Abstract
Malaria remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, accounting for more than one million deaths annually. We have focused on the reduction of ribonucleotides to 2'-deoxyribonucleotides, catalyzed by ribonucleotide reductase, which represents the rate-determining step in DNA replication as a target for antimalarial agents. We report the full-length DNA sequence corresponding to the large (PfR1) and small (PfR2) subunits of Plasmodium falciparum ribonucleotide reductase. The small subunit (PfR2) contains the major catalytic motif consisting of a tyrosyl radical and a dinuclear Fe site. Whereas PfR2 shares 59% amino acid identity with human R2, a striking sequence divergence between human R2 and PfR2 at the C terminus may provide a selective target for inhibition of the malarial enzyme. A synthetic oligopeptide corresponding to the C-terminal 7 residues of PfR2 inhibits mammalian ribonucleotide reductase at concentrations approximately 10-fold higher than that predicted to inhibit malarial R2. The gene encoding the large subunit (PfR1) contains a single intron. The cysteines thought to be involved in the reduction mechanism are conserved. In contrast to mammalian ribonucleotide reductase, the genes for PfR1 and PfR2 are located on the same chromosome and the accumulation of mRNAs for the two subunits follow different temporal patterns during the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF


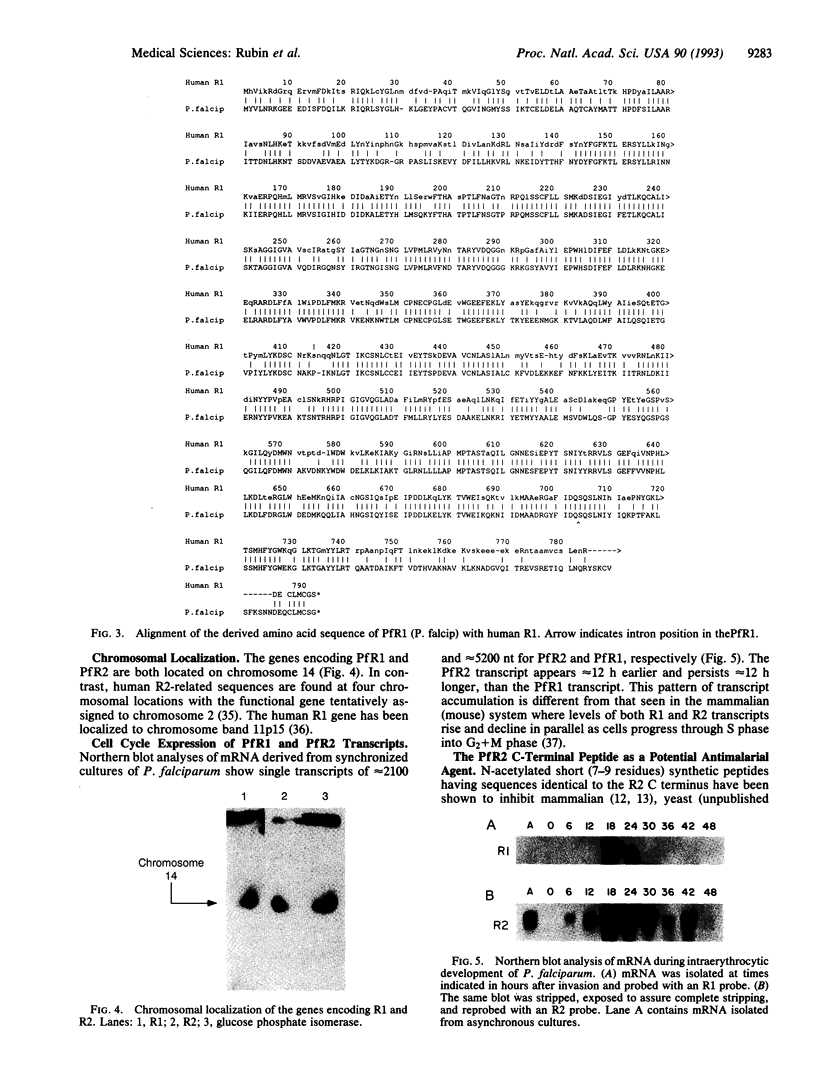
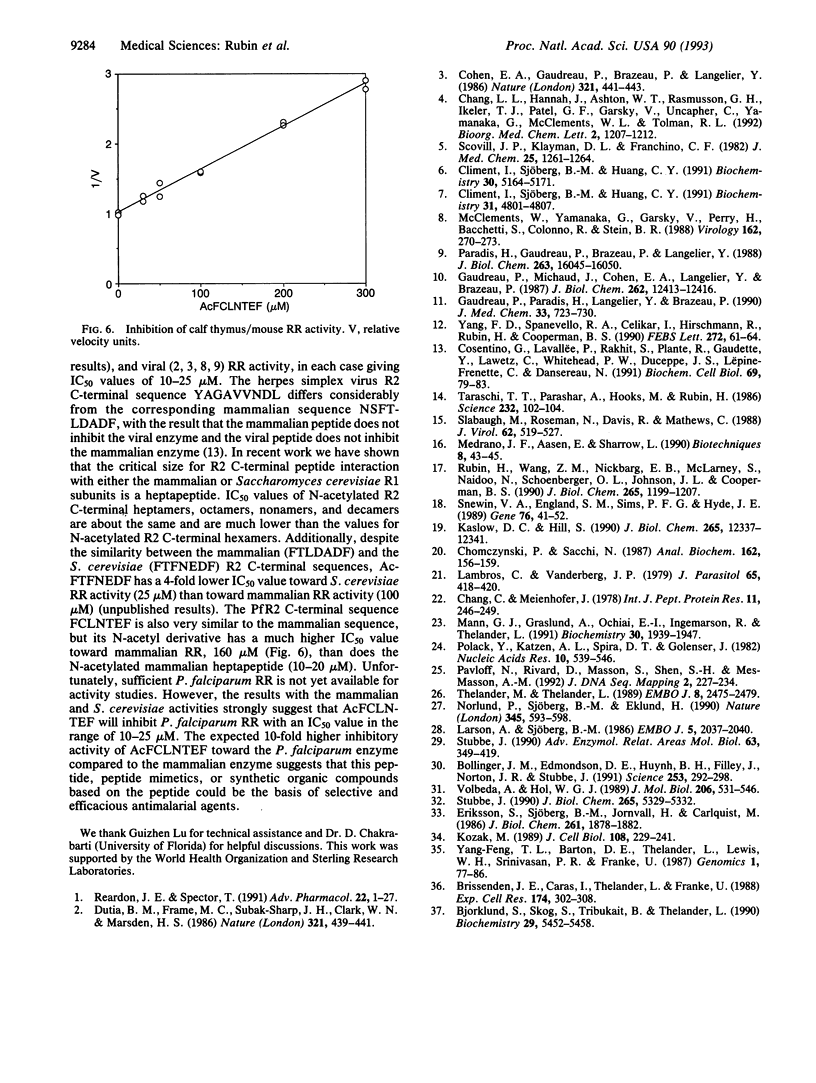
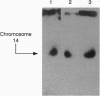
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björklund S., Skog S., Tribukait B., Thelander L. S-phase-specific expression of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase R1 and R2 subunit mRNAs. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5452–5458. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollinger J. M., Jr, Edmondson D. E., Huynh B. H., Filley J., Norton J. R., Stubbe J. Mechanism of assembly of the tyrosyl radical-dinuclear iron cluster cofactor of ribonucleotide reductase. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):292–298. doi: 10.1126/science.1650033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissenden J. E., Caras I., Thelander L., Francke U. The structural gene for the M1 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase maps to chromosome 11, band p15, in human and to chromosome 7 in mouse. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):302–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. D., Meienhofer J. Solid-phase peptide synthesis using mild base cleavage of N alpha-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonylamino acids, exemplified by a synthesis of dihydrosomatostatin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Mar;11(3):246–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Climent I., Sjöberg B. M., Huang C. Y. Carboxyl-terminal peptides as probes for Escherichia coli ribonucleotide reductase subunit interaction: kinetic analysis of inhibition studies. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5164–5171. