Abstract
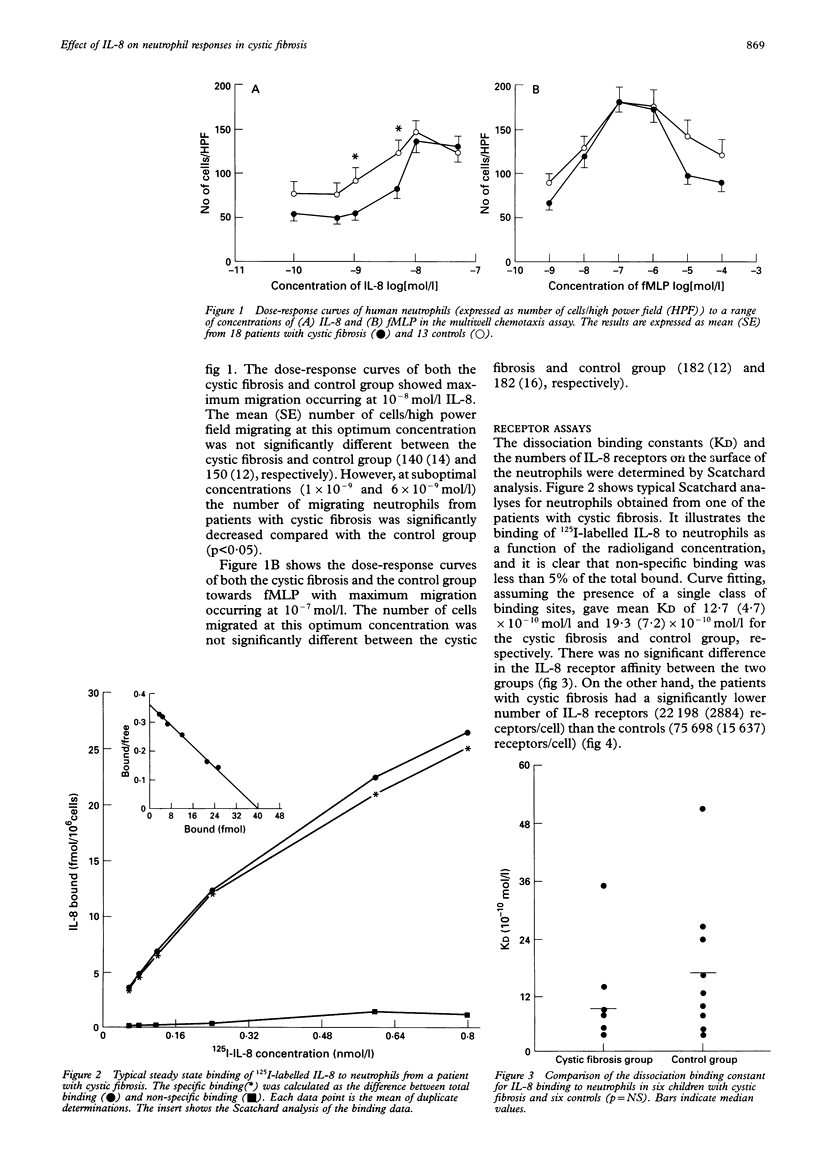
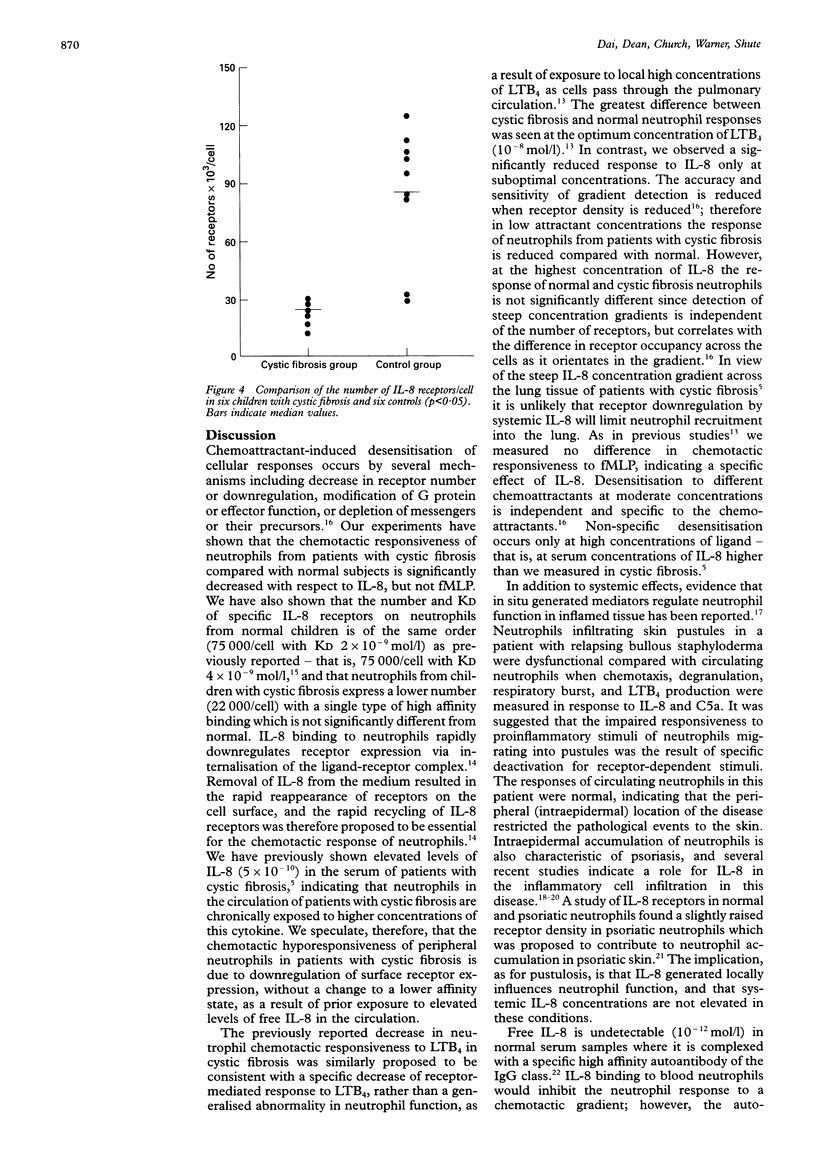
BACKGROUND--Inflammation associated with neutrophil infiltration is a commonly observed feature of children with cystic fibrosis. Production of the major neutrophil chemotactic cytokine interleukin 8 (IL-8) is potentially of great importance in the pathology of cystic fibrosis. Concentrations of IL-8 in both sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid have been found to be higher in children with cystic fibrosis than in controls. The IL-8 induced chemotactic response and numbers of IL-8 receptors on peripheral neutrophils obtained from children with cystic fibrosis have been compared with a control group of children. METHODS--Cells were isolated from 18 patients with cystic fibrosis (aged 4-20 years) and 13 controls (aged 5-12 years) by dextran centrifugation followed by separation on Lymphoprep. Chemotaxis was assayed using multiwell microchemotaxis chambers and 5 microns polycarbonate filters. Filters were fixed and stained with Haema-Gurr for counting. Results were expressed as numbers of neutrophils per high power field (HPF). RESULTS--At the optimum concentration (1 x 10(-8) mol/l) the number of cells migrating were similar for controls (150 (12)/HPF) and for the cystic fibrosis group (140 (14)/HPF)). At lower concentrations the numbers of neutrophils migrating were lower for the cystic fibrosis group. Scatchard analysis of 125I-labelled IL-8 binding revealed lower numbers of receptors on neutrophils from patients with cystic fibrosis (22,000 per cell) than from controls (75,000 per cell). CONCLUSIONS--Reduced responsiveness to IL-8 of neutrophils from patients with cystic fibrosis is associated with receptor desensitisation as a result of exposure to high systemic levels of IL-8.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anttila H. S., Reitamo S., Erkko P., Ceska M., Moser B., Baggiolini M. Interleukin-8 immunoreactivity in the skin of healthy subjects and patients with palmoplantar pustulosis and psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Jan;98(1):96–101. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12495817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenberger P., Kemény L., Süss R., Michel G., Peter R. U., Ruzicka T. Interleukin-8 receptors in normal and psoriatic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992 Sep;72(5):334–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. N., Griffiths C. E., Nickoloff B. J. NAP-1/IL-8 immunoreactivity in normal and psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Sep;97(3):606–608. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12481959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean T. P., Dai Y., Shute J. K., Church M. K., Warner J. O. Interleukin-8 concentrations are elevated in bronchoalveolar lavage, sputum, and sera of children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Res. 1993 Aug;34(2):159–161. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199308000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Zigmond S. H. Chemotaxis in eukaryotic cells: a focus on leukocytes and Dictyostelium. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:649–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. M., David E., Warren T. C., DeLeon R. P., Farina P. R., Homon C. A. Characterization of a receptor for human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor/interleukin-8. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8311–8316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Standiford T., Kasahara K., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 (IL-8): the major neutrophil chemotactic factor in the lung. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;17(1):17–23. doi: 10.3109/01902149109063278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. H., Sorrelli T. C. Decreased polymorphonuclear leucocyte chemotactic response to leukotriene B4 in cystic fibrosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Aug;89(2):321–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peichl P., Ceska M., Broell H., Effenberger F., Lindley I. J. Human neutrophil activating peptide/interleukin 8 acts as an autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Jan;51(1):19–22. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin J. A., Sylvester I., Smith S., Yoshimura T., Leonard E. J. Macrophages cultured in vitro release leukotriene B4 and neutrophil attractant/activation protein (interleukin 8) sequentially in response to stimulation with lipopolysaccharide and zymosan. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1556–1564. doi: 10.1172/JCI114875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe M. W., Kunkel S. L., Standiford T. J., Chensue S. W., Allen R. M., Evanoff H. L., Phan S. H., Strieter R. M. Pulmonary fibroblast expression of interleukin-8: a model for alveolar macrophage-derived cytokine networking. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Nov;5(5):493–501. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.5.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta A. K., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. Interleukin 8 (monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor) dynamically regulates its own receptor expression on human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):183–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Christophers E. Secretion of novel and homologous neutrophil-activating peptides by LPS-stimulated human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):244–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Christophers E. Identification of different charged species of a human monocyte derived neutrophil activating peptide (MONAP). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):277–284. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80711-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Christophers E. Purification and partial biologic characterization of a human lymphocyte-derived peptide with potent neutrophil-stimulating activity. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3534–3540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standiford T. J., Kunkel S. L., Basha M. A., Chensue S. W., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Toews G. B., Westwick J., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 gene expression by a pulmonary epithelial cell line. A model for cytokine networks in the lung. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1945–1953. doi: 10.1172/JCI114928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester I., Yoshimura T., Sticherling M., Schröder J. M., Ceska M., Peichl P., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil attractant protein-1-immunoglobulin G immune complexes and free anti-NAP-1 antibody in normal human serum. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):471–481. doi: 10.1172/JCI115883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester I., Yoshimura T., Sticherling M., Schröder J. M., Ceska M., Peichl P., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil attractant protein-1-immunoglobulin G immune complexes and free anti-NAP-1 antibody in normal human serum. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):471–481. doi: 10.1172/JCI115883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. O. Immunology of cystic fibrosis. Br Med Bull. 1992 Oct;48(4):893–911. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


