Abstract
Background and aims
Helicobacter pylori is the causative agent of gastric diseases and the main risk factor in the development of gastric adenocarcinoma. In vitro studies with this bacterial pathogen largely rely on the use of transformed cell lines as infection model. However, this approach is intrinsically artificial and especially inappropriate when it comes to investigating the mechanisms of cancerogenesis. Moreover, common cell lines are often defective in crucial signalling pathways relevant to infection and cancer. A long-lived primary cell system would be preferable in order to better approximate the human in vivo situation.
Methods
Gastric glands were isolated from healthy human stomach tissue and grown in Matrigel containing media supplemented with various growth factors, developmental regulators and apoptosis inhibitors to generate long-lasting normal epithelial cell cultures.
Results
Culture conditions were developed which support the formation and quasi-indefinite growth of three dimensional (3D) spheroids derived from various sites of the human stomach. Spheroids could be differentiated to gastric organoids after withdrawal of Wnt3A and R-spondin1 from the medium. The 3D cultures exhibit typical morphological features of human stomach tissue. Transfer of sheared spheroids into 2D culture led to the formation of dense planar cultures of polarised epithelial cells serving as a suitable in vitro model of H. pylori infection.
Conclusions
A robust and quasi-immortal 3D organoid model has been established, which is considered instrumental for future research aimed to understand the underlying mechanisms of infection, mucosal immunity and cancer of the human stomach.
Keywords: GASTRIC CANCER, HELICOBACTER PYLORI
Significance of this study.
What is already known on this subject?
Helicobacter pylori infects over half of the world's population and can cause inflammation, peptic ulcers and ultimately lead to gastric cancer.
Illuminating the molecular basis of H. pylori-induced carcinogenesis has been hampered by the absence of suitable in vitro infection models, because available cell lines are derived from neoplastic tissue, which has already undergone transformation.
So far, it has not been possible to culture normal human gastric primary epithelial cells long enough to permit experimental investigations into many of the processes that underlie gastric pathology.
What are the new findings?
We have established a quasi-immortal tissue culture model derived from normal, primary human gastric glands, which can be expanded in vitro in the form of three dimensional gastric spheroids.
Spheroids can be differentiated to organoids which recapitulate many facets of the normal gastric architecture and physiology, and can also be transferred to planar cultures.
The primary gastric cells can be infected with H. pylori to allow analysis of infection-induced changes and can also be genetically manipulated to investigate mechanisms of gastric pathology.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
Since even small biopsy specimens are sufficient to create large numbers of cells, our approach serves basic investigation and could soon find personalised medicine application for diagnostics of disease stages and pharmacological screening and ultimately for tissue regeneration purposes.
Introduction
Bacterial infections are gaining increasing attention as the initiating cause of human cancers.1 2 The paradigm of a cancer-inducing bacterium is Helicobacter pylori. This Gram-negative bacterium is prevalent in around 50% of the world’s population3 and is the only one classified as a type I carcinogen by the WHO.4 It causes persistent infection of the human gastric mucosa which often results in acute and chronic gastritis.5 While the majority of infections are asymptomatic, duodenal and gastric ulcers develop in 5%–10% of infected individuals. In a small subset of patients, gastritis progresses over years and decades via atrophic, metaplastic and dysplastic pathologies to gastric adenocarcinoma.6 This association between chronic H. pylori infections and the development of gastric adenocarcinoma, as well as its connection to the occurrence of mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue lymphoma is supported by vast epidemiological evidence.7 8
A major risk factor for the development of gastric adenocarcinoma is chronic inflammation caused by the persistent infection with H. pylori. One major virulence factor, the CagA protein, which is translocated into host cells via the pathogen's type IV secretion system (T4SS), has been directly implicated in the process of malignant transformation.9 10 Yet, the detailed mechanisms that trigger gastric cancer initiation are poorly understood. One major drawback is the lack of suitable animal models, capable of recapitulating crucial aspects of the human infection. For example, infected mice normally do not progress further than to the metaplastic stage.11 In contrast, infected gerbils reportedly develop tumours after a few weeks of infection12 and, besides lagging behind as an amenable genetic model, might not resemble the human situation. Consequently, current research largely depends on the use of transformed human epithelial cell lines as in vitro models of these infections, which were almost exclusively derived from gastric adenocarcinoma. Since such tumour cell lines already represent the end-point of Correa's cascade, and as such are the end-product of the process in question, they are badly suited for illuminating the early effects of H. pylori on the host. Therefore, a primary cell system is urgently needed in order to assess the early effects of an H. pylori infection on healthy epithelial cells.
During recent years, rapid advances have been made with respect to in vitro cultivation of three dimensional (3D) epithelial primary cell cultures, recapitulating organ physiology and structure. Several strategies have been pursued to enable long-term outgrowth of murine intestinal crypts to 3D crypt-villus-like structures: one protocol relies on stromal elements rather than extrinsically added growth factors and an air-liquid interface to support the growth of 3D epithelial structures13 whereas another one relies on distinct growth factors and extracellular support provided by laminin-rich Matrigel and produces pure epithelial crypt-villus organoids that resemble all differentiated epithelial cell types.14 Similar culture conditions have been described for murine pyloric epithelium and human colon, adenoma, adenocarcinoma, as well as Barrett´s epithelium.15 16 These seminal studies provided evidence for the existence of Lgr5+ stem cells, capable of generating long-lived organoid structures, even from single cells.15 More recently, 3D cultures from murine gastric corpus gland units have been established which harbour Troy+ cells, capable of forming murine gastric organoids.17
Nonetheless, it has been difficult until now to establish pure and long-lived normal epithelial cultures from human stomach and to use normal human gastric epithelial cells for the purpose of infection in vitro. Initial success was achieved by generating highly polarised epithelial spheroids from normal gastric biopsies.18 While exhibiting an outer apical surface, these vesicles reached a life time of up to 17 days. In an effort to accomplish more extended growth capacities of normal human gastric epithelial cells, we adjusted previously published protocols to human gastric epithelium.15–17 Here, we report on the generation of gastric organoids from normal human corpus mucosa as an advanced cell culture model, exhibiting quasi-permanent growth of epithelial cells, and demonstrate the suitability of this model for studies on the infection with H. pylori in vitro. We obtained considerable insight into the gene expression profiles of pure gastric epithelial cells under different growth and infection conditions which could serve as standards for future studies of infection and carcinogenesis of the gastric epithelium.
Materials and methods
Microarray data have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information and can be accessed with the GEO accession number GSE58473. For more information, see online supplementary methods.
Human tissue material
Gastric tissue samples were derived from the Clinics for General, Visceral and Transplant Surgery, and the Center of Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery, Charité University Medicine, Berlin, Germany. Pseudonymised samples were obtained from individuals undergoing gastrectomy or sleeve resection. Only anatomically normal gastric tissue samples were used for experiments and prepared within 3 h after removal.
Gastric gland isolation
Tissue samples were washed with cold Hank’s buffered saline solution (HBSS) and fat and connective tissue were removed. Samples were cut into pieces of approximately 5 mm, washed 8–10 times with cold HBSS until the supernatant was clear and incubated with chelating solution (distilled water with 5.6 mM Na2HPO4, 8.0 mM KH2PO4, 96.2 mM NaCl, 1.6 mM KCl, 43.4 mM sucrose, 54.9 mM D-sorbitol, 0.5 mM DL-dithiothreitol, 2 mM EDTA) for 30 min at 37°C on a shaking platform. Supernatant was then removed, tissue fragments placed in a petri dish and gently squeezed with a glass slide to isolate the gastric glands. Isolated glands were resuspended in medium containing 10% heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS; Biochrom), collected in a tube and allowed to settle for 1 min by gravity before the supernatant containing most of the isolated glands was transferred to a new tube. After five more washes, glands were counted under a microscope and centrifuged (250×g, 5 min) followed by three washes with advanced Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium/F12 (ADF; Invitrogen).
