Abstract
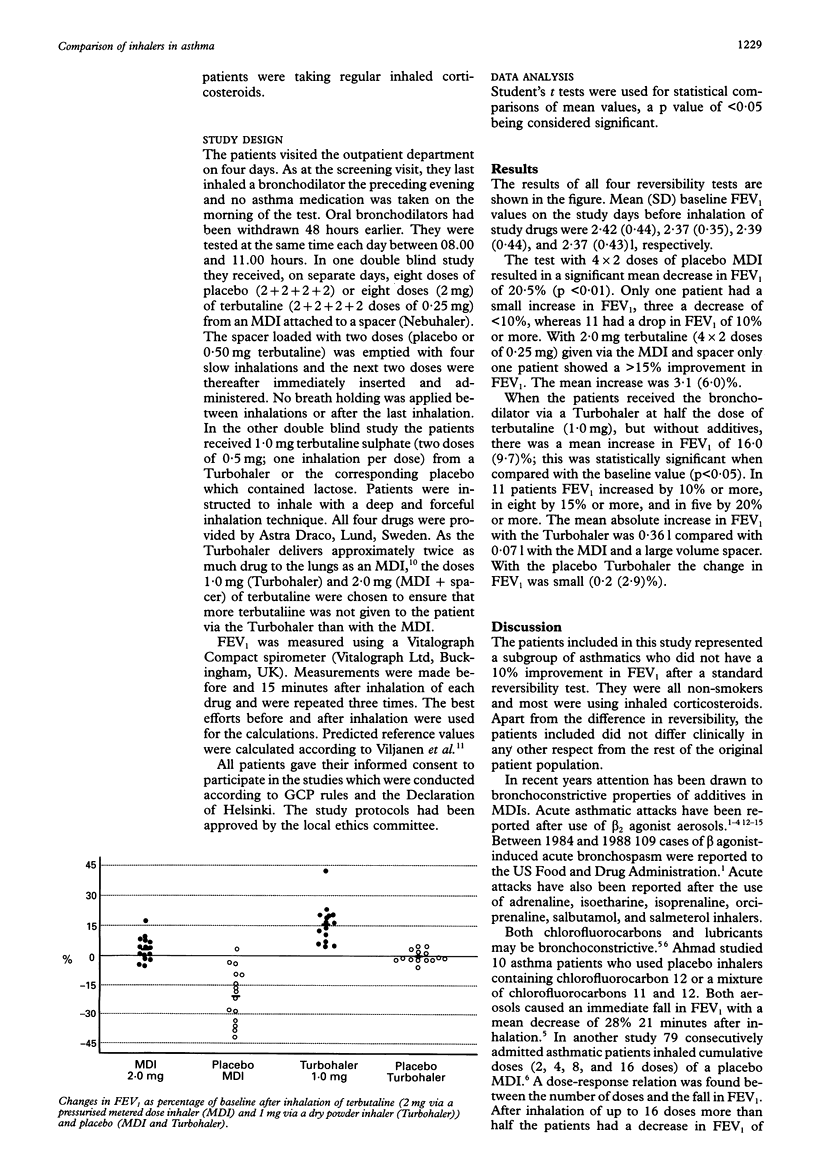
BACKGROUND--Reversibility after administration of an inhaled bronchodilator is not always demonstrable in patients with asthma. Bronchodilator aerosol-induced bronchoconstriction has also been reported to occur in some patients. METHODS--Fifteen selected patients showing < 10% improvement in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) when tested with four doses of salbutamol (0.1 mg/dose) or terbutaline (0.25 mg/dose) from a pressurised metered dose inhaler (MDI) participated in two randomised, double blind studies. They received 2.0 mg terbutaline (4 x 2 doses of 0.25 mg) or a corresponding placebo from an MDI connected to a 750 ml spacer, and 1.0 mg (2 x 0.5 mg) terbutaline or placebo from a multidose dry powder inhaler free of additives (Turbohaler). RESULTS--Inhalation of placebo MDI resulted in a mean (SD) decrease in FEV1 of 20.5 (14.1)% (range -42.9% to +2.6%). In 14 patients inhalation of 2.0 mg terbutaline MDI with spacer resulted in < 10% improvement (mean increase 3.1 (6.0)%). One mg of terbutaline via a Turbohaler resulted in improvements in FEV1 of > 15% in eight patients (mean increase 16.0 (9.7)%). The improvement was < 10% in four patients. Use of placebo Turbohaler did not affect airway calibre (mean change 0.2 (2.9)%). CONCLUSIONS--Additives of MDIs may cause bronchoconstriction in some patients with asthma. In these patients inhalation from a pressurised metered dose inhaler is more likely to decrease the bronchodilator response than inhalation from an additive-free inhaler. The frequency of this phenomenon is unknown.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown P. J., Greville H. W., Finucane K. E. Asthma and irreversible airflow obstruction. Thorax. 1984 Feb;39(2):131–136. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchetto D. M., Sykes R. S., Spector S. Paradoxical bronchospasm after use of inhalation aerosols: a review of the literature. J Asthma. 1991;28(1):49–53. doi: 10.3109/02770909109073370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson L., Ståhl E., Holgate S. T. Terbutaline via pressurised metered dose inhaled (P-MDI) and Turbuhaler in highly reactive asthmatic patients. Eur Respir J. 1994 Sep;7(9):1598–1601. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07091598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keighley J. F. Iatrogenic asthma associated with adrenergic aerosols. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Nov;65(5):985–995. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-65-5-985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzanowski M., Lebowitz M. D. Changes in chronic respiratory symptoms in two populations of adults studied longitudinally over 13 years. Eur Respir J. 1992 Jan;5(1):12–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas R. A. Paradoxical bronchospasm associated with the use of inhaled beta agonists. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 May;85(5):959–964. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90084-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman R. E. Asthma induced by adrenergic aerosols. Chest. 1973 Apr;63(Suppl):16S–16S. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.4_supplement.16s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shim C. S., Williams M. H., Jr Cough and wheezing from beclomethasone dipropionate aerosol are absent after triamcinolone acetonide. Ann Intern Med. 1987 May;106(5):700–703. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-5-700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautlein J., Allegra J., Field J., Gillin M. Paradoxic bronchospasm after inhalation of isoptroterenol. Chest. 1976 Dec;70(6):711–714. doi: 10.1378/chest.70.6.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljanen A. A., Halttunen P. K., Kreus K. E., Viljanen B. C. Spirometric studies in non-smoking, healthy adults. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1982;159:5–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. R., Roberts J. A., Bradding P., Holgate S. T., Howarth P. H. Paradoxical bronchoconstriction in asthmatic patients after salmeterol by metered dose inhaler. BMJ. 1992 Oct 17;305(6859):931–932. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6859.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarbrough J., Mansfield L. E., Ting S. Metered dose inhaler induced bronchospasm in asthmatic patients. Ann Allergy. 1985 Jul;55(1):25–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


