Abstract
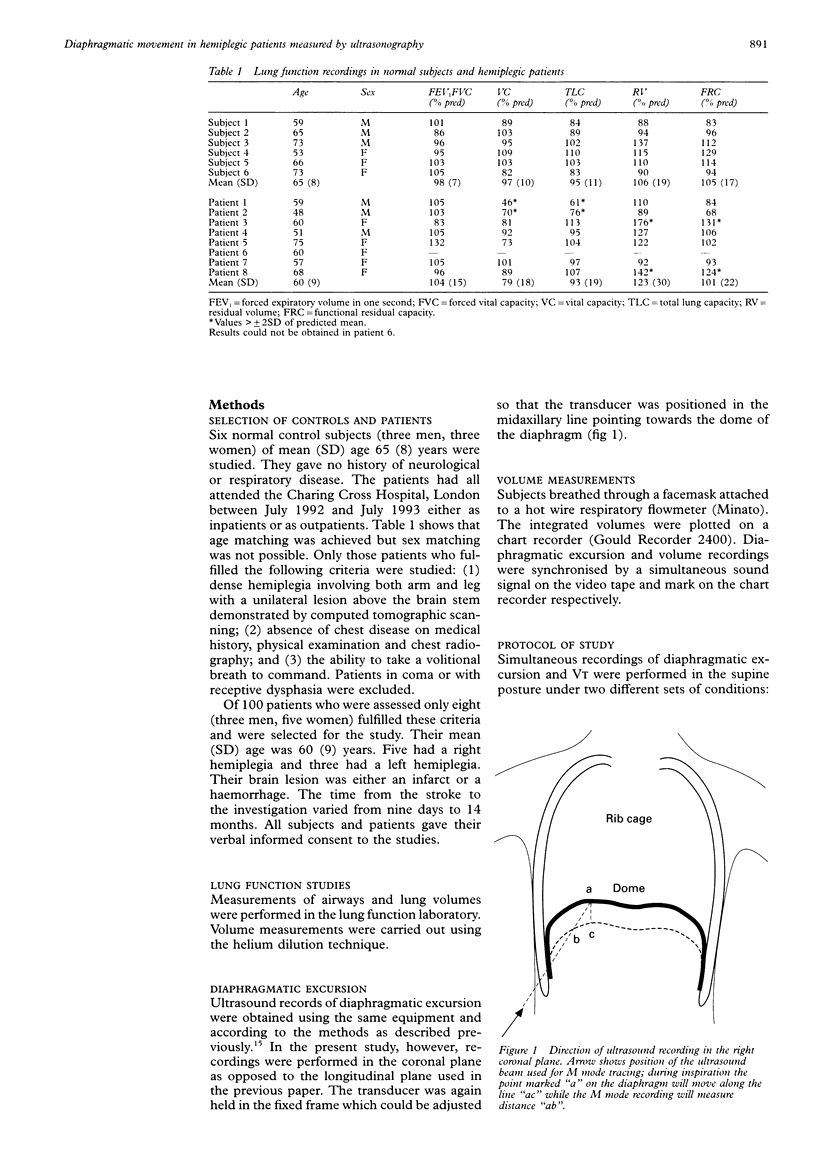
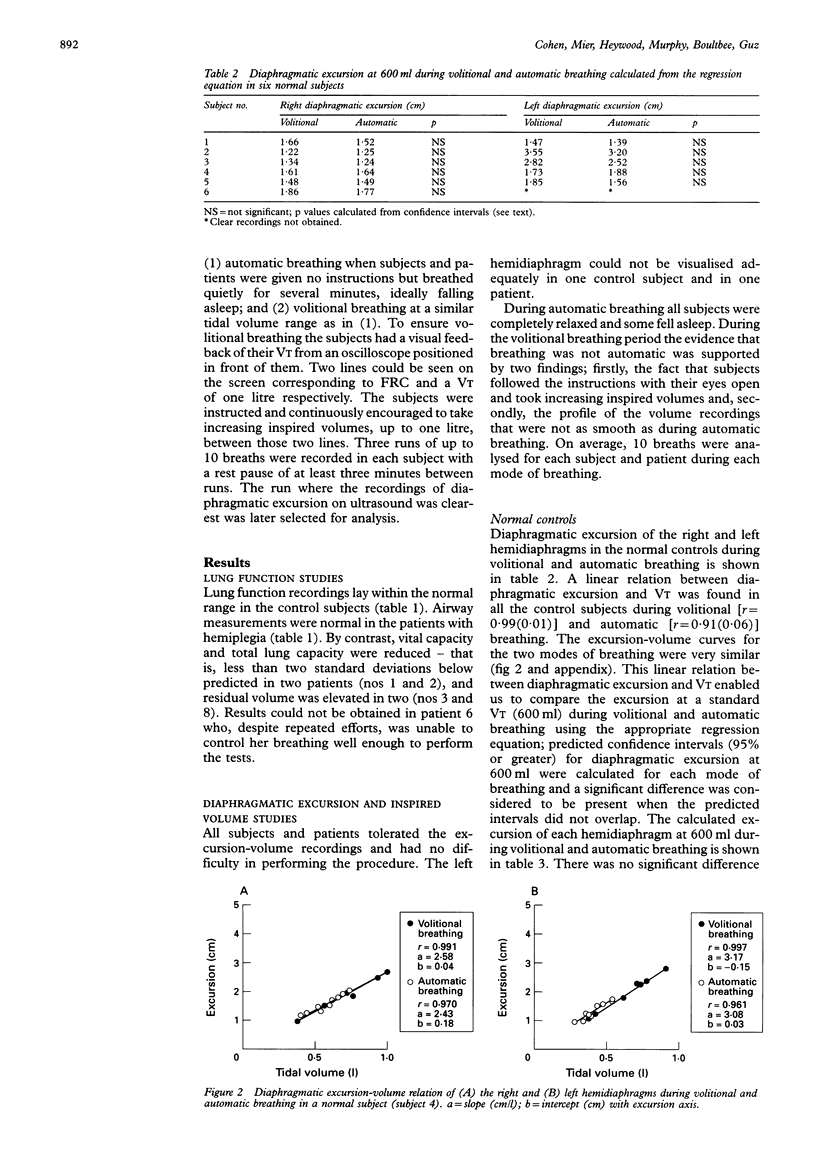
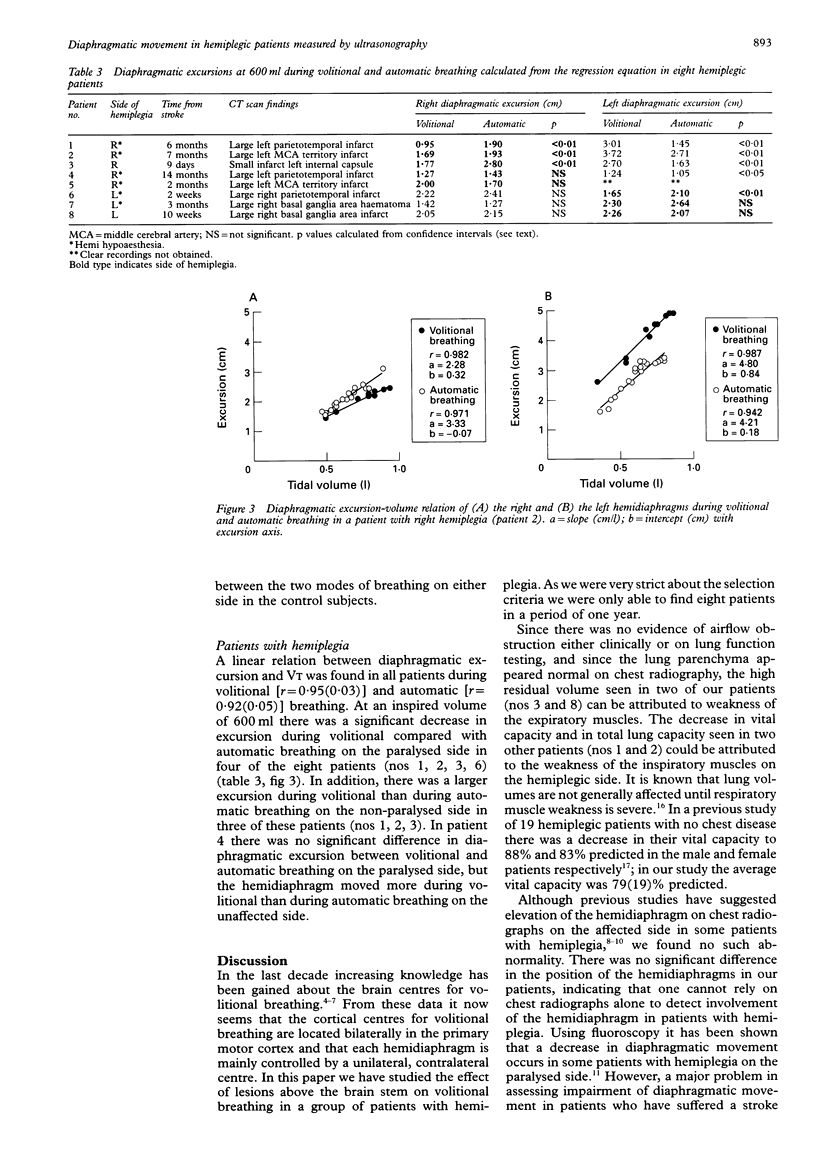
BACKGROUND--It is known that automatic breathing is controlled by centres in the lower brain stem, whereas volitional breathing is controlled by the cerebral cortical centres. In hemiplegia, lesions above the brain stem result in paralysis of limb muscles. This study was performed to determine whether the diaphragm might also be affected in patients with hemiplegia. METHODS--Studies were performed in six normal control subjects and in eight patients with complete hemiplegia caused by a lesion above the brain stem, all with no known chest disease. Full lung function tests were performed. Diaphragmatic excursion and inspired volume (VT) were measured simultaneously by M mode ultrasonography and respiratory airflow measurements. Recordings of diaphragmatic excursion were performed on each side separately during volitional and automatic breathing at a similar range of VT. RESULTS--Lung function tests lay within the normal range in all the control subjects. In the hemiplegic patients mean (SD) vital capacity was 79 (18)% and residual volume was 123(30)% of predicted. Total lung capacity and functional residual capacity were in the normal range. In the control subjects no significant difference in diaphragmatic excursion was found between volitional and automatic breathing for the same range of inspired volume. By contrast, there was a significant decrease in diaphragmatic excursion during volitional breathing compared with automatic breathing on the affected