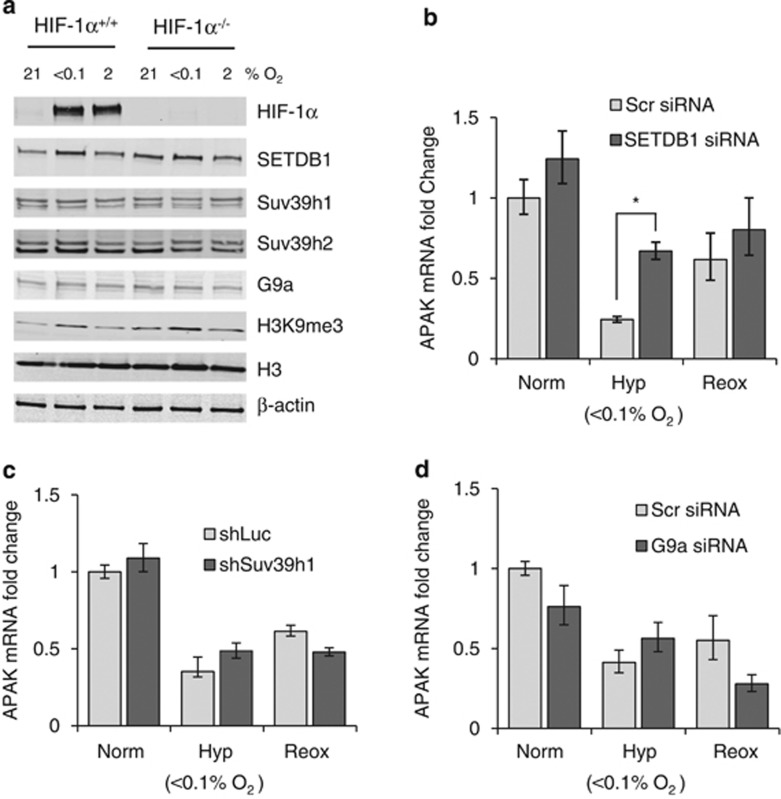
Figure 3.
SETDB1 mediates APAK repression in hypoxia. (a) RKO HIF-1α+/+ and HIF1α−/−cells were exposed to 21%, 2% or <0.1% O2 for 6 h and western blotting was carried out with the antibodies indicated: Suv39h1 and Suv39h2 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK); SETDB1, G9a and H3 (Cell Signaling); and H3K9me3 (Upstate/Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). (b) RKO cells were treated with Scramble (Stealth RNAi negative control (Invitrogen)) or SETDB1 siRNA (ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool, # L-020070-00-0005, Thermo Scientific) and exposed to 6 h of Norm (21% O2), Hyp (<0.1% O2) or Reox (6 h at <0.1% O2 followed by 2 h at 21% O2). APAK mRNA levels were assessed by qPCR as described. (c) APAK mRNA levels were measured by qPCR in RKO cells treated either with Luciferase control shRNA (pSMP-Luc 5′- CCCGCCTGAAGTCTCTGATTAA -3′) (Addgene plasmid 36394) (shLuc) or Suv39h1/2 (Suv39h1 (pSMP-Suv39h1 5′-GAGCTCACCTTTGATTACA-3′) (Addgene plasmid 36342), Suv39h2 (pSMP-Suv39h2 5′-CCCGTTACTGCTTCAGCAA-3′) (Addgene plasmid 36344). We thank Dr George Daley, Boston, MA, USA, for depositing these plasmids in Addgene. Cells were exposed to the same hypoxia/reoxygenation treatments as in (b). (d) APAK mRNA levels were assessed by qPCR in RKO cells treated with Scramble or G9a siRNA (5′-GGACCUUCAUCUGCGAGUA-3′ (Thermo Scientific)), and exposed to the same hypoxia/reoxygenation treatments as in (b), n=2.