Culture of gastric glands
Isolated gastric glands and fragments of gastric epithelium were mixed with ice-cold Matrigel (growth factor reduced, phenol red free; BD Biosciences) and seeded in pre-warmed 24-well plates at a density of ∼300 glands/fragments per 40 µL Matrigel/well. The Matrigel was polymerised for 15 min at 37°C and overlaid with 500 µL warm expansion medium (ADF, 50% conditioned Wnt3A-medium (as described in Willert et al19), 25% conditioned R-spondin1 medium supplemented with 10 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid, 1% Glutamax, 2% B27, 1% N2, 20 ng/mL human epidermal growth factor (EGF) (all Invitrogen), 150 ng/mL human noggin, 150 ng/mL human fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-10 (both Peprotech), 1.25 mM N-acetyl-L-cystein, 10 mM nicotinamide, 10 nM human gastrin, 2 µM SB202190 (all Sigma) and 1 µM A83–01 (Calbiochem). 7,5 µM Y-27632 (Sigma) was added for the first 3 days. Cultures were kept at 37°C, 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator.
Maintenance and differentiation of established spheroids
Culture medium was exchanged every 2–4 days and spheroids passaged every 10–21 days at a ratio of 1:8. For passaging, culture medium was removed and spheroids together with Matrigel dissolved in cold ADF. After transfer to a new 15 mL Falcon tube, spheroids were mechanically sheared by vigorous pipetting (8–10 times) with a fire-polished glass Pasteur pipette. Next, the sheared spheroids were centrifuged for 5 min at 4°C, 250×g and the resulting pellet incubated with TrypLE Express Enzyme (5 min; 37°C; Invitrogen). TrypLE was inactivated by addition of ADF+10% FCS and the sheared spheroids pelleted as above, followed by one wash in ADF and centrifugation as above. Supernatant was discarded, the pellet resuspended in cold Matrigel and re-seeded as described above.
For differentiation of spheroids into gastroids, cells were grown in expansion medium for 5 days. Differentiation was induced by culture in Wnt3A-free and Rspo-1-free expansion medium (differentiation medium) for a further 5 days. For differentiation by inhibition of Notch signalling, 1 µM DBZ (Calbiochem) was added to the expansion medium and cultures were kept for 5 days under these conditions before analysis. For long-term storage, spheroids were harvested in cold CryoSFM (1 mL per well; PromoCell), slowly frozen down at −80°C and transferred into liquid nitrogen. For recovery, spheroids were thawed rapidly, washed with ADF, pelleted and resuspended in Matrigel before seeding as described.
Culture of 2D gastric primary cells
Spheroids were prepared with the same protocol used for passaging, collected in two dimensional (2D) medium (ADF, 10% FCS, 2% B27, 1% N2, 10 mM nicotinamide, 50 ng/mL human EGF, 7,5 µM Y-27632 and 1 µM A83-01) and seeded in collagen-coated wells (type 1; 10 µg/cm2; Sigma). Cultures were kept at 37°C, 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator. For microscopy, cells were seeded on collagen-coated glass cover slips. Before processing, cells were washed twice with warm phosphate buffered saline (PBS, Gibco), fixed at 4°C with 3.7% paraformaldehyde overnight, washed three times with PBS and stored in PBS at 4°C until immunofluorescence labelling.
Results
Preparation of gastric spheroids
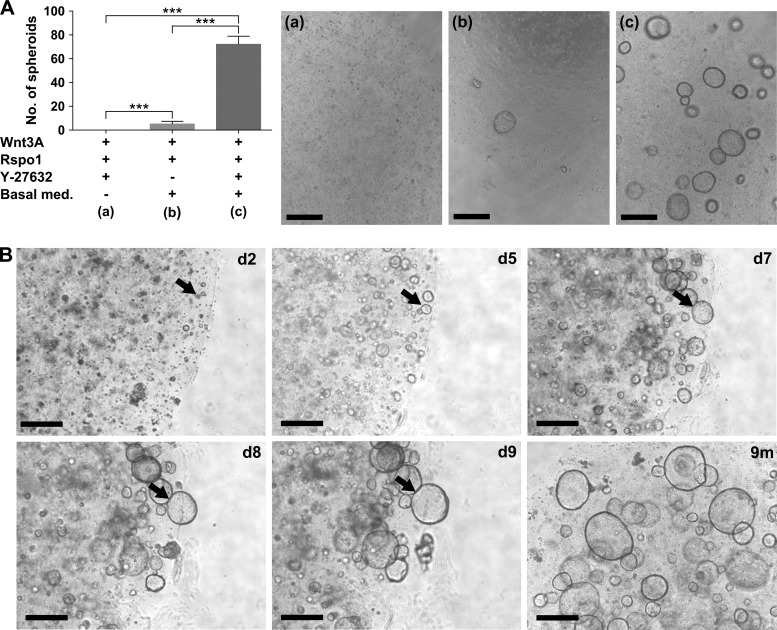
Units of gastric glands were isolated from healthy human stomach sections or biopsies and embedded in Matrigel supplemented with culture medium. The composition of the basic medium was following previously published protocols pioneered by the Clevers laboratory15–17 and contained EGF, noggin, FGF-10, nicotinamide, gastrin, A83-01 (an Alk4/5/7 inhibitor) and SB202190 (a p38 inhibitor). We observed the formation and outgrowth of gastric spheroids which was highly dependent on the presence of Wnt3A and R-spondin1. The spheroid formation efficiency was significantly increased by the addition of ρ-associated protein kinase inhibitor Y-27632 during the first 3 days of cultivation, which served to prevent anoikis (figure 1A). The spontaneously forming spheroids continued to grow to large 3D structures (see figure 1B and online supplementary movie 1), which needed to be passaged every 10–14 days and re-seeded in fresh Matrigel at a ratio of 1:8. This way, the gastric spheroids could be propagated and grown for more than 20 passages or >9 months without apparent loss of proliferative capacity (figure 1B, lower panel, right). These 3D cultures could be frozen and stored at −80°C. After thawing, 3D spheroids form again and continue to proliferate without any obvious morphological or proliferative changes (see online supplementary figure S1).
Figure 1.
Establishment of human gastric spheroid cultures. (A) The spheroid forming efficiency of human gastric glands is highly dependent on the addition of Wnt3A/R-spondin1 and Y-27632 to the basal medium. The number of spheroids per well was counted 14 days after seeding. Representative micrographs of spheroids grown in the three different culture conditions are shown in (a)–(c). Graph represents mean+SD of at least three biologically independent replicates; *** p<0.001, Student t test. (B) Representative examples of human gastric spheroids cultured from isolated human gastric glands for between 2 and 9 days (black arrows identify the same spheroid over the course of 8 days), as well as after 9 months (m). Scale bars: 500 µm.
