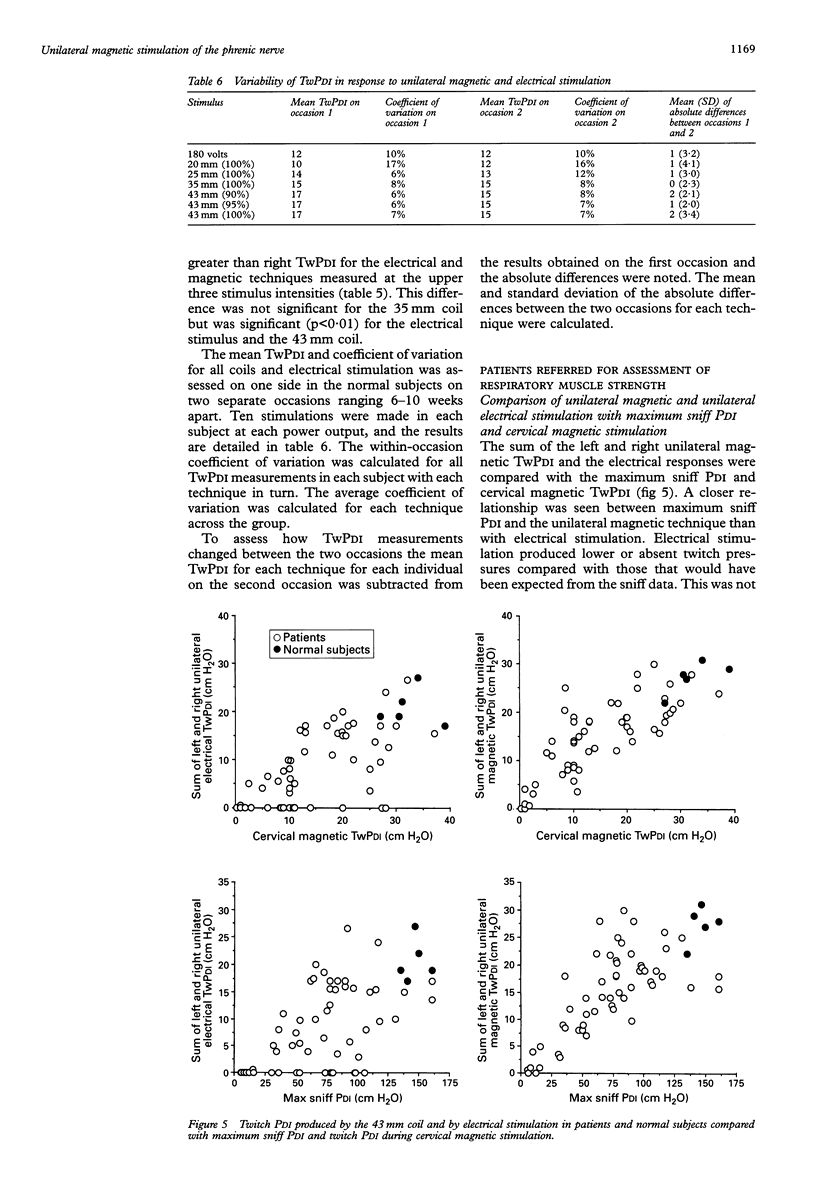
BACKGROUND--Electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerve is a useful non-volitional method of assessing diaphragm contractility. During the assessment of hemidiaphragm contractility with electrical stimulation, low twitch transdiaphragmatic pressures may result from difficulty in locating and stimulating the phrenic nerve. Cervical magnetic stimulation overcomes some of these problems, but this technique may not be absolutely specific and does not allow the contractility of one hemidiaphragm to be assessed. This study assesses both the best means of producing supramaximal unilateral magnetic phrenic stimulation and its reproducibility. This technique is then applied to patients. METHODS--The ability of four different magnetic coils to produce unilateral phrenic stimulation in five normal subjects was assessed from twitch transdiaphragmatic pressure (TwPDI) measurements and diaphragmatic electromyogram (EMG) recordings. The results from magnetic stimulation were compared with those from electrical stimulation. To determine whether the magnetic field affects the contralateral phrenic nerve as well as the intended phrenic nerve, EMG recordings from each hemidiaphragm were compared during stimulation on the same side and the opposite side relative to the recording electrodes. The EMG recordings were made from skin surface electrodes in five normal subjects and from needle electrodes placed in the diaphragm during cardiac surgery in six patients. Similarly, the direction of hemidiaphragm movement was evaluated by ultrasonography. To determine the usefulness of the technique in patients the 43 mm mean diameter double coil was used in 54 patients referred for assessment of possible respiratory muscle weakness. These results were compared with unilateral electrical phrenic stimulation, maximum sniff PDI, and TwPDI during cervical magnetic stimulation. RESULTS--In the five normal subjects supramaximal stimulation was established for eight out of 10 phrenic nerves with the 43 mm double coil. Supramaximal unilateral magnetic stimulation produced a higher TwPDI than electrical stimulation (mean (SD) 13.4 (2.5) cm H2O with 35 mm coil; 14.1 (3.8) cm H2O with 43 mm coil; 10.0 (1.7) cm H2O with electrical stimulation). Spread of the magnetic field to the opposite phrenic nerve produced a small amplitude contralateral diaphragm EMG measured from skin surface electrodes which reached a mean of 15% of the maximum EMG amplitude produced by ipsilateral stimulation. Similarly, in six patients with EMG activity recorded directly from needle electrodes, the contralateral spread of the magnetic field produced EMG activity up to a mean of 3% and a maximum of 6% of that seen with ipsilateral