Abstract
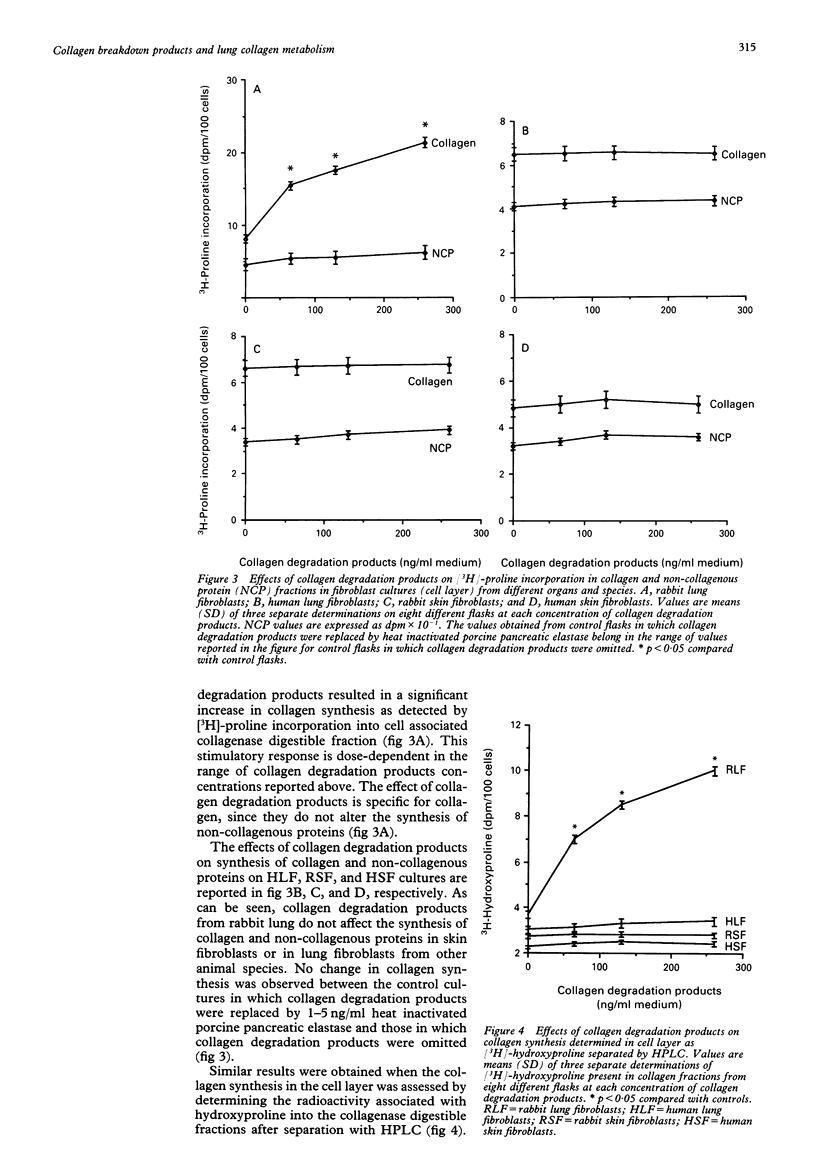
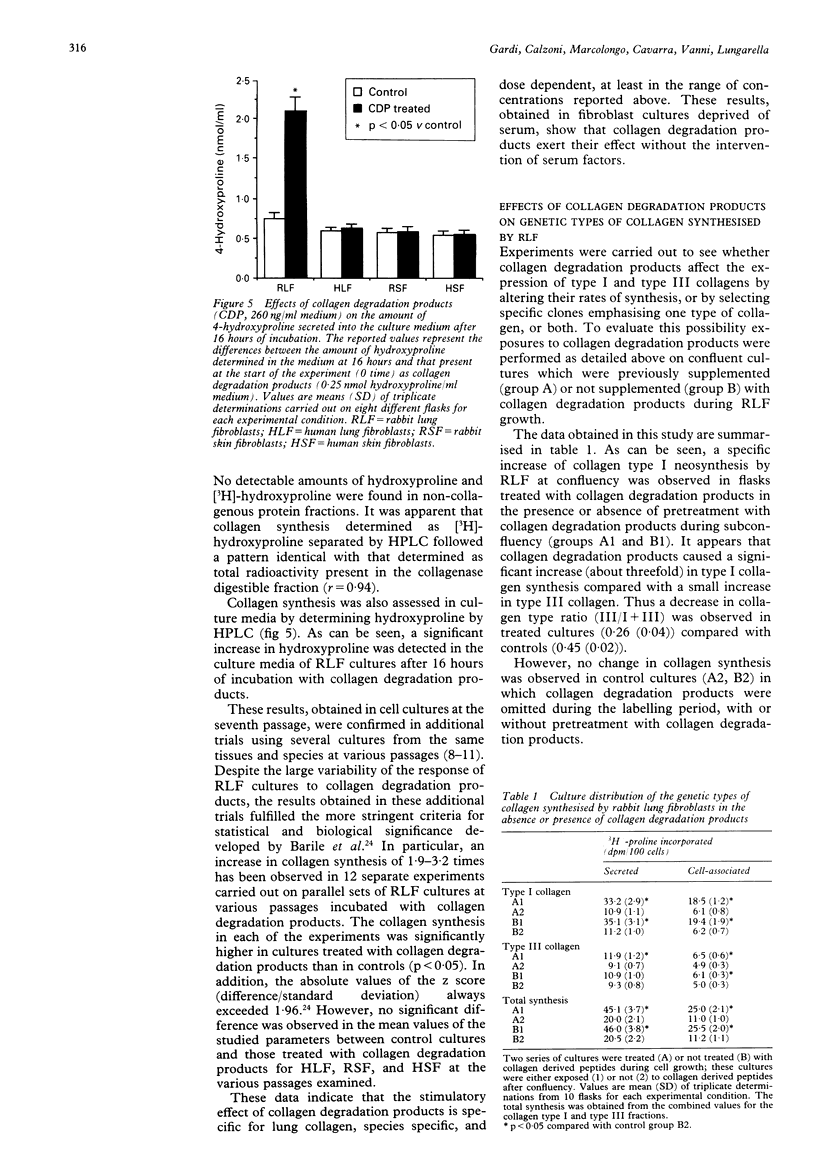
BACKGROUND--In fibrotic diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis there is evidence suggesting enhanced synthesis and degradation of lung connective tissue components, including collagen. It has therefore been hypothesised that products of collagen degradation may have a role in the promotion of collagen deposition. In support of this hypothesis, it has recently been shown that intravenous injection of lung collagen degradation products in experimental animals stimulated collagen synthesis leading to increased collagen deposition and diffuse interstitial lung disease. METHODS--Rabbit and human fibroblast cultures from lung and skin were used as an in vitro model to study the responses of these cells to rabbit collagen degradation products. The effects of an acute exposure to collagen degradation products on synthesis of collagen and noncollagenous protein have been studied in confluent cultures by [3H]-proline incorporation. The effects of collagen degradation products on fibroblast proliferation and production of genetic types of collagen have also been investigated. RESULTS--The acute exposure of rabbit lung fibroblast cultures to collagen degradation products significantly increased collagen synthesis without affecting non-collagenous protein synthesis. This effect was dose related, specific for lung fibroblasts, and species specific. Collagen degradation products altered the rate of synthesis of genetic types of collagen with a consequent decrease of type III/I+III collagen ratio (0.26 (0.04) treated with collagen degradation products; 0.45 (0.02) controls). These effects occurred without the intervention of serum factors. In addition, collagen degradation products neither affected fibroblast proliferation nor selected specific clones emphasising one type of collagen. CONCLUSIONS--These results suggest that collagen degradation products can influence lung collagen metabolism by stimulating collagen synthesis. The regulation of collagen mass by collagen degradation products may be of importance in lung collagen homeostasis in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barile F. A., Guzowski D. E., Ripley C., Siddiqi Z. A., Bienkowski R. S. Ammonium chloride inhibits basal degradation of newly synthesized collagen in human fetal lung fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Jan;276(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90018-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrakasan G., Bhatnagar R. S. Stimulation of collagen synthesis in fibroblast cultures by superoxide. Cell Mol Biol. 