Gastric spheroids resemble stomach tissue and exhibit stable features upon cultivation
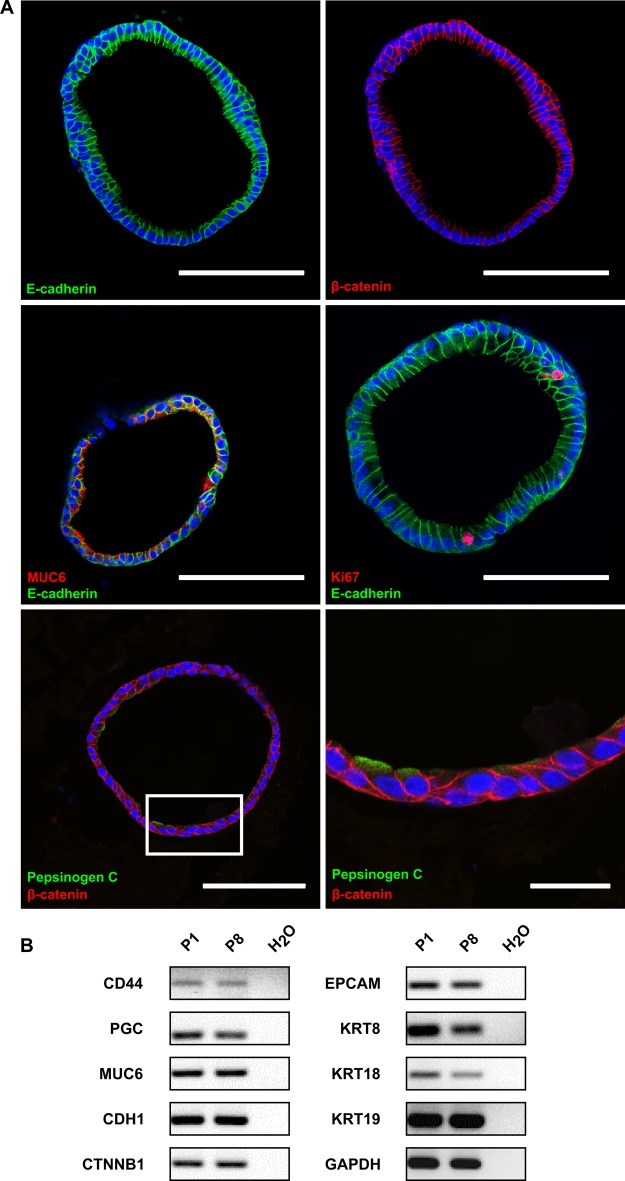
The spheroids appeared as hollow structures with a sealed lumen surrounded by a single layer of cylindrical epithelial cells, as visualised by staining with E-cadherin and β-catenin (figure 2A, upper panel). Evidently, the spheroid epithelial cells exhibited a high degree of polarisation and no atypical cell types were detected. Most cells were positive for the major gastric mucin MUC6, a key mucin of the gland mucous cells (figure 2A, middle panel, left). Furthermore, the MUC6 signal was only found on the apical side of the cells pointing towards the lumen and not on the basolateral side, confirming proper functional polarisation of the cells. Occasional staining with the proliferation marker Ki67 demonstrates the presence of active proliferation within the cultured spheroids (figure 2A, middle panel right). Moreover, the chief cell marker pepsinogen C (PGC) was robustly expressed (figure 2A, lower panel). Markers for parietal or endocrine cells, however, could not be detected by immunolabelling.
Figure 2.
Characterisation of human gastric spheroids. (A) Confocal micrographs of human gastric spheroids (cross sections), fluorescently labelled with antibodies against the epithelial marker E-cadherin (green), the polarisation marker β-catenin (red), the gland mucous cell marker MUC6 (red), the proliferation marker Ki67 (red) or the chief cell marker pepsinogen C (green); nuclei were counterstained with Draq5 (blue). Scale bars: 100 µm; and 25 µm for bottom right panel; for technical reasons smaller spheroids were chosen here compared with the organoids shown in figure 3D. (B) Expression analysis of gastric-specific and epithelial-specific genes from early (P1) and late (P8) passage spheroids, using semi-quantitative RT-PCR. Photomicrographs are presented in reversed colours. PGC, pepsinogen C; EPCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; GADPH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Correct polarisation of the cells was confirmed by labelling with the tight junction marker occludin (see online supplementary figure S2A), which was visible as distinct dots between cells at their luminal side. Addition of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labelled dextran to the culture medium revealed the functionality of these junctions, since no dextran entered the lumen of the 3D cultures even after several hours of incubation. The chelating agent ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA), however, led to a disruption of the functional tight junctions and this could be seen by the influx of labelled dextran into the lumen after EGTA addition (see online supplementary figure S2B). This reaction occurred quickly, leading to maximal disruption of tight junctions within 20 min (see online supplementary figure S2C).
Comparison of gastric spheroids between early and later passages revealed striking conservation of both morphology (figure 1B, lower panel right) and gene expression (figure 2B). In particular, no trans-differentiation to mesenchymal cell types (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) was observed, a frequent phenomenon encountered during cultivation of primary cells. The expression of general epithelial cell markers E-cadherin (CDH1), β-catenin (CTNNB1), epithelial cell adhesion molecule, KRT8, KRT18 and KRT19 remained stable during longer periods of cultivation. In particular, the gastric epithelial markers PGC and MUC6 were expressed in early and late passage cultures and the gastric stem cell marker CD44 was also robustly expressed over time suggesting the maintenance of stemness. Altogether, this demonstrates a strong and continual conservation of the authentic epithelial features during the propagation of human gastric spheroids in vitro.
Differentiation of gastric spheroids
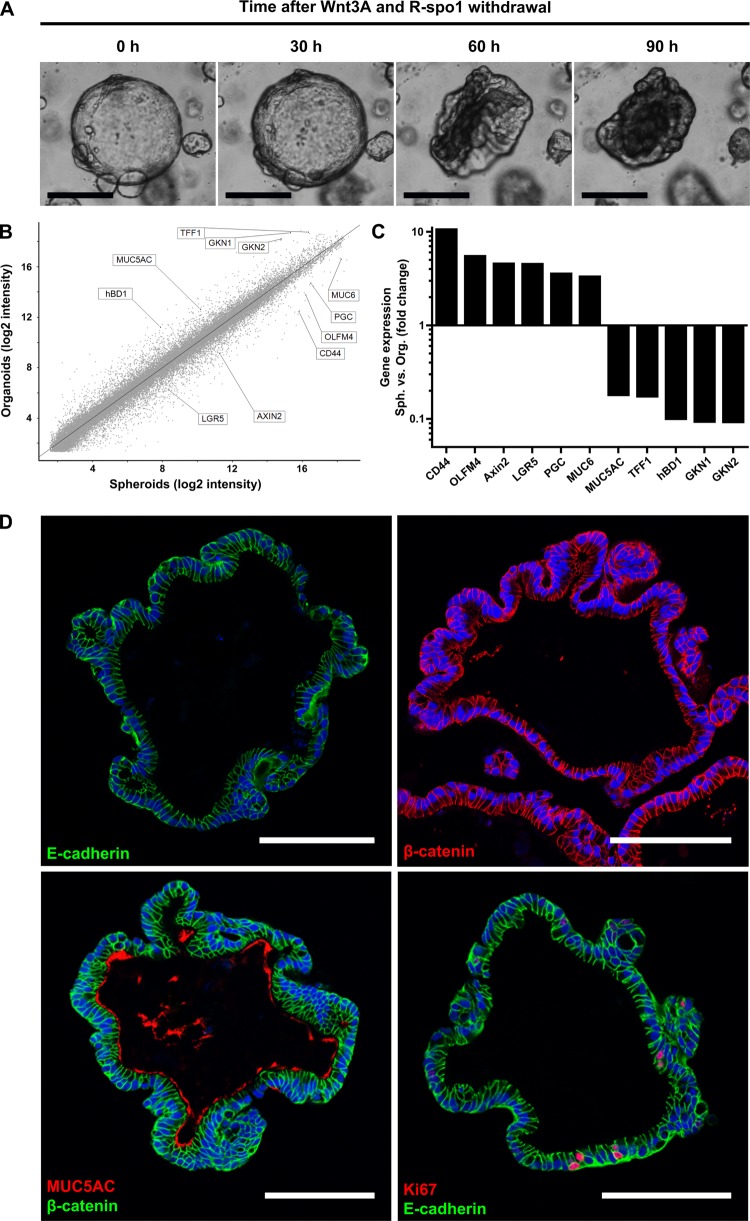
While human gastric spheroids constitute an undifferentiated and highly proliferative stage, it is possible to differentiate them into gastric organoids by withdrawing the mitogenic factors Wnt3A and R-spondin1 (figure 3A). The perfectly round spheroids change their morphology by folding to differentiated, more compact and seemingly smaller cauliflower-shaped organoids. This striking morphological change is accompanied by marked alterations of gene expression. Microarray analysis revealed the modulation of important marker genes (figure 3B, C). On one hand, expression of the stem cell markers CD44, OLFM4 and LGR5 decreases during differentiation of organoids. On the other hand, gastric differentiation markers such as TFF1 and gastrokines 1 and 2 (GKN1, 2) are upregulated. Interestingly, there is a switch from MUC6-producing gland mucous cells in spheroids to MUC5AC-producing pit mucous cells in organoids. Similarly, the production of human β-defensin 1 (hBD1), which is constitutively expressed in gastric glands,20 is turned on during conversion to organoids, while the expression of the chief cell marker PGC is strongly reduced.
