Abstract
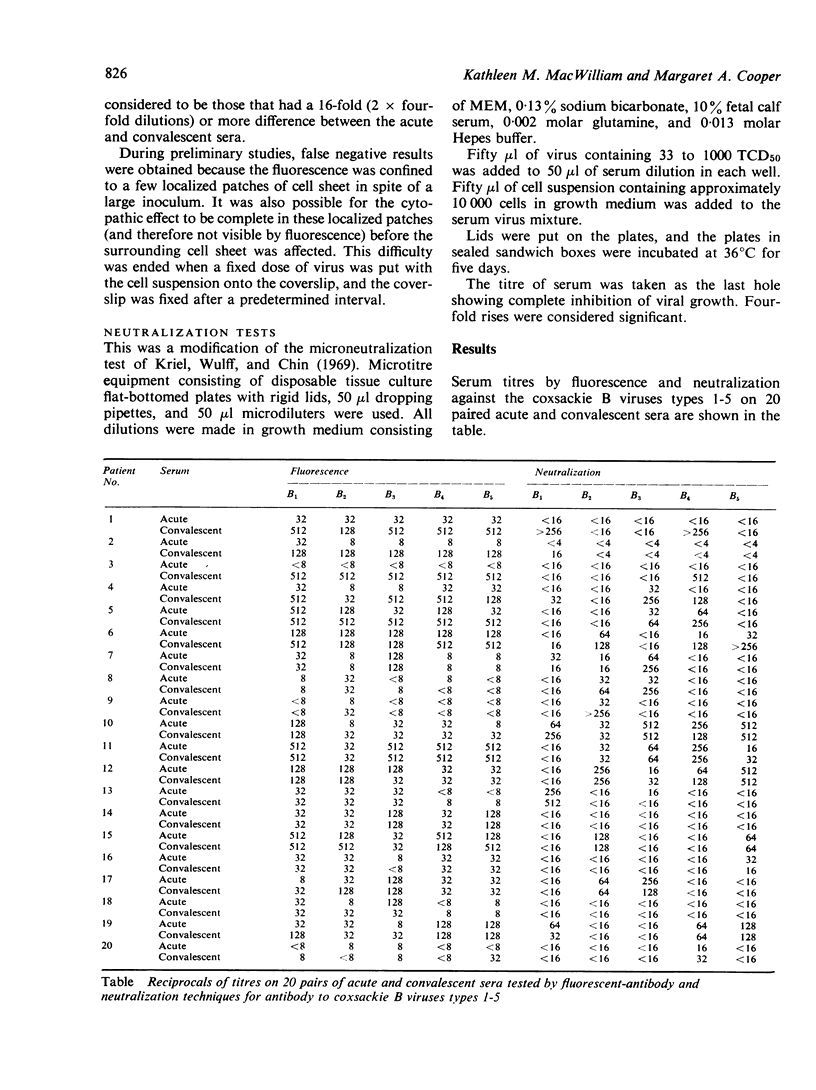
Twenty pairs of acute and convalescent sera were tested for antibody to the coxsackie B viruses types 1-5 by neutralization and fluorescent-antibody techniques. Results by fluorescence were difficult to read and sensitivity was therefore reduced. Rises by neutralization were type specific in the majority of cases, while those by fluorescence were always against more than one viral type.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- French M. L., Schmidt N. J., Emmons R. W., Lennette E. H. Immunofluorescence staining of group B coxsackieviruses. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):54–61. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.54-61.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriel R. L., Wulff H., Chin T. D. Microneutralization test for determination of rhinovirus and coxsackievirus A antibody in human diploid cells. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Apr;17(4):611–613. doi: 10.1128/am.17.4.611-613.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS J. L., BROWN G. C. Application of direct and indirect immunofluorescence for identification of enteroviruses and titrating their antibodies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Aug-Sep;110:833–837. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW E. D., NEWTON A., POWELL A. W., FRIDAY C. J. Fluorescent antigen-antibody reactions in Coxsackie and ECHO enteroviruses. Virology. 1961 Oct;15:208–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90239-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


