Abstract
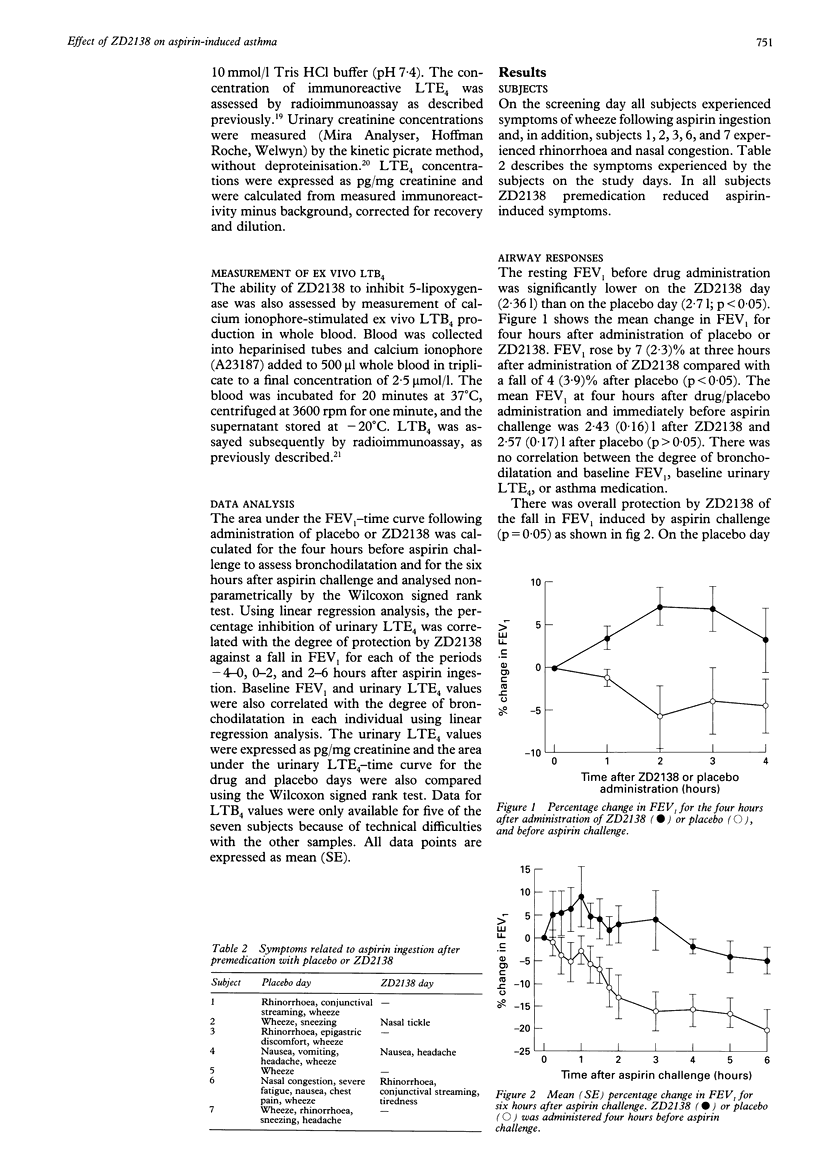
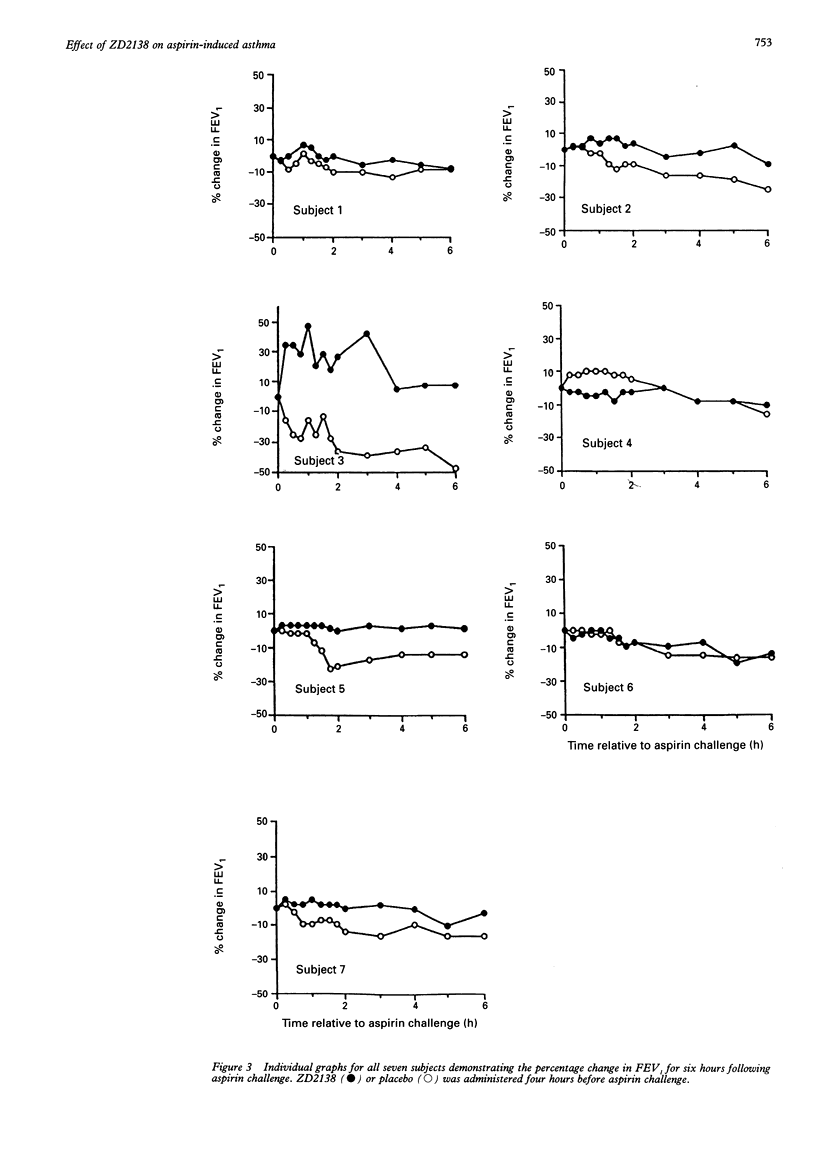
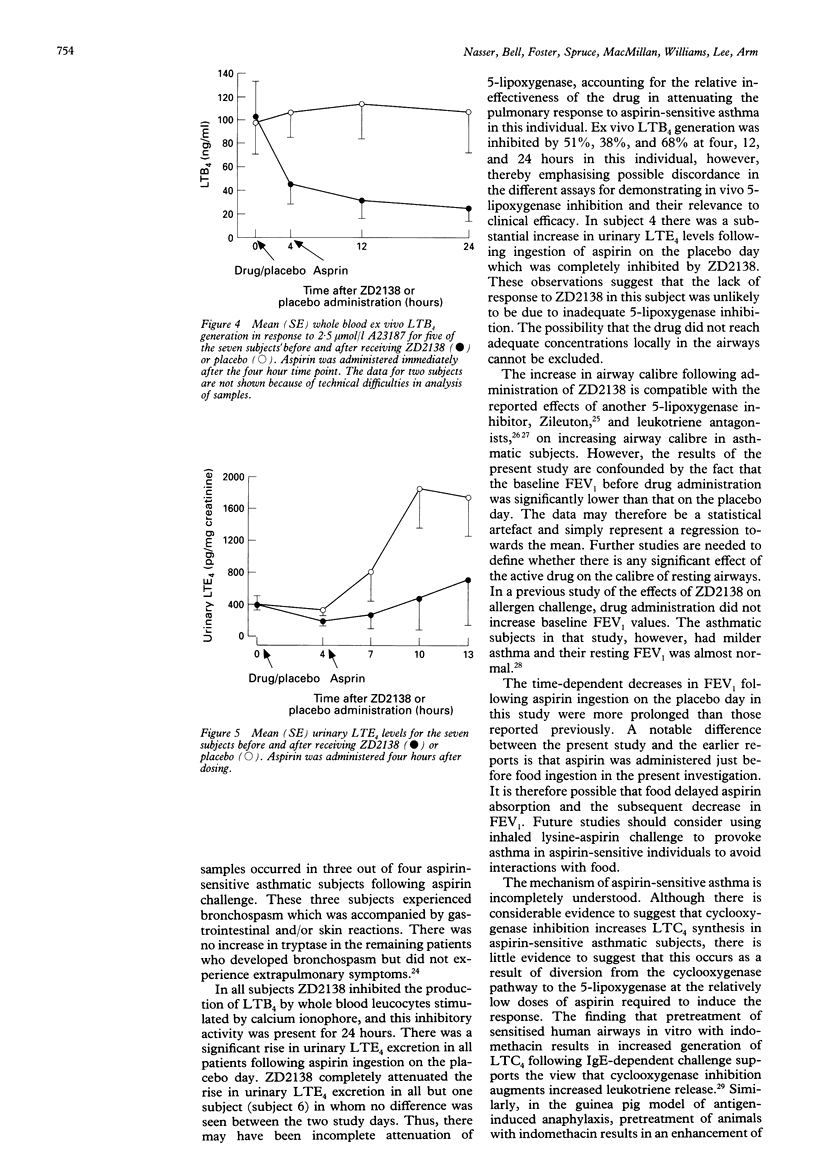
BACKGROUND--The cysteinyl leukotrienes may play a central part in the mechanisms of aspirin-sensitive asthma. Previous work has shown that individuals with aspirin-sensitive asthma have high basal urinary LTE4 levels which increase further upon aspirin ingestion, and that sulphidopeptide leukotriene receptor antagonists attenuate aspirin-induced airflow obstruction. If the cysteinyl leukotrienes cause aspirin-induced asthmatic reactions, inhibition of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway should prevent aspirin-induced bronchospasm. This hypothesis has been tested with ZD2138, a specific non-redox 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. METHODS--Seven subjects (four men) with aspirin-sensitive asthma with baseline FEV1 values > 67% were studied. ZD2138 (350 mg) or placebo was given on two separate occasions two weeks apart in a randomised double blind fashion. A single dose of aspirin was administered four hours after dosing and FEV1 was measured for six hours. Inhibition of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway by ZD2138 was assessed by measurements of urinary LTE4 levels and ex vivo calcium ionophore stimulated LTB4 generation in whole blood, before administration of drug or placebo and at regular time intervals after dosing and aspirin administration. RESULTS--ZD2138 protected against the aspirin-induced reduction in FEV1 with a 20.3 (4.9)% fall in FEV1 following placebo compared with 4.9 (2.9)% following ZD2138. This was associated with 72% inhibition of ex vivo LTB4 generation in whole blood at 12 hours and a 74% inhibition of the rise in urinary LTE4 excretion at six hours after aspirin ingestion. CONCLUSIONS--In aspirin-sensitive asthma the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor ZD2138 inhibits the fall in FEV1 induced by aspirin and this is associated with substantial inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arm J. P., O'Hickey S. P., Hawksworth R. J., Fong C. Y., Crea A. E., Spur B. W., Lee T. H. Asthmatic airways have a disproportionate hyperresponsiveness to LTE4, as compared with normal airways, but not to LTC4, LTD4, methacholine, and histamine. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Nov;142(5):1112–1118. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.5.1112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R., Morton D. R., Jr Solubilization and characterization of the leukotriene C4 synthetase of rat basophil leukemia cells: a novel, particulate glutathione S-transferase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90426-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels H., Böhmer M., Heierli C. Serum Kreatinibestimmung ohne Enteiweissen. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Mar;37:193–197. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90432-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey F., Forder R. A. Radioimmunoassay of LTB4 and 6-trans LTB4: analytical and pharmacological characterisation of immunoreactive LTB4 in ionophore stimulated human blood. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1986 Apr;22(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(86)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. E., Smith C. M., Lee T. H. The potent and selective sulfidopeptide leukotriene antagonist, SK&F 104353, inhibits aspirin-induced asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Oct;144(4):957–958. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.4.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. E., Tagari P., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Black C., Markendorf A., Schmitz-Schumann M., Lee T. H. Urinary leukotriene E4 after lysine-aspirin inhalation in asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Dec;146(6):1531–1534. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.6.1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie P. E., Tagari P., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Charlesson S., Chee P., Arm J. P., Lee T. H. Urinary leukotriene E4 concentrations increase after aspirin challenge in aspirin-sensitive asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 May;143(5 Pt 1):1025–1029. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.5_Pt_1.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G. The enhancement of inflammatory injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jul;136(1):1–2. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlén B., Kumlin M., Margolskee D. J., Larsson C., Blomqvist H., Williams V. C., Zetterström O., Dahlén S. E. The leukotriene-receptor antagonist MK-0679 blocks airway obstruction induced by inhaled lysine-aspirin in aspirin-sensitive asthmatics. Eur Respir J. 1993 Jul;6(7):1018–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Austen K. F., Lewis R. A., Clark D. A., Goto G., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Comparative airway and vascular activities of leukotrienes C-1 and D in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4354–4358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreri N. R., Howland W. C., Stevenson D. D., Spiegelberg H. L. Release of leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and histamine into nasal secretions of aspirin-sensitive asthmatics during reaction to aspirin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):847–854. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B. S., Bel E. H., Buntinx A., Tanaka W., Han Y. H., Shingo S., Spector R., Sterk P. Oral leukotriene inhibitor (MK-886) blocks allergen-induced airway responses. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Apr;147(4):839–844. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.4.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaddy J. N., Margolskee D. J., Bush R. K., Williams V. C., Busse W. W. Bronchodilation with a potent and selective leukotriene D4 (LTD4) receptor antagonist (MK-571) in patients with asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Aug;146(2):358–363. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.2.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heavey D. J., Soberman R. J., Lewis R. A., Spur B., Austen K. F. Critical considerations in the development of an assay for sulfidopeptide leukotrienes in plasma. Prostaglandins. 1987 May;33(5):693–708. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(87)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui K. P., Barnes N. C. Lung function improvement in asthma with a cysteinyl-leukotriene receptor antagonist. Lancet. 1991 May 4;337(8749):1062–1063. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91709-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui K. P., Taylor I. K., Taylor G. W., Rubin P., Kesterson J., Barnes N. C., Barnes P. J. Effect of a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor on leukotriene generation and airway responses after allergen challenge in asthmatic patients. Thorax. 1991 Mar;46(3):184–189. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.3.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel E., Fischer A. R., Rosenberg M. A., Lilly C. M., Callery J. C., Shapiro J., Cohn J., Rubin P., Drazen J. M. The pivotal role of 5-lipoxygenase products in the reaction of aspirin-sensitive asthmatics to aspirin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Dec;148(6 Pt 1):1447–1451. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.6_Pt_1.1447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp H. R., Sladek K., Fitzgerald G. A. Increased excretion of leukotriene E4 during aspirin-induced asthma. J Lab Clin Med. 1992 Jan;119(1):48–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumlin M., Dahlén B., Björck T., Zetterström O., Granström E., Dahlén S. E. Urinary excretion of leukotriene E4 and 11-dehydro-thromboxane B2 in response to bronchial provocations with allergen, aspirin, leukotriene D4, and histamine in asthmatics. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Jul;146(1):96–103. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Israel E., Drazen J. M., Leitch A. G., Ravalese J., 3rd, Corey E. J., Robinson D. R., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Enhancement of plasma levels of biologically active leukotriene B compounds during anaphylaxis in guinea pigs pretreated by indomethacin or by a fish oil-enriched diet. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2575–2582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Austen K. F., Soberman R. J. Leukotrienes and other products of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. Biochemistry and relation to pathobiology in human diseases. N Engl J Med. 1990 Sep 6;323(10):645–655. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009063231006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumry W. R., Curd J. G., Stevenson D. D. Aspirin-sensitive asthma and rhinosinusitis: current concepts and recent advances. Ear Nose Throat J. 1984 Feb;63(2):66, 68-70, 72-4 passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. R., Mathison D. A., Stevenson D. D. Aspirin intolerance in asthma. Detection by oral challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972 Oct;50(4):198–207. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R. M., Spruce K. E., Crawley G. C., Walker E. R., Foster S. J. Pre-clinical pharmacology of ICI D2138, a potent orally-active non-redox inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):1042–1047. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Taylor G. W., Piper P. J., Tippins J. R. Structure of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis from guinea-pig lung. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):104–106. doi: 10.1038/285104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasser S. M., Bell G. S., Hawksworth R. J., Spruce K. E., MacMillan R., Williams A. J., Lee T. H., Arm J. P. Effect of the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor ZD2138 on allergen-induced early and late asthmatic responses. Thorax. 1994 Aug;49(8):743–748. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.8.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortolani C., Mirone C., Fontana A., Folco G. C., Miadonna A., Montalbetti N., Rinaldi M., Sala A., Tedeschi A., Valente D. Study of mediators of anaphylaxis in nasal wash fluids after aspirin and sodium metabisulfite nasal provocation in intolerant rhinitic patients. Ann Allergy. 1987 Nov;59(5 Pt 2):106–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samter M., Beers R. F., Jr Intolerance to aspirin. Clinical studies and consideration of its pathogenesis. Ann Intern Med. 1968 May;68(5):975–983. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-5-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B. Leukotrienes: mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):568–575. doi: 10.1126/science.6301011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. M., Hawksworth R. J., Thien F. C., Christie P. E., Lee T. H. Urinary leukotriene E4 in bronchial asthma. Eur Respir J. 1992 Jun;5(6):693–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. L., Wangaard C. H., Farr R. S. Aspirin and concomitant idiosyncrasies in adult asthmatic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Dec;64(6 Pt 1):500–506. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson D. D., Mathison D. A., Tan E. M., Vaughan J. H. Provoking factors in bronchial asthma. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Jun;135(6):777–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczeklik A., Gryglewski R. J., Czerniawska-Mysik G. Relationship of inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis by analgesics to asthma attacks in aspirin-sensitive patients. Br Med J. 1975 Jan 11;1(5949):67–69. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5949.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