Figure 3.
Human gastric spheroids can be differentiated into organoids. (A) Representative micrographs of different stages of a single spheroid during the differentiation process induced by withdrawal of Wnt3A and R-spondin1. (B) Global overview of differential gene expression upon withdrawal of Wnt3A and R-spondin1 for 5 days as determined by microarray analysis comparing undifferentiated corpus spheroids with differentiated corpus organoids. (C) Expression changes for a selection of gastric-specific and differentiation-specific genes highlighted in the global overview in (B) provided by microarray analysis. For genes with multiple probes, those with the largest difference were chosen. (D) Confocal micrographs of human corpus organoids (cross sections), fluorescently labelled with antibodies against the epithelial marker E-cadherin (green), the polarisation marker β-catenin (red), the pit mucous cell maker MUC5A (red) or the proliferation marker Ki67 (red); nuclei were counterstained with Draq5 (blue). Scale bars: 100 µm.
Confocal microscopy of human gastric organoids shows that—similar to spheroids—they consist of a single layer of cylindrical, highly polarised epithelial cells, as indicated by E-cadherin and β-catenin immunolabelling (figure 3D, upper panel). In contrast to the perfectly rounded spheroids, the organoids exhibit folded, gland-like structures typically found in healthy gastric mucosa. Consistent with the direction of their polarisation, organoids secrete MUC5AC into the lumen, constituting the apical side (figure 3D, lower panel left). Active proliferation within the cultured organoids is indicated by randomly distributed Ki67 positive cells, which are observed with approximately the same frequency as in spheroids (figure 3D, lower panel right). However, endocrine and parietal cells, typically present in the corpus mucosa, could not be unequivocally detected by immunolabelling.
Notch signalling is thought to play an important role in lineage specification in the stomach. Likewise, the addition of the Notch inhibitor DBZ to undifferentiated spheroid cultures for 5 days caused a strong decrease in the expression of stem cell markers, as well as an increase in gastrokine expression (see online supplementary figure S3A). However, the effect on differentiation in response to DBZ was not as strong as in response to the withdrawal of Wnt3a/R-spo1 as no change in morphology and mucous composition was observed.
Maintenance of region-specific molecular differences in spheroids from antrum and corpus
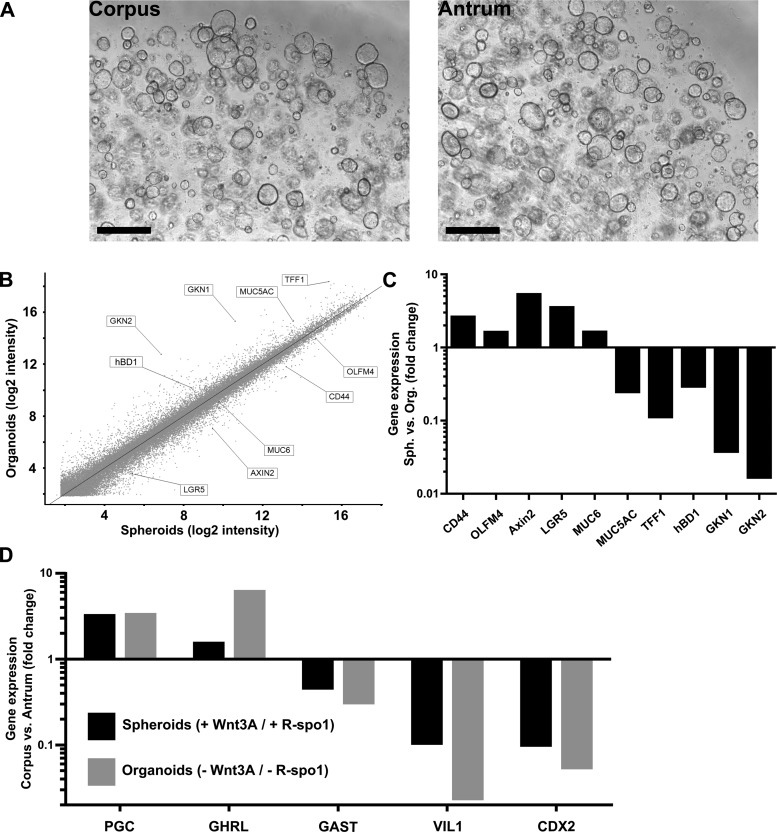
This cultivation protocol was equally successful for glands from various anatomical regions of the human stomach. Using the same medium, isolated glands from antrum behaved similarly to corpus glands by forming 3D spheroids, which could be passaged for long periods of time (figure 4A). Antrum cultures were morphologically identical to those from the corpus, and also showed a switch from undifferentiated, perfectly round spheroids to folded organoids after withdrawal of Wnt-3A and R-spondin1. Microarray analysis revealed that, during differentiation into organoids, the expression of marker genes was also modulated in the same way (figure 4B, C), reflected by a reduced expression of stem cell marker genes like OLFM4, CD44 and LGR5 and an elevated expression of differentiation markers like TFF1, GKN1 and GKN2. Similarly, there was a switch from MUC6 towards MUC5AC producing cells, as well as expression of hBD1. Treatment with the Notch inhibitor DBZ caused similar effects to those seen in corpus spheroids, that is, a strong decrease in the expression of stem cell markers and a concomitant increase of gastrokine production (see online supplementary figure S3B).
Figure 4.
Region-specific molecular differences are maintained in three dimensional cultures from antrum and corpus. (A) Representative micrographs showing spheroid cultures growing with the same efficiency from isolated gastric glands from the corpus and antrum region of the human stomach. Scale bars: 500 µm. (B) Global overview of differential gene expression upon withdrawal of Wnt3A and R-spondin1 for 5 days as determined by microarray analysis comparing undifferentiated antrum spheroids with differentiated antrum organoids. (C) Expression changes for a selection of gastric-specific and differentiation-specific genes as determined by microarray analysis highlighted in the global overview in (B) provided by microarray analysis. (D) Region-specific differences in expression of the region-specific markers. Upregulated pepsinogen C (PGC) and ghrelin (GHRL) expression is elevated in corpus-derived cultures, while expression of gastrin (GAST), villin1 (VIL1) and CDX2 is elevated in antrum-derived cultures.