1991;37(7):751–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Freundlich B., Adams S., Rosenbloom J. Regulation of human lung fibroblast collagen production by recombinant interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor, and interferon-gamma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;580:233–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonzi L., Lungarella G. Correlation between biochemical and morphological repair in rabbit lungs after elastase injury. Lung. 1980;158(3):165–171. doi: 10.1007/BF02713719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. A., Rich C. B., Miller M. F. Pulmonary fibroblasts: an in vitro model of emphysema. Regulation of elastin gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15544–15549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardi C., Calzoni P., Cavarra E., Pacini A., Lungarella G. An elastolytic proteinase from rabbit leukocytes: purification and partial characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Oct;290(1):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90613-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardi C., Pacini A., de Santi M. M., Calzoni P., Viti A., Corradeschi F., Lungarella G. Development of interstitial lung fibrosis by long-term treatment with collagen breakdown products in rabbits. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1990 May;68(2):235–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hance A. J., Crystal R. G. Rigid control of synthesis of collagen types I and III by cells in culture. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):152–154. doi: 10.1038/268152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn M., Malkowicz S. B. Regulatory pathways in tumor growth and invasion. Lab Invest. 1991 Sep;65(3):262–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama K., Seyer J. M., Raghow R., Kang A. H. Regulation of extracellular matrix production by chemically synthesized subfragments of type I collagen carboxy propeptide. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7097–7104. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P., Robert L., Courtois Y., Laurent M. Selective decrease of type I collagen synthesis in Fraser mice skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 18;826(4):174–179. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivirikko K. I., Laitinen O., Prockop D. J. Modifications of a specific assay for hydroxyproline in urine. Anal Biochem. 1967 May;19(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C., Yu S. Y., Chraplyvy M., Linder H. E., Senior R. M. The induction of emphysema with elastase. II. Changes in connective tissue. Lab Invest. 