side in four of the eight hemiplegic patients. CONCLUSIONS--In four of eight hemiplegic patients reduced diaphragmatic movement was present on the paralysed side during volitional inspiration when compared with automatic inspiration. The hemidiaphragm may be involved on the affected side in patients with hemiplegia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander C. Diaphragm movements and the diagnosis of diaphragmatic paralysis. Clin Radiol. 1966 Jan;17(1):79–83. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(66)80128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aminoff M. J., Sears T. A. Spinal integration of segmental, cortical and breathing inputs to thoracic respiratory motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):557–575. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E., Mier A., Heywood P., Murphy K., Boultbee J., Guz A. Excursion-volume relation of the right hemidiaphragm measured by ultrasonography and respiratory airflow measurements. Thorax. 1994 Sep;49(9):885–889. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.9.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colebatch J. G., Adams L., Murphy K., Martin A. J., Lammertsma A. A., Tochon-Danguy H. J., Clark J. C., Friston K. J., Guz A. Regional cerebral blood flow during volitional breathing in man. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:91–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., Rothwell J. C. Activation of the human diaphragm from the motor cortex. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:109–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A., Rusk H. A., Pelosof H., Adam J. R. Respiratory function in hemiplegic patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1967 Apr;48(4):174–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston J. G., Morris A. D., Howie C. A., Reid J. L., McMillan N. Technical report: quantitative assessment of diaphragmatic movement--a reproducible method using ultrasound. Clin Radiol. 1992 Dec;46(6):405–407. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(05)80688-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korczyn A. D., Hermann G., Don R. Diaphragmatic involvement in hemiplegia and hemiparesis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Dec;32(6):588–590. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.6.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korczyn A. D., Leibowitz U., Bruderman I. Involvement of the diaphragm in hemiplegia. Neurology. 1969 Jan;19(1):97–100. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskill D., Murphy K., Mier A., Owen M., Guz A. Motor cortical representation of the diaphragm in man. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:105–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santamaria J., Ruiz C. Diaphragmatic elevation in stroke. Eur Neurol. 1988;28(2):81–83. doi: 10.1159/000116235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A., Simon G. Certain movements measured on inspiration-expiration chest radiographs correlated with pulmonary function studies. Clin Radiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(72)80132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