While the cultures from different anatomical regions of the human stomach exhibited strong overall similarity of morphology and highly consistent responses to differentiation induced by the culture medium they still retained the distinct molecular characteristics of their site of origin. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) showed that the expression profiles of region-specific cultures correlated with the expression profiles of the corresponding regions of the stomach (see online supplementary figure S4A, B). This interesting result was based on previously published microarray data from healthy human antrum and corpus biopsies21 which we compared with the regulated genes identified by microarray analysis after Wnt3A and R-spo1 withdrawal. The GSEA analysis for the antrum cultures (see online supplementary figure S4B) showed a highly significant enrichment of genes upregulated in antrum tissue among those genes upregulated in antrum organoids. The correlation of regulated genes between corpus organoids and tissue showed somewhat lower consistency, including several genes for which direction of expression changes did not agree (see online supplementary figure S4A). Interestingly, the discordant genes had functions in the production of gastric acid production (eg, H+/K+-ATPase), which we found absent in the corpus cultures.
Gene-specific analysis of the differences between antrum and corpus cultures revealed consistent differences in specific marker genes (figure 4D). On one hand, antrum samples could be clearly identified by their elevated expression of the G cell marker gastrin, villin1 and CDX2. On the other hand, the major corpus markers were missing because no acid-producing parietal cells could be detected in these cultures. However, elevated expression of PGC and ghrelin clearly identified their origin from the corpus region.
Transfer from 3D to 2D planar culture
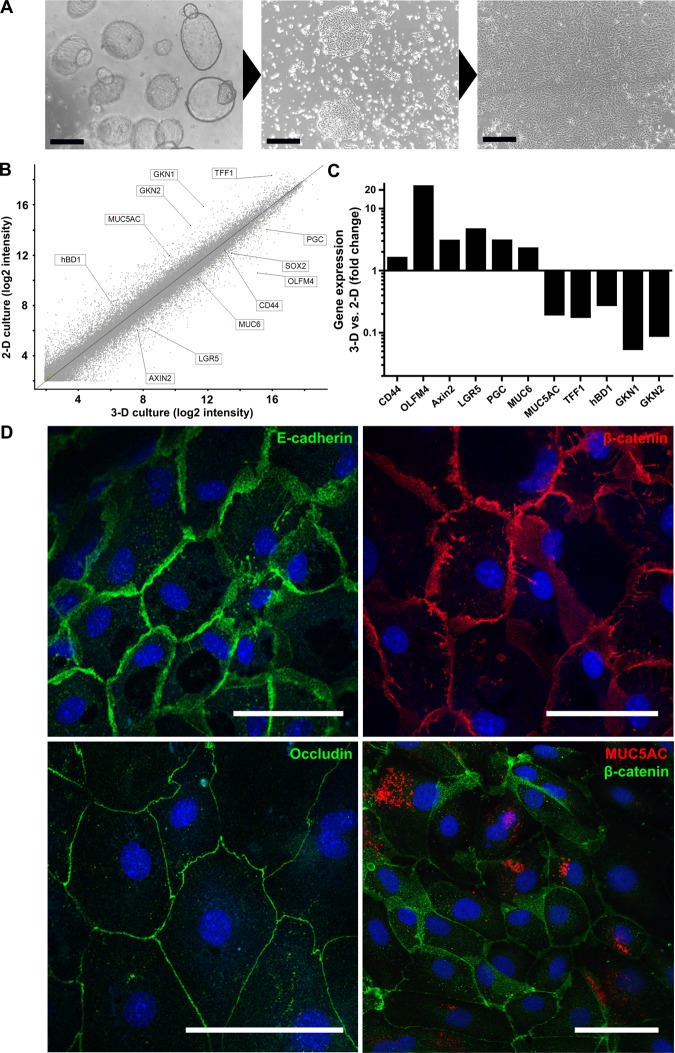
Next, we transferred the actively replicating 3D cultures to standard culture dishes in order to establish convenient conditions for experimental manipulation. For this purpose, spheroids were sheared and seeded into collagen-coated wells. The 2D culture medium contained nicotinamide, human EGF, Y-27632 and A83-01 to support epithelial cell survival and proliferation, but paracrine factors stimulating 3D formation were omitted. After seeding, cells rapidly attached and formed epithelial islands after 1 day. These islands further grew out to form confluent monolayers within about 3 days (figure 5A).
Figure 5.
Human gastric spheroids represent an unlimited source of planar two dimensional (2D) gastric primary cells. (A) Representative photomicrographs of three dimensional (3D) human gastric spheroids from corpus cultures during conversion to a 2D monolayer of adherent primary cells. Scale bars: 500 µm (B) Global overview of differential gene expression as determined by microarray analysis comparing 3D human gastric spheroids with 2D adherent gastric primary cells. (C) Expression changes for a selection of gastric-specific and differentiation-specific genes as determined by microarray analysis highlighted in the global overview in (B) provided by microarray analysis. (D) Confocal micrographs of adherent human gastric primary cell cross-sections fluorescently labelled with antibodies against the epithelial marker E-cadherin (green), the polarisation marker β-catenin (red), the tight junction marker occludin (red) and the pit mucous cell maker MUC5A (red); nuclei were counterstained with Draq5 (blue). Scale bars: 50 µm.
The gastric primary cells cultured under 2D conditions exhibited gene expression patterns reminiscent of differentiated gastric organoids rather than of non-differentiated spheroids (figure 5B, C; see also figure 3B, C). Stem cell markers (CD44, OLFM4 and LGR5) were downregulated, while gastric differentiation markers (TFF1, GKN1 and GKN2) were upregulated. Additionally, there was a switch from MUC6 to MUC5AC producing cells, and the production of hBD1 was turned on. These findings are consistent with confocal imaging (figure 5D). Moreover, the cells cultured in 2D exhibited epithelial characteristics of fully functional epithelium as cells appeared to be well polarised, as indicated by fluorescent immunolabelling of the tight junction marker occludin (figure 5D, lower panel left), and also of E-cadherin and β-catenin (figure 5D, upper panel). MUC5AC production could be observed in ∼50% of cells (figure 5D, lower panel right). Thus, we established a novel planar gastric epithelial cell model comprising important features of the gastric epithelial surface.