1976 Apr;34(4):372–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays P. K., McAnulty R. J., Laurent G. J. Age-related changes in lung collagen metabolism. A role for degradation in regulating lung collagen production. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Aug;140(2):410–416. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monboisse V., Monboisse J. C., Borel J. P., Randoux A. Nonisotopic evaluation of collagen in fibroblasts cultures. Anal Biochem. 1989 Feb 1;176(2):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramoto K., Ramachandran J., Hall J., Hui A., Stern R. A rapid sensitive assay for the quantitation of elastin. Connect Tissue Res. 1984;12(3-4):307–317. doi: 10.3109/03008208409013693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Inoue S., Abiko S., Aoki H., Takeo K. Improved separation of alpha chains of collagen type I, type III, and type V by noninterrupted electrophoresis using thioglycolic acid as a negatively charged reducer. Electrophoresis. 1989 Jan;10(1):29–33. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacini A., Gardi C., Corradeschi F., Viti A., Belli C., Calzoni P., Lungarella G. In vivo stimulation of lung collagen synthesis by collagen derived peptides. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;68(1):89–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Thrall R. S., Williams C. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Effects of steroid on lung collagen metabolism. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Oct;124(4):428–434. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.4.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanheimer R. G. Inhibition of collagen production by diabetic rat serum: response to insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I added in vitro. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3018–3026. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. M., Blanchard B., Zava D. T. A simple method to determine whole cell uptake of radiolabelled oestrogen and progesterone and their subcellular localization in breast cancer cell lines in monolayer culture. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 May;20(5):1083–1088. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiestner M., Krieg T., Hörlein D., Glanville R. W., Fietzek P., Müller P. K. Inhibiting effect of procollagen peptides on collagen biosynthesis in fibroblast cultures. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7016–7023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. Y., Keller N. R. Synthesis of lung collagen in hamsters with elastase-induced emphysema. Exp Mol Pathol. 1978 Aug;29(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(78)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]