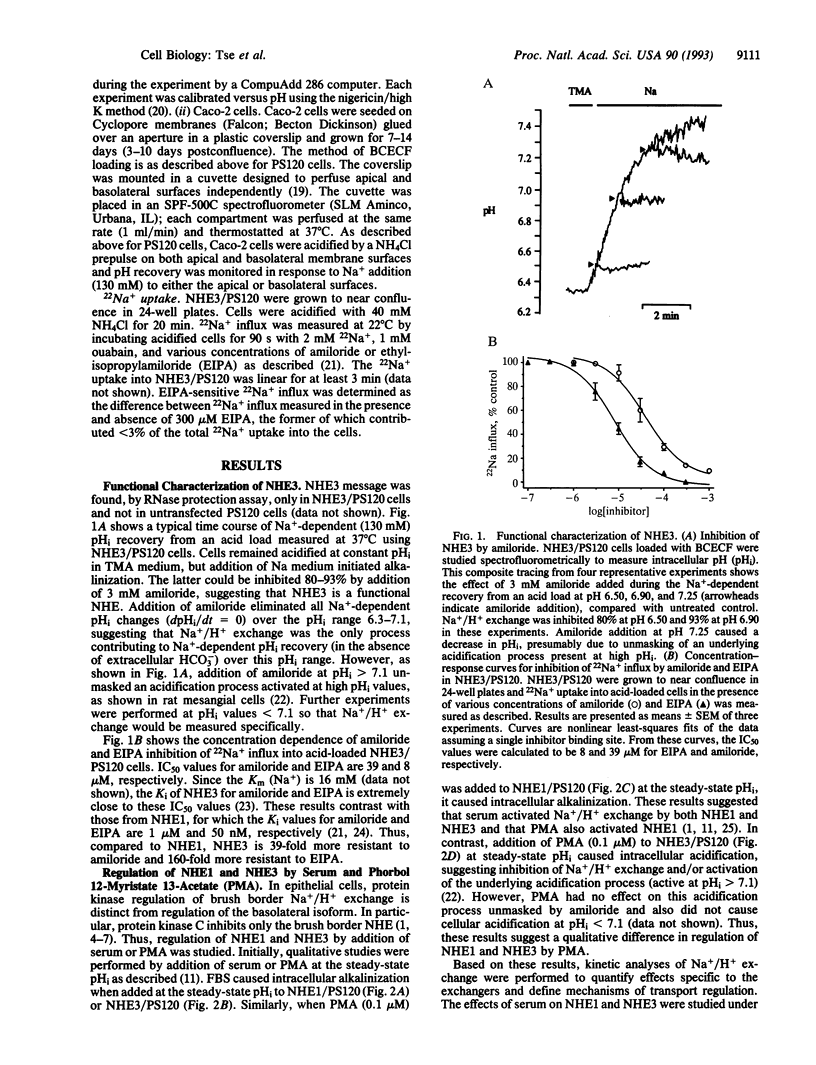
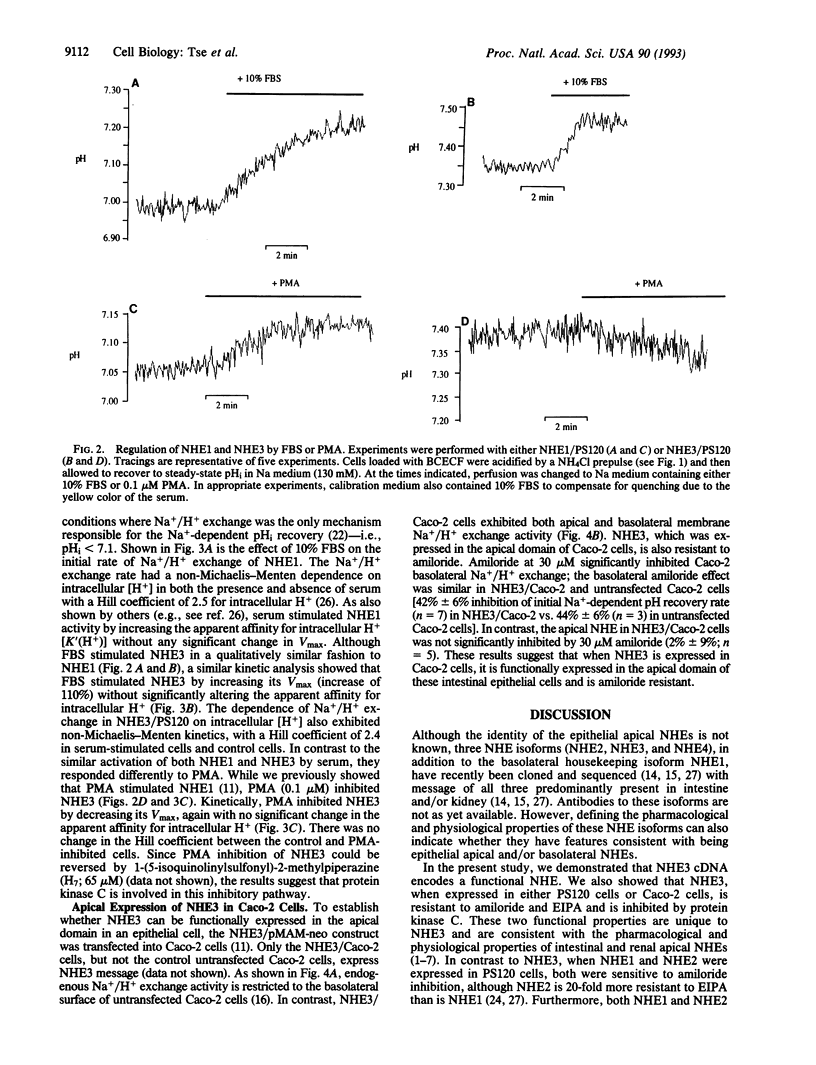
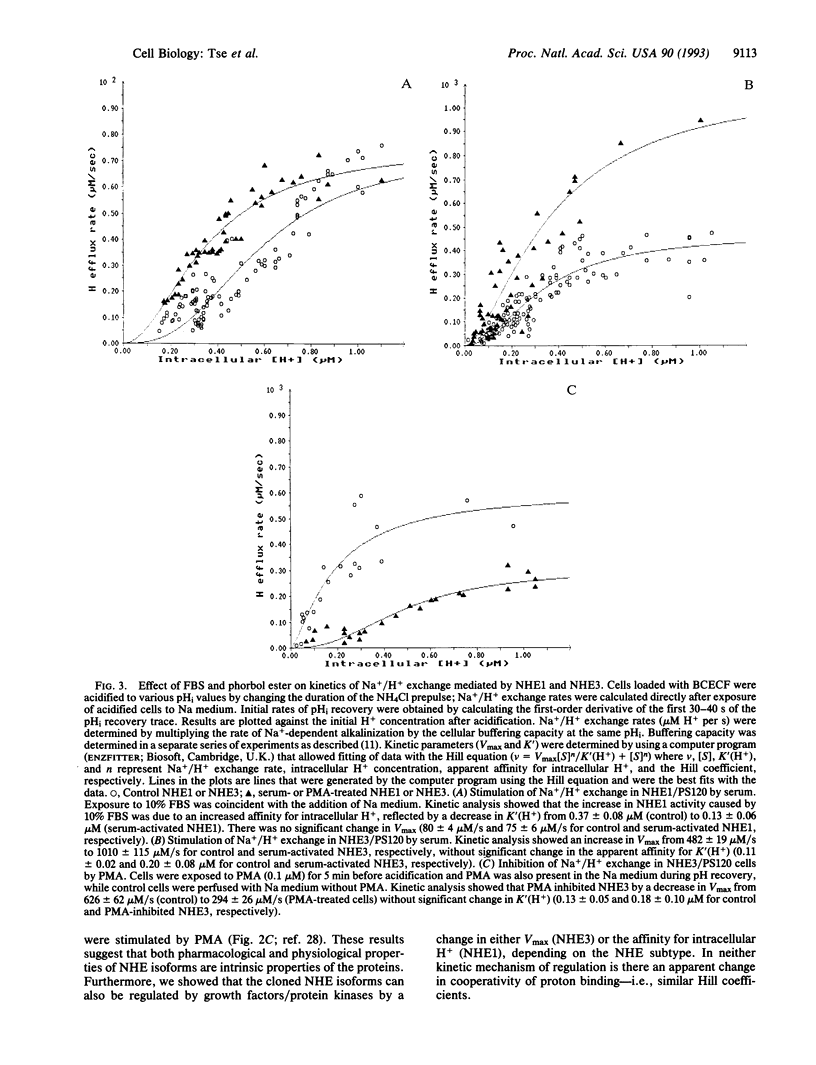
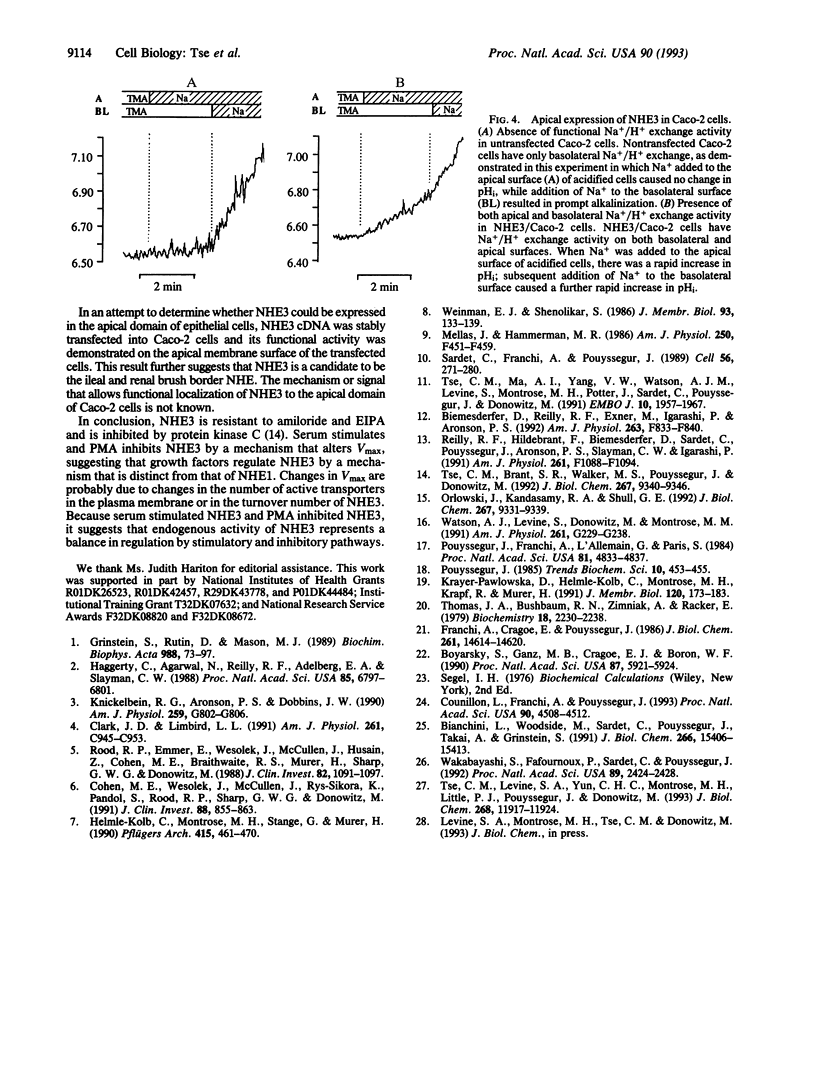
Abstract
We previously cloned an isoform Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE3), which was expressed only in intestine, kidney, and stomach. We show here the functional characteristics of NHE3 as a Na+/H+ exchanger by stably transfecting NHE3 cDNA into PS120 cells, a fibroblast cell line that lacks endogenous Na+/H+ exchangers. NHE3 was 39- and 160-fold more resistant to inhibition by amiloride and ethylisopropyl amiloride, respectively, than NHE1, the housekeeping Na+/H+ exchanger isoform. Although both exchangers were stimulated by serum, NHE3 was inhibited by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), which stimulated NHE1. Mechanistically, serum and PMA stimulated NHE1 by an increase in the apparent affinity of the exchanger for intracellular H+. In contrast, serum stimulated and PMA inhibited NHE3 by a Vmax change. When NHE3 was stably expressed in Caco-2 cells, an intestinal epithelial cell line, NHE3 was functionally expressed in the apical membrane. Thus, NHE3 is a good candidate to be an epithelial brush border Na+/H+ exchanger. Furthermore, Na+/H+ exchangers can be rapidly regulated by mechanisms that change either the Vmax or the affinity for intracellular H+, depending on the Na+/H+ exchanger subtype.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianchini L., Woodside M., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Takai A., Grinstein S. Okadaic acid, a phosphatase inhibitor, induces activation and phosphorylation of the Na+/H+ antiport. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15406–15413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemesderfer D., Reilly R. F., Exner M., Igarashi P., Aronson P. S. Immunocytochemical characterization of Na(+)-H+ exchanger isoform NHE-1 in rabbit kidney. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):F833–F840. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.5.F833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyarsky G., Ganz M. B., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Boron W. F. Intracellular-pH dependence of Na-H exchange and acid loading in quiescent and arginine vasopressin-activated mesangial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5921–5924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Limbird L. E. Na(+)-H+ exchanger subtypes: a predictive review. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):C945–C953. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.6.C945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. E., Wesolek J., McCullen J., Rys-Sikora K., Pandol S., Rood R. P., Sharp G. W., Donowitz M. Carbachol- and elevated Ca(2+)-induced translocation of functionally active protein kinase C to the brush border of rabbit ileal Na+ absorbing cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):855–863. doi: 10.1172/JCI115387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counillon L., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. A point mutation of the Na+/H+ exchanger gene (NHE1) and amplification of the mutated allele confer amiloride resistance upon chronic acidosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4508–4512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchi A., Cragoe E., Jr, Pouysségur J. Isolation and properties of fibroblast mutants overexpressing an altered Na+/H+ antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14614–14620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rotin D., Mason M. J. Na+/H+ exchange and growth factor-induced cytosolic pH changes. Role in cellular proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 18;988(1):73–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Agarwal N., Reilly R. F., Adelberg E. A., Slayman C. W. Pharmacologically different Na/H antiporters on the apical and basolateral surfaces of cultured porcine kidney cells (LLC-PK1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6797–6801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmle-Kolb C., Montrose M. H., Stange G., Murer H. Regulation of Na+/H+ exchange in opossum kidney cells by parathyroid hormone, cyclic AMP and phorbol esters. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jan;415(4):461–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00373624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knickelbein R. G., Aronson P. S., Dobbins J. W. Characterization of Na(+)-H+ exchangers on villus cells in rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 1):G802–G806. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.5.G802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krayer-Pawlowska D., Helmle-Kolb C., Montrose M. H., Krapf R., Murer H. Studies on the kinetics of Na+/H+ exchange in OK cells: introduction of a new device for the analysis of polarized transport in cultured epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1991 Mar;120(2):173–183. doi: 10.1007/BF01872400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellas J., Hammerman M. R. Phorbol ester-induced alkalinization of canine renal proximal tubular cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 2):F451–F459. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.3.F451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J., Kandasamy R. A., Shull G. E. Molecular cloning of putative members of the Na/H exchanger gene family. cDNA cloning, deduced amino acid sequence, and mRNA tissue expression of the rat Na/H exchanger NHE-1 and two structurally related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9331–9339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Sardet C., Franchi A., L'Allemain G., Paris S. A specific mutation abolishing Na+/H+ antiport activity in hamster fibroblasts precludes growth at neutral and acidic pH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly R. F., Hildebrandt F., Biemesderfer D., Sardet C., Pouysségur J., Aronson P. S., Slayman C. W., Igarashi P. cDNA cloning and immunolocalization of a Na(+)-H+ exchanger in LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 2):F1088–F1094. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.6.F1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rood R. P., Emmer E., Wesolek J., McCullen J., Husain Z., Cohen M. E., Braithwaite R. S., Murer H., Sharp G. W., Donowitz M. Regulation of the rabbit ileal brush-border Na+/H+ exchanger by an ATP-requiring Ca++/calmodulin-mediated process. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1172/JCI113665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90901-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Brant S. R., Walker M. S., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and sequencing of a rabbit cDNA encoding an intestinal and kidney-specific Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-3). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9340–9346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Levine S. A., Yun C. H., Montrose M. H., Little P. J., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and expression of a rabbit cDNA encoding a serum-activated ethylisopropylamiloride-resistant epithelial Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-2). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11917–11924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Ma A. I., Yang V. W., Watson A. J., Levine S., Montrose M. H., Potter J., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Molecular cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding the rabbit ileal villus cell basolateral membrane Na+/H+ exchanger. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):1957–1967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07725.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Fafournoux P., Sardet C., Pouysségur J. The Na+/H+ antiporter cytoplasmic domain mediates growth factor signals and controls "H(+)-sensing". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson A. J., Levine S., Donowitz M., Montrose M. H. Kinetics and regulation of a polarized Na(+)-H+ exchanger from Caco-2 cells, a human intestinal cell line. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):G229–G238. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.2.G229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Shenolikar S. Protein kinase C activates the renal apical membrane Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;93(2):133–139. doi: 10.1007/BF01870805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