Use of planar gastric cell cultures as H. pylori infection model
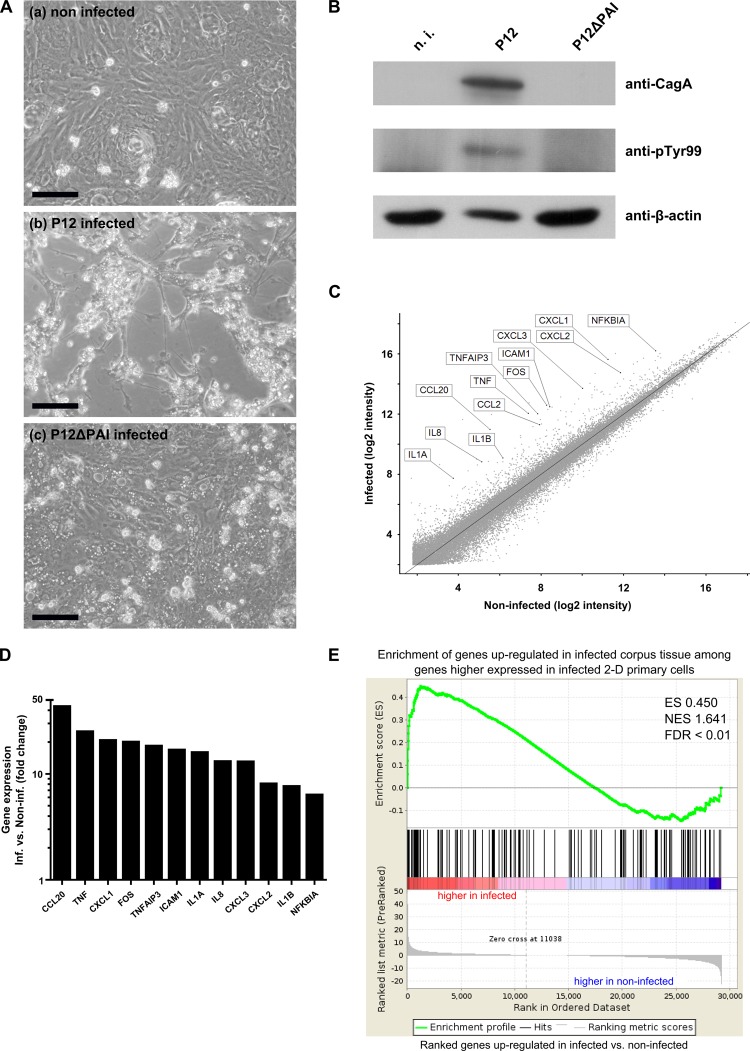
The planar monolayers of gastric primary epithelial cells were then used to investigate infection with the gastric pathogen H. pylori. Cells were infected with the Cag pathogenicity island (CagPAI) positive strain P12 (MOI 100) and monitored for 22 h. Interestingly, infected primary cells showed major hallmarks of a successful infection: the characteristic ‘hummingbird’ phenotype (figure 6A) concomitant with host-cell elongation and cell dispersal.22–24 This morphological feature is dependent on translocation of the bacterial virulence factor CagA by the T4SS into the host cells, where it is phosphorylated by Src kinases to interact with cellular scaffolding and signalling factors.25–27 Host cell translocation and phosphorylation of CagA could also be shown directly by immunoblotting (figure 6B). Accordingly, phosphorylated CagA was detectable after P12 wild type infection but not in cells infected with a H. pylori mutant lacking CagPAI (P12ΔPAI) which neither produces nor secretes CagA. However, infection with the CagPAI deletion mutant revealed a marked vacuolisation of target cells (figure 6A lower panel), which is due to another main virulence factor, the vacuolating cytotoxin A.28 29 Finally, the global response to H. pylori was investigated by microarray analysis. A strong inflammatory response could be observed (figure 6C, D). Most of the strongly upregulated genes were involved in the nuclear factor (NF)-κB signalling pathway, a prominent and known feature of H. pylori infections.30 31 In particular, the chemokine interleukin (IL)-8, a well-known target of NF-κB, is strongly upregulated and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α signalling is induced, leading to the production of chemokines CCL20, CXCL1 and CXCL8. Moreover, GSEA of upregulated genes revealed a significant enrichment of several gene sets involved in the inflammatory response (see online supplementary figure S5). Genes upregulated after infection were strongly correlated with the gene sets ‘upregulated TNF targets’,32 ‘upregulated NF-κB targets’33 and ‘inflammatory response to LPS’.34 A comparison of the upregulated genes in infected primary cells with upregulated genes in infected corpus biopsies from previously published microarrays21 also shows a striking enrichment (figure 6E).
Figure 6.
Planar human gastric cell cultures can be successfully infected with Helicobacter pylori. (A) Representative micrographs of adherent gastric primary cells (a) non-infected, (b) infected with the human-adapted H. pylori strain P12 (MOI 100) or (c) infected with the P12 mutant P12ΔPAI, which is missing the pathogenicity island (MOI 100) for 22 h. Scale bars: 100 µm. (B) Western blotting analysis of non-infected and infected adherent gastric primary cells 22 h after infection, using antibodies against the virulence factor CagA and phospho-tyrosine 99, which detects phosphorylated CagA. β-actin was used as loading control. (C) Global overview of differential gene expression as determined by microarray analysis comparing H. pylori-infected two dimensional primary cells (MOI 100, 3 h infection) generated from corpus cultures with the non-infected control. (D) Expression changes for a selection of strongly upregulated genes as determined by microarray analysis highlighted in the global overview in (C) provided by microarray analysis (E) Gene set enrichment analysis of upregulated genes identified by microarray analysis after 3 h infection with H. pylori (MOI 100) correlated with publically available data from H. pylori-upregulated genes in infected corpus tissue sample. The analysis reveals a significant enrichment of genes upregulated in infected corpus tissue among those genes upregulated in infected 2D primary cells compared with non-infected primary cells. ES, enrichment score; NES, normalised enrichment score; FDR, false discovery rate.
Taken together, infected primary cells show all hallmarks of a successful infection and similar response as infected tissue. Therefore, this novel 2D model lays the groundwork for future infection studies of human gastric primary cells.
Lentiviral genetic manipulation of host cell background
Future studies addressing the function of host cell determinants as well as other research applications will depend on the ability to genetically manipulate gene expression in normal human cell cultures. We have been testing several different procedures previously suggested to transform primary cells. Of these, the lentiviral infection of sheared organoids proved most successful for introducing foreign DNA into spheroids. As proof of principle, sheared human gastric spheroids were infected with a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-transducing lentivirus. After infection, spheroids formed again and started to proliferate. GFP expression was detectable 24 h after infection and increased over time (see online supplementary figure S6). Furthermore, successive passaging of the manipulated spheroids turned out to be well feasible.
Discussion
Here, we present a robust experimental model for the long-term to near-indefinite cultivation of human gastric primary epithelial cells in 3D structures. By extrapolating on recently published procedures for the cultivation of murine intestine and pylorus,14 15 as well as human colon,16 the new protocol applied for the expansion of human gastric cells is an invaluable addition along these lines. The key advances of our protocol are the quasi-indefinite growth and versatile culture options for normal human gastric cells, which bear a marked advantage over the current usage of mutant cancer cell lines. This new approach now allows for extensive experimentation with normal human cells, bearing ‘virgin’, that is, non-mutated genomes, likely capable of expressing a full spectrum of authentic phenotypes, including cellular pathways and critical signalling routes involved in both gastric infections and cancer initiation. Thus, we expect at least several research areas—infection biology, mucosal immunology, as well as cancer research—to benefit from this work.
Past attempts to grow human gastric primary cells in long-term culture have been essentially unsuccessful. Terano et al35 were able to culture human primary gastric epithelial cells in 2D-monolayers, however, cell growth was limited to 2 weeks and cultures could not be passaged. Similarly, gastric spheroid-like cultures, although highly polarised, showed limited survival.18 This limitation can be partially attributed to the fact that normal cells lose their proliferative capacity after a number of cell divisions to undergo cellular senescence,36 a phenomenon also referred to as the ‘Hayflick limit’.37 Nevertheless, several recent studies also report on the long-term cultivation of gastric primary cells and their use as H. pylori infection models.38–40 While Wroblewski and colleagues generated gastric organoids from murine gastric glands, McCracken and colleagues achieved this from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Moreover, Bartfeld and colleagues grew organoids from isolated human gastric glands similar to the approach taken here.
Infection experiments in these studies were carried out by injection of H. pylori into the lumen of the 3D structures. In contrast, we present here a 2D primary cell infection model, which is novel in that it makes use of 3D cultures as unlimited cell source. In our hands, the 2D infection model is easier to handle as compared with the labour-intensive injection method and provides reliable infection conditions. This model conclusively recapitulates key hallmarks of H. pylori-induced pathogenesis (‘hummingbird’-phenotype, cellular vacuolisation, and CagA phosphorylation), which is less evident for the reported 3D infection models. Our study also demonstrates the resolution of tissue site-specific gene expression patterns (eg, antrum vs corpus) and the maintenance of these patterns during organoid cultivation in vitro.
