Abstract
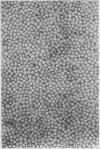
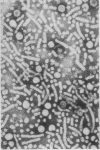
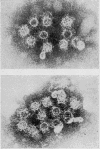
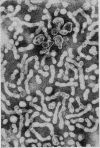
Attempts to detect hepatitis B antigen in faeces and bile should take into account the degradation and disappearance of the surface antigens in an environment containing proteolytic enzymes in the presence of bile salts as in the intestinal lumen. The cores of the Dane particles are much more stable than the surface antigens and these may best be identified by immune electron microscopy using core antibody.
Full text
PDF
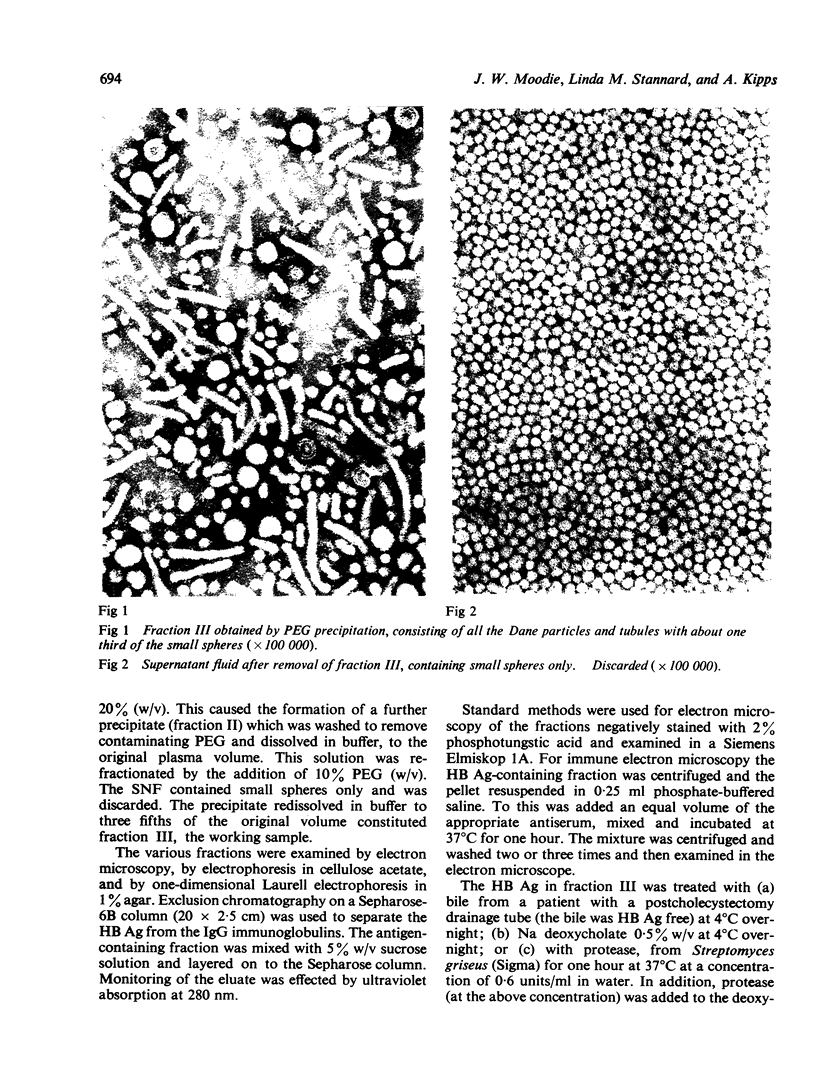
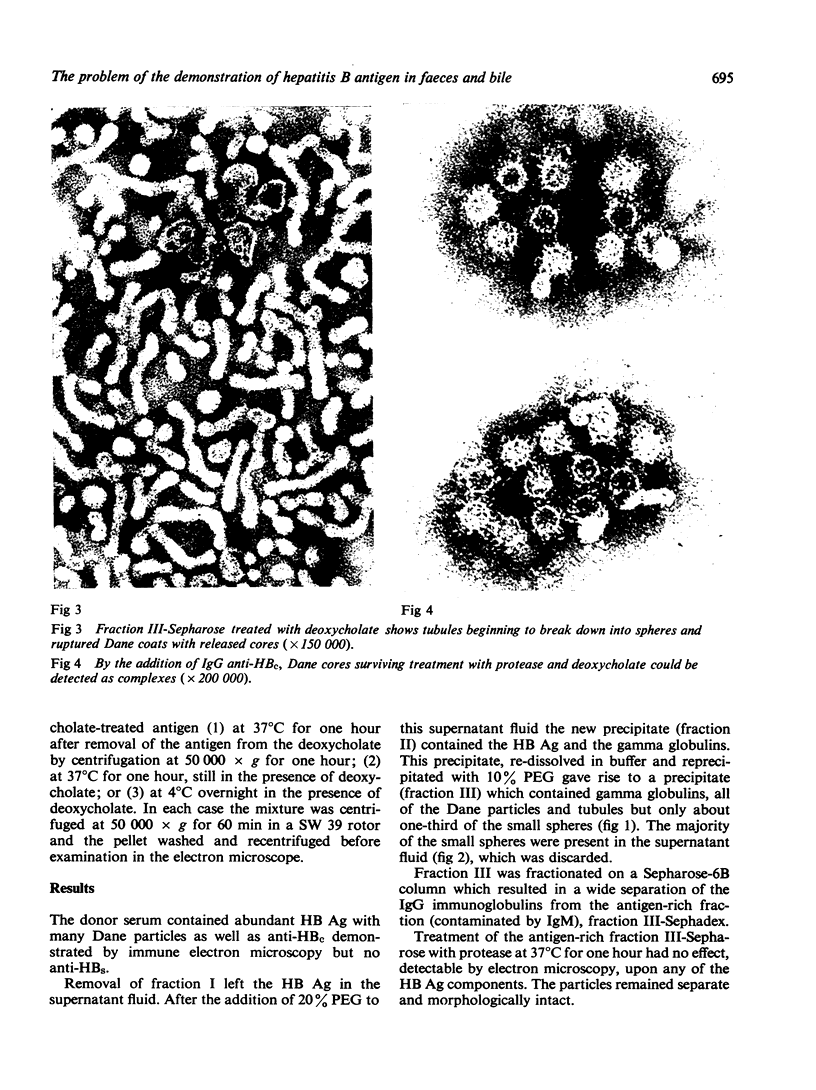


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akdamar K. A., Maumus L., Cherrie Epps A., Leach R., Warren S. S.H. antigen in bile. Lancet. 1971 May 1;1(7705):909–909. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Rubenstein D., Stott E. J. New antigen-antibody system in Australia-antigen-positive hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart Y. E., Vahrman J. Studies of Australia-SH antigen in sporadic viral hepatitis in London. Br Med J. 1970 Feb 14;1(5693):403–405. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5693.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris A. A. Antigen in infectious hepatitis. Br Med Bull. 1972 May;28(2):131–133. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabow W. O., Prozesky O. W. Isolation and purification of hepatitis-associated antigen by affinity chromatography with baboon antiserum. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):183–186. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grob P. J., Jemelka H. Faecal S.H. (Australia) antigen in acute hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Jan 30;1(7692):206–208. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90949-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gust I. D., Kaldor J., Cross G. F., Waugh M., Ferris A. A. Virus-like particles associated with a faecal antigen from hepatitis patients and with Australia antigen. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1971 Feb;49(1):1–9. doi: 10.1038/icb.1971.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gust I. D., Kaldor J., Nastasi M. Absence of Au antigen in faeces of patients with Au-positive sera. Lancet. 1971 Apr 17;1(7703):797–797. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91234-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. N., Groh V. Immunoagglutination electron microscopic study on virus-like particles and Australia antigen in liver tissue. Lab Invest. 1973 Oct;29(4):353–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piazza M., Di Stasio G., Maio G., Marzano L. A. Hepatitis B antigen inhibitor in human faeces and intestinal mucosa. Br Med J. 1973 May 12;2(5862):334–337. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5862.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serpeau D., Mannoni P., Dhumeaux D., Berthelot P. Hepatitis-associated antigen in human bile. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1266–1266. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stannard L. M., Polson A., Kipps A., Parker J. R. Two antigen-antibody systems in serum hepatitis: preparation of immunoglobulins and their reaction with Australia antigen and particles in liver cell homogenates. Microbios. 1973 Sep-Oct;8(30):87–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]