Abstract
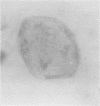
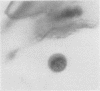
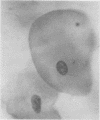
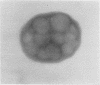
The cellular content of amniotic fluid is primarily composed of desquamated squamous cells. Depending on their site of origin and maturation, the staining characteristics of the nuclei and cytoplasm differ. Prenatal foetal sex was determined by comparing the proportion of anucleate pyknotic nuclei to vesicular nuclei using Papanicolaou's stain and the proportion of red cells to blue cells using Shorr's stain.
Both techniques allow an accurate assessment of prenatal sex to be made after 30 week's gestation. There is a close correlation between the two methods.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arendzen J. H., Huisjes H. J. A simple method for prenatal determination of sex. Acta Cytol. 1971 May-Jun;15(3):316–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. J., Morris H. H., Davey D. A. The influence of fetal sex upon liquor cytology as a means of estimating gestational age. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1972 Apr;79(4):340–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1972.tb15806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop E. H., Corson S. Estimation of fetal maturity by cytologic examination of amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1968 Nov 1;102(5):654–664. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(68)90379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain O. A., Sinclair L. Studies on the cytology of amniotic fluid and of the newborn infant's skin in relation to maturity of the infant. Proc R Soc Med. 1971 Dec;64(12):1213–1217. doi: 10.1177/003591577106401219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelbaum B., Evans T. N. Life in the amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1969 Jun 1;104(3):365–377. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)34189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]