The generated gene expression profiles are highly suggestive for the presence of adult gastric stem cell niches in our cultures which are considered responsible for the long-term expansion capacity of the cells. We have refrained here from an explicit definition of a stem cell in our gastric cultures, mainly because a major attribute of adult stem cells is their high plasticity, giving rise to varying expression patterns, yet maintaining stemness.41 Seminal work has recently led to the identification of Lgr5+ cells as key drivers of the intestinal crypt as well as other tissues.14 15 42–44 However, additional markers, including Sox2 and CD44, have been identified as labels of GI stem cells.45 46 The antrum represents the distal part of the human stomach and is in close proximity to the duodenum. Due to this proximity, which is also reflected ontogenetically, one might expect considerable similarity between the gastric antrum and the Lgr5-driven intestine. Conversely, the antral and corporal stem cell compartments are likely to differ. Consistent with this assumption, a set of differentiated Troy+ chief cells have recently been suggested as reserve stem cells of the corpus in the mouse stomach.17 Surprisingly though, we could apply identical culture conditions to both antrum and corpus with the same success. This indicates that these gastric cells respond with similar efficiency yet maintain distinct expression patterns. Therefore, the future definition of stem cells may more usefully be geared towards global features, such as genome methylation patterns, than to single markers.
Adult tissue stem cells can be defined on the basis of two key properties: ability to self-renew and potential for multilineage differentiation.47 In nature, these two features are especially important for maintaining tissue homeostasis and injury repair. Adult stem cells are also thought to depend on the surroundings of the stem cell niche in order to maintain their properties.48 In the culture system presented here, Matrigel was used to provide a suitable stem cell niche for the complete gastric glands embedded. This gave rise to the formation of 3D structures, recapitulating the in vivo situation in that both spheroids and organoids shed cells into the lumen, indicative of rapid cellular turnover and proliferation. Together with the observed longevity, this strongly supports the notion of adult stem cells being the driving force of proliferation in our culture system.
The inner surface of the human stomach is lined by the gastric mucosa which is organised as multiple gastric units forming small pits called faveolae gastricae. Three to seven individual flask-shaped gastric glands feed into one pit. Depending on the anatomical region of the stomach, these gastric units differ in structure and composition.49 The most abundant cell types are mucous-producing gland mucous and pit mucous cells alongside minor populations of acid-secreting parietal cells, chief cells and enteroendocrine cells. The 3D cultures in many ways resemble the stomach morphology. In gastric spheroids, MUC6-producing gland mucous cells are predominant, reminiscent of the gastric glands from which they originate. In contrast, the differentiated organoids exhibit a strong prevalence of MUC5AC-producing pit mucous cells, the most abundant cell type in normal stomach. Interestingly though, epithelial cultures did not detectably express markers of parietal cells in either spheroids or organoids. Markers of the enteroendocrine cells could not be detected with immunolabelling either, however, microarray analysis at least revealed the expression of gastrin and ghrelin. The 3D culture conditions applied, therefore, seem to favour mucous-producing cells.
An important observation that our extensive microarray analysis brought to light was the apparent stability of gastric region-specific features in the derived spheroids and organoids. While the corpus and antrum spheroids maintained the expression of a majority of markers of their authentic gastric regions, they responded similarly to extrinsic changes influencing their differentiation status. Thus, the 3D spheroid model conveys region-specific features of the gastric mucosa. However, there seemed to be a major exception to this rule for the corpus region, where we failed to identify the expected parietal cells in the derived spheroids. Whether this reflects the need for an additional trigger to generate these cells or perhaps the existence of an as yet unknown, distinct stem cell compartment within the corpus mucosa remains to be seen in future studies. With respect to future applications, it is useful that spheroid cultures can serve as a continuous source of 2D epithelial cell monolayer cultures. The 2D cultures turn out to be suitable for experimental infection with H. pylori in that infected cells present the typical H. pylori-specific signs, including the well-known hummingbird phenotype. GSEA revealed a strong correlation between the in vitro and the in vivo setting, emphasising the relevance of this novel infection model.21 In particular, we observed a strong activation of TNF-α and NF-κB signalling in infected 2D gastric primary cells, a feature frequently reported for infected human and murine cell lines.30 50 51 Indeed, the vast majority of infection studies are currently performed with transformed cancer cells lines. However, they represent the end-point of Correa's cascade and thus exhibit cancer-related mutations and degeneration of signalling routes. The new system instead opens up avenues of approach to investigate the effects exerted by H. pylori on healthy, untransformed cells. It will thus help to shed light on the early events caused by H. pylori that lead to the initiation of Correa's cascade and its most fatal outcome, gastric adenocarcinoma.
Microarray expression profiling of non-differentiated spheroid cultures versus differentiated organoids revealed strong similarities to the transition from non-differentiated 3D cultures to 2D cultures. This suggests that the 2D cultures presented here are more closely related to differentiated cells found in the luminal regions of gastric glands. Further such studies might help to fully characterise the particularities of the 2D cultures and guide alternative culture conditions that mimic distinct areas of the gastric mucosal surface. It is also interesting that we observed differential expression of certain antimicrobial peptides in response to differentiation. Likewise, hBD1, a constitutively expressed defence molecule, was upregulated in highly differentiated organoids. Similarly, cytokine receptors for, for example, IL-1β and IL-22, appear to be present and differentially expressed. These observations promise that the organoid model will be useful for future in-depth analyses of the innate epithelial immune response as well as the defence mechanisms against the major gastric pathogen, H. pylori.
Apart from its use as an infection model, the established primary cell culture system could serve a variety of other purposes. Similar to previously published work,52 53 we managed to manipulate 3D primary cell cultures with lentiviruses and to expand these manipulated cells as apparently homogenous cultures. A tantalising application could be the use for various screening purposes including microbiological, toxicological or pharmacological studies that could constitute major advancements over current cancer cell line models. Finally, we found that even small human biopsy specimens are sufficient to generate these cultures (data not shown), which finally could be used for transplantation purposes. Therefore, in conclusion, the cell culture system presented here holds great promise for future investigations, especially as a novel standard for investigating H. pylori infection in vitro.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank J. Angermann, S. Banhart, S. Jackisch, O. Thieck and I. Wagner for excellent technical support and M. Kerr for useful advice. We also thank M. Koch and M. Kessler for critical reviewing and R. Zietlow for editing the manuscript.
Footnotes
Contributors: PS and TFM designed experiments which were performed by PS and BT with initial support from SB; HJM and HB analysed the microarray data, SCS, MG and JO selected the patients and provided the human gastric tissue samples, PS analysed the data, PS and TFM wrote the manuscript, TFM conceived and supervised the project.
Funding: This study was supported in part through DFG grant SFB633-B8 to TFM and through EMBO short-term fellowship to SB. PS was a fellow of the International Max Planck Research School (IMPRS-IDI). The funders did not play any role in the study design or in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data.
Competing interests: None.
Ethics approval: Ethics committee of the Charité University Medicine, Berlin (EA1/058/11 and EA1/129/12).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: Microarray data have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information and can be assessed with the GEO accession number GSE58473.
