FIG 5 .
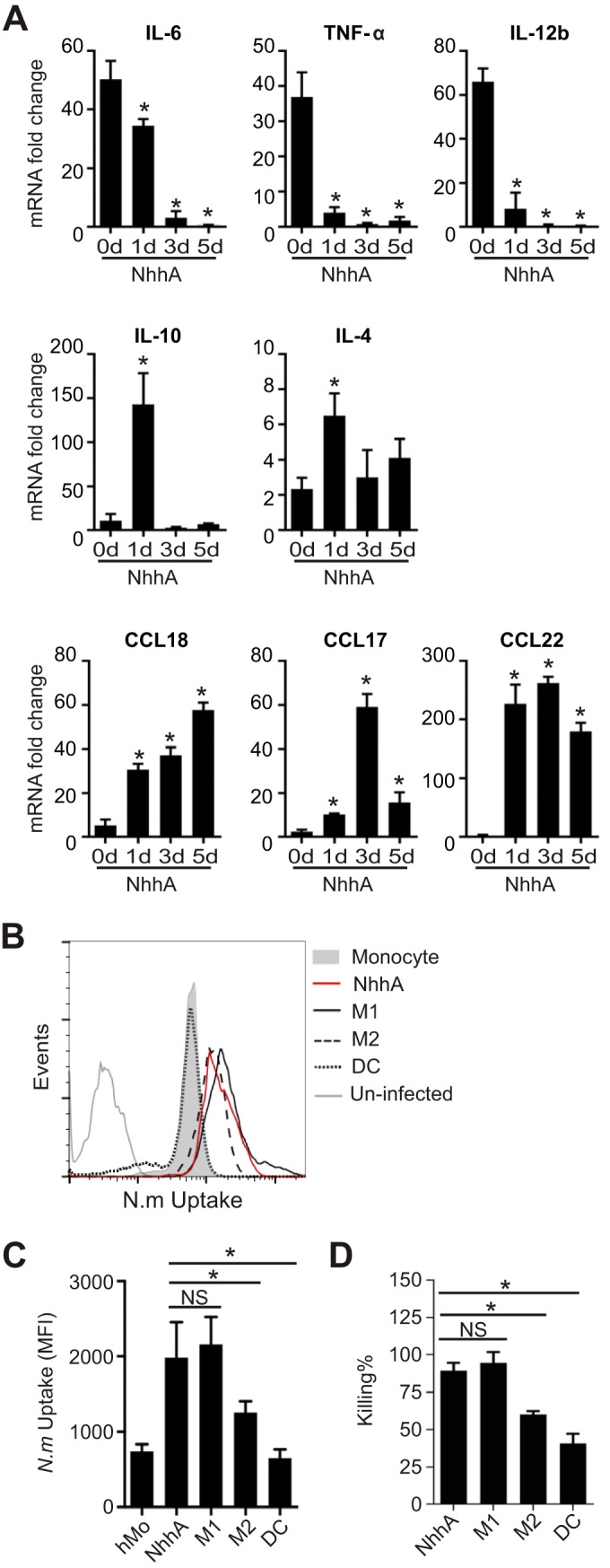
NhhA-Mφ are hyporesponsive to Neisseria meningitidis stimulation but retain the potential to eliminate bacteria. (A) Mo were differentiated with 50 nM NhhA for the indicated time points and subsequently challenged with FAM20 (MOI, 100) for 3 h. The RNA was isolated, and qPCR was performed to estimate the transcription levels of the indicated cytokines or chemokines. Normalized data, shown as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments, are presented as fold change compared with uninfected Mo (day 0). *, P < 0.05 compared with control at day 0 using ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test. (B and C) NhhA-Mφ, M1Mφ, M2Mφ, or DCs, generated as described in Materials and Methods, were challenged with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled N. meningitidis FAM20 (MOI, 100) for 40 min at 37°C. The intracellular fluorescence intensity was determined by flow cytometry, and a representative plot is shown in panel B. Quantitative data for median fluorescence intensity (MFI), shown as medians with interquartile ranges from three independent experiments, are presented in panel C. *, P < 0.05 using ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test. (D) NhhA-Mφ, M1Mφ, M2Mφ, or DCs, generated as described for panel B, were challenged with live FAM20 (MOI, 100) for 40 min. After intensive washing and antibiotic treatment to kill extracellular bacteria, survival of intracellular bacteria was determined by a modified gentamicin protection assay, as described in Materials and Methods. The data represent the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 using ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test. NS, not significant.
