Abstract
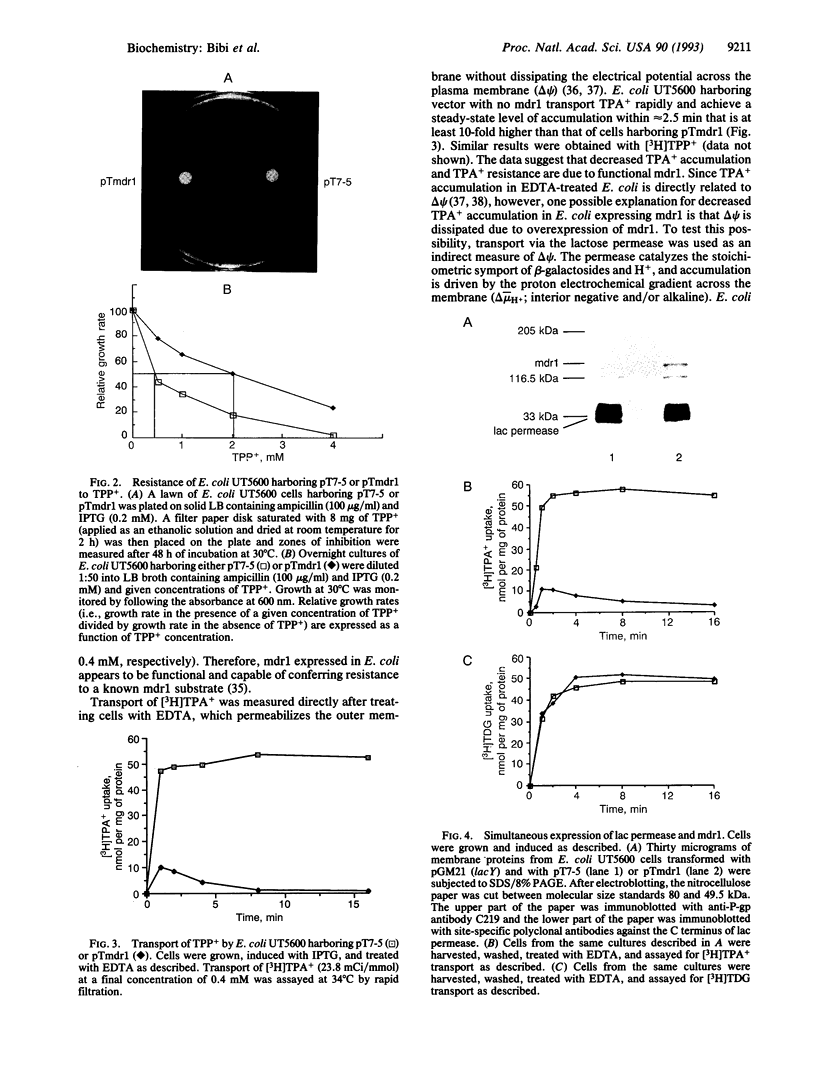
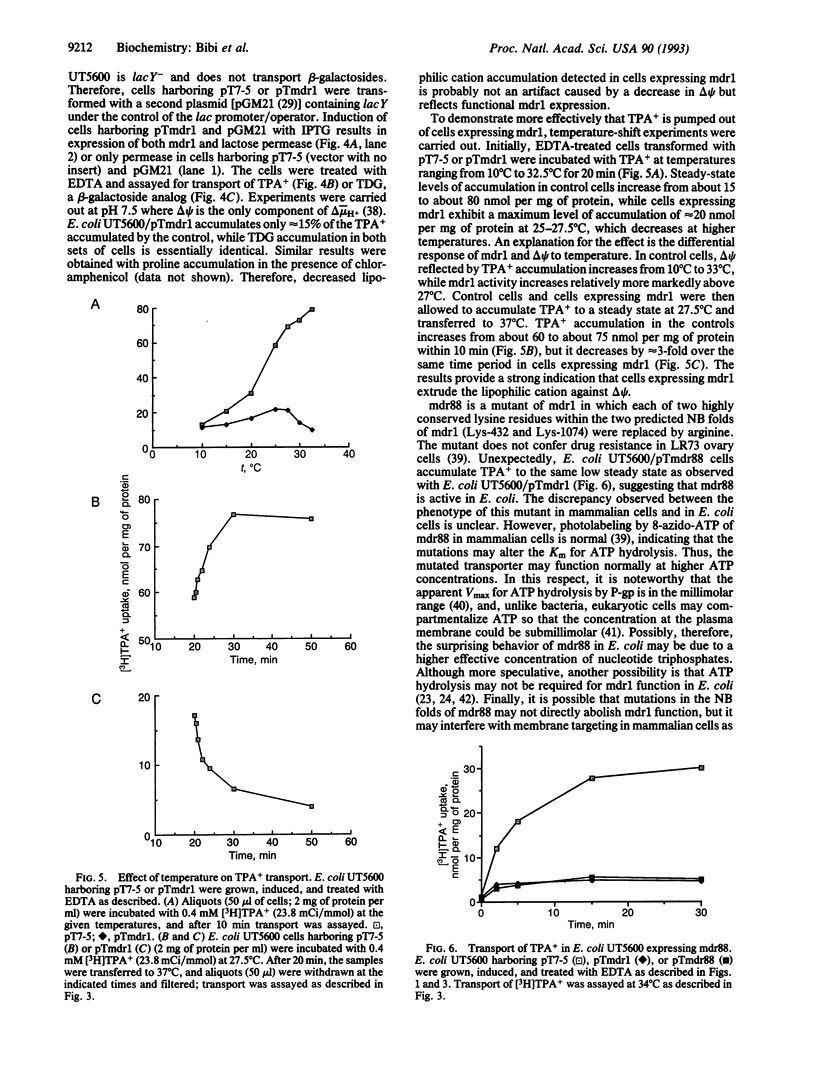
We describe functional expression of the mouse multidrug-resistance protein (P-glycoprotein; P-gp) in an Escherichia coli mutant defective in the outer membrane protease ompT. Heterologously expressed mdr1 appears as an unglycosylated species with an apparent molecular mass of 140 kDa in the membrane of the mutant. Unglycosylated mdr1 retains the ability to bind the photoactivatable drug analog [125I]iodoarylazidoprazosin and confers resistance to tetraphenylphosphonium (TPP+) and tetraphenylarsonium (TPA+), known mdr1 substrates. In vivo resistance is linked to reduced cellular accumulation and energy-dependent efflux of the lipophilic cations. Surprisingly, discrete mutations in the predicted nucleotide binding folds of mdr1 that abolish drug resistance in mammalian cells have no apparent effect on TPA+ efflux via mdr1 in E. coli.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham E. H., Prat A. G., Gerweck L., Seneveratne T., Arceci R. J., Kramer R., Guidotti G., Cantiello H. F. The multidrug resistance (mdr1) gene product functions as an ATP channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):312–316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aflalo C. Biologically localized firefly luciferase: a tool to study cellular processes. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;130:269–323. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzaria M., Schurr E., Gros P. Discrete mutations introduced in the predicted nucleotide-binding sites of the mdr1 gene abolish its ability to confer multidrug resistance. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5289–5297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibi E., Kaback H. R. In vivo expression of the lacY gene in two segments leads to functional lac permease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4325–4329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Gregory R. J., Marshall J., Paul S., Souza D. W., White G. A., O'Riordan C. R., Smith A. E. Defective intracellular transport and processing of CFTR is the molecular basis of most cystic fibrosis. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):827–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. H., Chen C. J., Kriegler M., Roninson I. B. An altered pattern of cross-resistance in multidrug-resistant human cells results from spontaneous mutations in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90568-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell M. M., Safa A. R., Felsted R. L., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Membrane vesicles from multidrug-resistant human cancer cells contain a specific 150- to 170-kDa protein detected by photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3847–3850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell M. M., Tsuruo T., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. ATP-binding properties of P glycoprotein from multidrug-resistant KB cells. FASEB J. 1987 Jul;1(1):51–54. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.1.2886389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Gros P. Two members of the mouse mdr gene family confer multidrug resistance with overlapping but distinct drug specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1652–1663. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine S. E., Ling V., Melera P. W. Amino acid substitutions in the sixth transmembrane domain of P-glycoprotein alter multidrug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4564–4568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J. A., Ling V. The biochemistry of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:137–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felle H., Porter J. S., Slayman C. L., Kaback H. R. Quantitative measurements of membrane potential in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3585–3590. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges E., Bradley G., Gariepy J., Ling V. Detection of P-glycoprotein isoforms by gene-specific monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hyde S. C., Higgins C. F., Valverde M. A., Mintenig G. M., Sepúlveda F. V. Separation of drug transport and chloride channel functions of the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90263-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Ben Neriah Y. B., Croop J. M., Housman D. E. Isolation and expression of a complementary DNA that confers multidrug resistance. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):728–731. doi: 10.1038/323728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Buschman E. The mouse multidrug resistance gene family: structural and functional analysis. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;137C:169–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Croop J., Housman D. Mammalian multidrug resistance gene: complete cDNA sequence indicates strong homology to bacterial transport proteins. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Dhir R., Croop J., Talbot F. A single amino acid substitution strongly modulates the activity and substrate specificity of the mouse mdr1 and mdr3 drug efflux pumps. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7289–7293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Talbot F., Tang-Wai D., Bibi E., Kaback H. R. Lipophilic cations: a group of model substrates for the multidrug-resistance transporter. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 25;31(7):1992–1998. doi: 10.1021/bi00122a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzlinger D., Carrasco N., Kaback H. R. Functional and immunochemical characterization of a mutant of Escherichia coli energy uncoupled for lactose transport. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):221–229. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Gottesman M. M. Is the multidrug transporter a flippase? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):18–21. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90419-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hyde S. C., Mimmack M. M., Gileadi U., Gill D. R., Gallagher M. P. Binding protein-dependent transport systems. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Aug;22(4):571–592. doi: 10.1007/BF00762962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi A. K., Ahmed S., Ferro-Luzzi Ames G. Energy coupling in bacterial periplasmic transport systems. Studies in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2126–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajiji S., Talbot F., Grizzuti K., Van Dyke-Phillips V., Agresti M., Safa A. R., Gros P. Functional analysis of P-glycoprotein mutants identifies predicted transmembrane domain 11 as a putative drug binding site. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 27;32(16):4185–4194. doi: 10.1021/bi00067a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo T. W., Clarke D. M. Functional consequences of proline mutations in the predicted transmembrane domain of P-glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3143–3149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimura C. S., Holbrook S. R., Ames G. F. Structural model of the nucleotide-binding conserved component of periplasmic permeases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinton P. M., Reddy M. M. Control of CFTR chloride conductance by ATP levels through non-hydrolytic binding. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):79–81. doi: 10.1038/360079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepe P. D. Analysis of the steady-state and initial rate of doxorubicin efflux from a series of multidrug-resistant cells expressing different levels of P-glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 22;31(50):12555–12564. doi: 10.1021/bi00165a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safa A. R., Glover C. J., Meyers M. B., Biedler J. L., Felsted R. L. Vinblastine photoaffinity labeling of a high molecular weight surface membrane glycoprotein specific for multidrug-resistant cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6137–6140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safa A. R., Mehta N. D., Agresti M. Photoaffinity labeling of P-glycoprotein in multidrug resistant cells with photoactive analogs of colchicine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1402–1408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90830-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safa A. R., Stern R. K., Choi K., Agresti M., Tamai I., Mehta N. D., Roninson I. B. Molecular basis of preferential resistance to colchicine in multidrug-resistant human cells conferred by Gly-185----Val-185 substitution in P-glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7225–7229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Price E. M., Boucher R. C., Germann U. A., Scarborough G. A. Expression of the human multidrug resistance cDNA in insect cells generates a high activity drug-stimulated membrane ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4854–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. Membrane potential and active transport in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5451–5461. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr E., Raymond M., Bell J. C., Gros P. Characterization of the multidrug resistance protein expressed in cell clones stably transfected with the mouse mdr1 cDNA. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2729–2733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimabuku A. M., Nishimoto T., Ueda K., Komano T. P-glycoprotein. ATP hydrolysis by the N-terminal nucleotide-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4308–4311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skach W. R., Calayag M. C., Lingappa V. R. Evidence for an alternate model of human P-glycoprotein structure and biogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):6903–6908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Bramhall J., Riede I., Wright J. K., Fürst M., Aichele G., Wilhelm U., Overath P. Lactose carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Structure and expression of plasmids carrying the Y gene of the lac operon. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):223–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traxler B., Boyd D., Beckwith J. The topological analysis of integral cytoplasmic membrane proteins. J Membr Biol. 1993 Feb;132(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00233047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumble W. R., Viitanen P. V., Sarkar H. K., Poonian M. S., Kaback H. R. Site-directed mutagenesis of cys148 in the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 30;119(3):860–867. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90853-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. T., Ling V. Study of membrane orientation and glycosylated extracellular loops of mouse P-glycoprotein by in vitro translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18224–18232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]