References
- 1.Correa P. Bacterial infections as a cause of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2003;95:E3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Plummer M, Franceschi S, Vignat J, et al. . Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to pylori. Int J Cancer 2015;136:487–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Parkin DM. The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer 2006;118:3030–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.IARC. Schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Lyon, 7–14 June 1994. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 1994;61:1–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Malfertheiner P, Chan FK, McColl KE. Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet 2009;374:1449–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Correa P, Piazuelo MB. The gastric precancerous cascade. J Dig Dis 2012;13:2–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Blaser MJ, Perez-Perez GI, Kleanthous H, et al. . Infection with Helicobacter pylori strains possessing cagA is associated with an increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Cancer Res 1995;55:2111–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Eck M, Schmausser B, Haas R, et al. . MALT-type lymphoma of the stomach is associated with Helicobacter pylori strains expressing the CagA protein. Gastroenterology 1997;112:1482–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hatakeyama M. Helicobacter pylori CagA and gastric cancer: a paradigm for hit-and-run carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2014;15:306–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ohnishi N, Yuasa H, Tanaka S, et al. . Transgenic expression of Helicobacter pylori CagA induces gastrointestinal and hematopoietic neoplasms in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008;105:1003–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Toller IM, Hitzler I, Sayi A, et al. . Prostaglandin E2 prevents Helicobacter-induced gastric preneoplasia and facilitates persistent infection in a mouse model. Gastroenterology 2010;138:1455–67, 67.e1–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Noto JM, Gaddy JA, Lee JY, et al. . Iron deficiency accelerates Helicobacter pylori-induced carcinogenesis in rodents and humans. J Clin Invest 2013;123:479–92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ootani A, Li X, Sangiorgi E, et al. . Sustained in vitro intestinal epithelial culture within a Wnt-dependent stem cell niche. Nat Med 2009;15:701–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sato T, Vries RG, Snippert HJ, et al. . Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009;459:262–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Barker N, Huch M, Kujala P, et al. . Lgr5(+ve) stem cells drive self-renewal in the stomach and build long-lived gastric units in vitro. Cell Stem Cell 2010;6:25–36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sato T, Stange DE, Ferrante M, et al. . Long-term expansion of epithelial organoids from human colon, adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and Barrett's epithelium. Gastroenterology 2011;141:1762–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stange DE, Koo BK, Huch M, et al. . Differentiated Troy+ chief cells act as reserve stem cells to generate all lineages of the stomach epithelium. Cell 2013;155:357–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Boxberger HJ, Sessler MJ, Grausam MC, et al. . Isolation and culturing of highly polarized primary epithelial cells from normal human stomach (antrum) as spheroid-like vesicles. Methods Cell Sci 1997;19:169–78. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, et al. . Wnt proteins are lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature 2003;423:448–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kaiser V, Diamond G. Expression of mammalian defensin genes. J Leukoc Biol 2000;68:779–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nookaew I, Thorell K, Worah K, et al. . Transcriptome signatures in Helicobacter pylori-infected mucosa identifies acidic mammalian chitinase loss as a corpus atrophy marker. BMC Med Genomics 2013;6:41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Amieva MR, Vogelmann R, Covacci A, et al. . Disruption of the epithelial apical-junctional complex by Helicobacter pylori CagA. Science 2003;300:1430–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Selbach M, Moese S, Hurwitz R, et al. . The Helicobacter pylori CagA protein induces cortactin dephosphorylation and actin rearrangement by c-Src inactivation. EMBO J 2003;22:515–28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Suzuki M, Mimuro H, Suzuki T, et al. . Interaction of CagA with Crk plays an important role in Helicobacter pylori-induced loss of gastric epithelial cell adhesion. J Exp Med 2005;202:1235–47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Higashi H, Tsutsumi R, Muto S, et al. . SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase as an intracellular target of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Science 2002;295:683–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Selbach M, Moese S, Hauck CR, et al. . Src is the kinase of the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 2002;277:6775–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Stein M, Bagnoli F, Halenbeck R, et al. . c-Src/Lyn kinases activate Helicobacter pylori CagA through tyrosine phosphorylation of the EPIYA motifs. Mol Microbiol 2002;43:971–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cover TL, Blaser MJ. Purification and characterization of the vacuolating toxin from Helicobacter pylori. J Biol Chem 1992;267:10570–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Montecucco C, de Bernard M. Immunosuppressive and proinflammatory activities of the VacA toxin of Helicobacter pylori. J Exp Med 2003;198:1767–71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bartfeld S, Hess S, Bauer B, et al. . High-throughput and single-cell imaging of NF-kappaB oscillations using monoclonal cell lines. BMC Cell Biol 2010;11:21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ferrero RL. Innate immune recognition of the extracellular mucosal pathogen, Helicobacter pylori. Mol Immunol 2005;42:879–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Phong MS, Van Horn RD, Li S, et al. . p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase promotes cell survival in response to DNA damage but is not required for the G(2) DNA damage checkpoint in human cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 2010;30:3816–26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hinata K, Gervin AM, Jennifer Zhang Y, et al. . Divergent gene regulation and growth effects by NF-kappa B in epithelial and mesenchymal cells of human skin. Oncogene 2003;22:1955–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, et al. . TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med 2007;13:1324–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Terano A, Mach T, Stachura J, et al. . A monolayer culture of human gastric epithelial cells. Dig Dis Sci 1983;28:595–603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Campisi J, d'Adda di Fagagna F. Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007;8:729–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hayflick L, Moorhead PS. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res 1961;25:585–621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bartfeld S, Bayram T, van de Wetering M, et al. . In vitro expansion of human gastric epithelial stem cells and their responses to bacterial infection. Gastroenterology Published Online First: 9 Oct 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.McCracken KW, Cata EM, Crawford CM, et al. . Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids. Nature Published Online first: 12 Feb 2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wroblewski LE, Piazuelo MB, Chaturvedi R, et al. . Helicobacter pylori targets cancer-associated apical-junctional constituents in gastroids and gastric epithelial cells. Gut 2015;64:720–30.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lakshmipathy U, Verfaillie C. Stem cell plasticity. Blood Rev 2005;19:29–38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Barker N, Rookmaaker MB, Kujala P, et al. . Lgr5(+ve) stem/progenitor cells contribute to nephron formation during kidney development. Cell Rep 2012;2:540–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jaks V, Barker N, Kasper M, et al. . Lgr5 marks cycling, yet long-lived, hair follicle stem cells. Nat Genet 2008;40:1291–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Koo BK, Clevers H. Stem cells marked by the R-spondin receptor Lgr5. Gastroenterology 2014;147:289–302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Arnold K, Sarkar A, Yram MA, et al. . Sox2(+) adult stem and progenitor cells are important for tissue regeneration and survival of mice. Cell Stem Cell 2011;9:317–29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Khurana SS, Riehl TE, Moore BD, et al. . The hyaluronic acid receptor CD44 coordinates normal and metaplastic gastric epithelial progenitor cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 2013;288:16085–97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wagers AJ, Weissman IL. Plasticity of adult stem cells. Cell 2004;116:639–48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xie T, Li L. Stem cells and their niche: an inseparable relationship. Development 2007;134:2001–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hoffmann W. Regeneration of the gastric mucosa and its glands from stem cells. Curr Med Chem 2008;15:3133–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bauer B, Moese S, Bartfeld S, et al. . Analysis of cell type-specific responses mediated by the type IV secretion system of Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun 2005;73:4643–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Backert S, Naumann M. What a disorder: proinflammatory signaling pathways induced by Helicobacter pylori. Trends Microbiol 2010;18:479–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Koo BK, Stange DE, Sato T, et al. . Controlled gene expression in primary Lgr5 organoid cultures. Nat Methods 2012;9:81–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Li X, Nadauld L, Ootani A, et al. . Oncogenic transformation of diverse gastrointestinal tissues in primary organoid culture. Nat Med 2014;20:769–77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.