Abstract
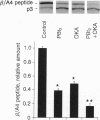
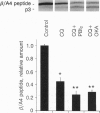
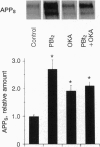
The major component of amyloid plaque cores and cerebrovascular amyloid deposits found in Alzheimer disease is the beta/A4 peptide, which is derived from the Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor (APP). Recent evidence suggests that abnormalities in beta/A4 peptide production or beta/A4 peptide aggregation may underlie cerebral amyloidosis. In the present study, treatment of cells with phorbol dibutyrate, which activates protein kinase C, and/or okadaic acid, which inhibits protein phosphatases 1 and 2A, reduced beta/A4 peptide production by 50-80%. These effects were observed with APP695 and APP751 expressed in stably transfected CHO cells, as well as with endogenous APP in human glioma (Hs 683) cells. Phorbol dibutyrate also decreased beta/A4 peptide production in cells expressing various mutant forms of APP associated with familial Alzheimer disease, one of which was reported to manifest greatly increased beta/A4 peptide production in cultured cells. Mastoparan and mastoparan X, compounds which can activate phospholipase C and hence protein kinase C, also decreased beta/A4 peptide production in CHO cells stably transfected with APP695. A model is presented in which decreases in beta/A4 peptide production can be achieved by accelerating the metabolism of APP through a nonamyloidgenic secretory pathway.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buxbaum J. D., Gandy S. E., Cicchetti P., Ehrlich M. E., Czernik A. J., Fracasso R. P., Ramabhadran T. V., Unterbeck A. J., Greengard P. Processing of Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein: modulation by agents that regulate protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):6003–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum J. D., Oishi M., Chen H. I., Pinkas-Kramarski R., Jaffe E. A., Gandy S. E., Greengard P. Cholinergic agonists and interleukin 1 regulate processing and secretion of the Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10075–10078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai X. D., Golde T. E., Younkin S. G. Release of excess amyloid beta protein from a mutant amyloid beta protein precursor. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):514–516. doi: 10.1126/science.8424174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso G. L., Gandy S. E., Buxbaum J. D., Greengard P. Chloroquine inhibits intracellular degradation but not secretion of Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2252–2256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso G. L., Gandy S. E., Buxbaum J. D., Ramabhadran T. V., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation regulates secretion of Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3055–3059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartier-Harlin M. C., Crawford F., Houlden H., Warren A., Hughes D., Fidani L., Goate A., Rossor M., Roques P., Hardy J. Early-onset Alzheimer's disease caused by mutations at codon 717 of the beta-amyloid precursor protein gene. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):844–846. doi: 10.1038/353844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron M., Oltersdorf T., Haass C., McConlogue L., Hung A. Y., Seubert P., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Lieberburg I., Selkoe D. J. Mutation of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in familial Alzheimer's disease increases beta-protein production. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):672–674. doi: 10.1038/360672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Keim P. S., Beattie E. C., Blacher R. W., Culwell A. R., Oltersdorf T., McClure D., Ward P. J. Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.2111583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estus S., Golde T. E., Kunishita T., Blades D., Lowery D., Eisen M., Usiak M., Qu X. M., Tabira T., Greenberg B. D. Potentially amyloidogenic, carboxyl-terminal derivatives of the amyloid protein precursor. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):726–728. doi: 10.1126/science.1738846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiso J., Wisniewski T., Vidal R., Rostagno A., Frangione B. Epitope map of two polyclonal antibodies that recognize amyloid lesions in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 1;282(Pt 2):517–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2820517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde T. E., Estus S., Younkin L. H., Selkoe D. J., Younkin S. G. Processing of the amyloid protein precursor to potentially amyloidogenic derivatives. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):728–730. doi: 10.1126/science.1738847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Hung A. Y., Schlossmacher M. G., Teplow D. B., Selkoe D. J. beta-Amyloid peptide and a 3-kDa fragment are derived by distinct cellular mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3021–3024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Koo E. H., Mellon A., Hung A. Y., Selkoe D. J. Targeting of cell-surface beta-amyloid precursor protein to lysosomes: alternative processing into amyloid-bearing fragments. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):500–503. doi: 10.1038/357500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Schlossmacher M. G., Hung A. Y., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Mellon A., Ostaszewski B. L., Lieberburg I., Koo E. H., Schenk D., Teplow D. B. Amyloid beta-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):322–325. doi: 10.1038/359322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Carman M. D., Fernandez-Madrid I. J., Power M. D., Lieberburg I., van Duinen S. G., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Mutation of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid gene in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage, Dutch type. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1124–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.2111584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullan M., Crawford F., Axelman K., Houlden H., Lilius L., Winblad B., Lannfelt L. A pathogenic mutation for probable Alzheimer's disease in the APP gene at the N-terminus of beta-amyloid. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):345–347. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrell J., Farlow M., Ghetti B., Benson M. D. A mutation in the amyloid precursor protein associated with hereditary Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):97–99. doi: 10.1126/science.1925564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse S., Igarashi S., Kobayashi H., Aoki K., Inuzuka T., Kaneko K., Shimizu T., Iihara K., Kojima T., Miyatake T. Mis-sense mutation Val----Ile in exon 17 of amyloid precursor protein gene in Japanese familial Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1991 Apr 20;337(8747):978–979. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch R. M., Slack B. E., Wurtman R. J., Growdon J. H. Release of Alzheimer amyloid precursor derivatives stimulated by activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):304–307. doi: 10.1126/science.1411529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Jin L. W., Saitoh T., Cole G. The regulation of amyloid beta protein precursor secretion and its modulatory role in cell adhesion. Neuron. 1989 Dec;3(6):689–694. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Oltersdorf T., Lee M. G., Barbour R., Blomquist C., Davis D. L., Bryant K., Fritz L. C., Galasko D., Thal L. J. Secretion of beta-amyloid precursor protein cleaved at the amino terminus of the beta-amyloid peptide. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):260–263. doi: 10.1038/361260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Esch F., Lee M., Dovey H., Davis D., Sinha S., Schlossmacher M., Whaley J., Swindlehurst C. Isolation and quantification of soluble Alzheimer's beta-peptide from biological fluids. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):325–327. doi: 10.1038/359325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji M., Golde T. E., Ghiso J., Cheung T. T., Estus S., Shaffer L. M., Cai X. D., McKay D. M., Tintner R., Frangione B. Production of the Alzheimer amyloid beta protein by normal proteolytic processing. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):126–129. doi: 10.1126/science.1439760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisodia S. S., Koo E. H., Beyreuther K., Unterbeck A., Price D. L. Evidence that beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease is not derived by normal processing. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):492–495. doi: 10.1126/science.1691865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., McClatchey A. I., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L., Gusella J. F., Neve R. L. Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):528–530. doi: 10.1038/331528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Broeckhoven C., Haan J., Bakker E., Hardy J. A., Van Hul W., Wehnert A., Vegter-Van der Vlis M., Roos R. A. Amyloid beta protein precursor gene and hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis (Dutch). Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1120–1122. doi: 10.1126/science.1971458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann A., König G., Bunke D., Fischer P., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, biogenesis, and localization of precursors of Alzheimer's disease A4 amyloid protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Miki T., Katsuya T., Ogihara T., Sakaki Y. The 717Val----Ile substitution in amyloid precursor protein is associated with familial Alzheimer's disease regardless of ethnic groups. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1141–1146. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91011-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]