stimulation. Unilateral magnetic stimulation of the phrenic nerve was rapidly achieved and well tolerated. In the 54 patients unilateral magnetic TwPDI was more closely related than unilateral electrical TwPDI to transdiaphragmatic pressure produced during maximum sniffs and cervical magnetic stimulation. Unilateral magnetic stimulation eliminated the problem of producing a falsely low TwPDI because of technical difficulties in locating and adequately stimulating the nerve. Eight patients with unilateral phrenic nerve paresis, as indicated by a unilaterally elevated hemidiaphragm on a chest radiograph and maximum sniff PDI consistent with hemidiaphragm weakness, were all accurately identified by unilateral magnetic stimulation. CONCLUSIONS--Unilateral magnetic phrenic nerve stimulation is easy to apply and is a reproducible technique in the assessment of hemidiaphragm contractility. It is well tolerated and allows hemidiaphragm contractility to be rapidly and reliably assessed because precise positioning of the coils is not necessary. This may be particularly useful in patients. In addition, the anterolateral positioning of the coil allows the use of the magnet in the supine patient such as in the operating theatre or intensive care unit.
Full text
PDF



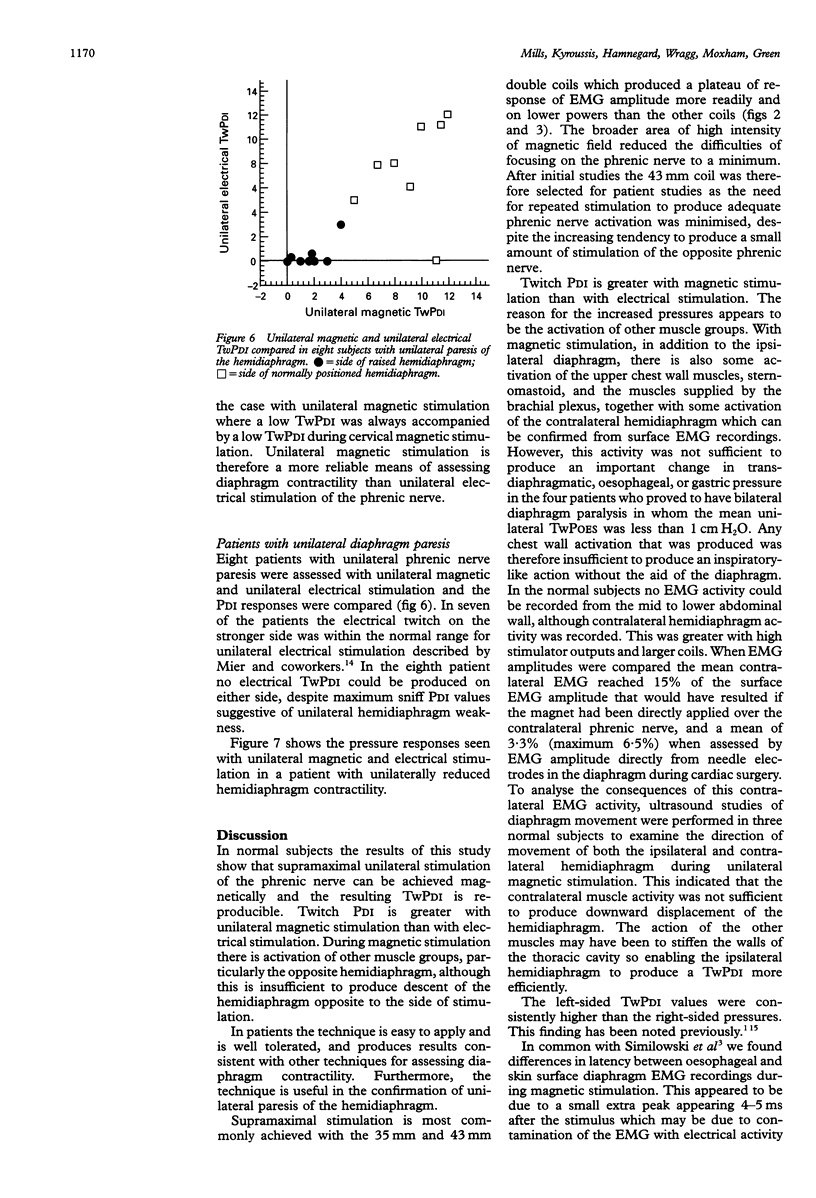


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baydur A., Behrakis P. K., Zin W. A., Jaeger M., Milic-Emili J. A simple method for assessing the validity of the esophageal balloon technique. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):788–791. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Bigland-Ritchie B. Assessment of human diaphragm strength and activation using phrenic nerve stimulation. Respir Physiol. 1984 Dec;58(3):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(84)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellemare F., Bigland-Ritchie B., Woods J. J. Contractile properties of the human diaphragm in vivo. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Sep;61(3):1153–1161. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.3.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laroche C. M., Mier A. K., Moxham J., Green M. Diaphragm strength in patients with recent hemidiaphragm paralysis. Thorax. 1988 Mar;43(3):170–174. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.3.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lekven J. Myocardial blood flow distribution. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976 Jan;36(1):1–6. doi: 10.1080/00365517609068011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILIC-EMILI J., MEAD J., TURNER J. M., GLAUSER E. M. IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR ESTIMATING PLEURAL PRESSURE FROM ESOPHAGEAL BALLOONS. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Mar;19:207–211. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mador M. J., Magalang U. J., Kufel T. J. Twitch potentiation following voluntary diaphragmatic contraction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Mar;149(3 Pt 1):739–743. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.149.3.8118645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier-Jedrzejowicz A., Brophy C., Moxham J., Green M. Assessment of diaphragm weakness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):877–883. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier A., Brophy C., Moxham J., Green M. Twitch pressures in the assessment of diaphragm weakness. Thorax. 1989 Dec;44(12):990–996. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.12.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. M., Moxham J., Green M. The maximal sniff in the assessment of diaphragm function in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Jul;69(1):91–96. doi: 10.1042/cs0690091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey D. A., Aquilina R. J., Elliott M. W., Moxham J., Green M. Diaphragmatic dysfunction in neuralgic amyotrophy: an electrophysiologic evaluation of 16 patients presenting with dyspnea. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jan;147(1):66–71. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussos C., Fixley M., Gross D., Macklem P. T. Fatigue of inspiratory muscles and their synergic behavior. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 May;46(5):897–904. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.5.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Similowski T., Fleury B., Launois S., Cathala H. P., Bouche P., Derenne J. P. Cervical magnetic stimulation: a new painless method for bilateral phrenic nerve stimulation in conscious humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Oct;67(4):1311–1318. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.4.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wragg S., Aquilina R., Moran J., Ridding M., Hamnegard C., Fearn T., Green M., Moxham J. Comparison of cervical magnetic stimulation and bilateral percutaneous electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves in normal subjects. Eur Respir J. 1994 Oct;7(10):1788–1792. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07101788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wragg S., Hamnegard C., Road J., Kyroussis D., Moran J., Green M., Moxham J. Potentiation of diaphragmatic twitch after voluntary contraction in normal subjects. Thorax. 1994 Dec;49(12):1234–1237. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.12.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