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Climent I., Sjöberg B. M., Huang C. Y. Site-directed mutagenesis and deletion of the carboxyl terminus of Escherichia coli ribonucleotide reductase protein R2. Effects on catalytic activity and subunit interaction. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4801–4807. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. A., Gaudreau P., Brazeau P., Langelier Y. Specific inhibition of herpesvirus ribonucleotide reductase by a nonapeptide derived from the carboxy terminus of subunit 2. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):441–443. doi: 10.1038/321441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosentino G., Lavallée P., Rakhit S., Plante R., Gaudette Y., Lawetz C., Whitehead P. W., Duceppe J. S., Lépine-Frenette C., Dansereau N. Specific inhibition of ribonucleotide reductases by peptides corresponding to the C-terminal of their second subunit. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;69(1):79–83. doi: 10.1139/o91-011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutia B. M., Frame M. C., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Clark W. N., Marsden H. S. Specific inhibition of herpesvirus ribonucleotide reductase by synthetic peptides. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):439–441. doi: 10.1038/321439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Sjöberg B. M., Jörnvall H., Carlquist M. A photoaffinity-labeled allosteric site in Escherichia coli ribonucleotide reductase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1878–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudreau P., Michaud J., Cohen E. A., Langelier Y., Brazeau P. Structure-activity studies on synthetic peptides inhibiting herpes simplex virus ribonucleotide reductase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12413–12416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudreau P., Paradis H., Langelier Y., Brazeau P. Synthesis and inhibitory potency of peptides corresponding to the subunit 2 C-terminal region of herpes virus ribonucleotide reductases. J Med Chem. 1990 Feb;33(2):723–730. doi: 10.1021/jm00164a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow D. C., Hill S. Cloning metabolic pathway genes by complementation in Escherichia coli. Isolation and expression of Plasmodium falciparum glucose phosphate isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12337–12341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson A., Sjöberg B. M. Identification of the stable free radical tyrosine residue in ribonucleotide reductase. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):2037–2040. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann G. J., Gräslund A., Ochiai E., Ingemarson R., Thelander L. Purification and characterization of recombinant mouse and herpes simplex virus ribonucleotide reductase R2 subunit. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 19;30(7):1939–1947. doi: 10.1021/bi00221a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClements W., Yamanaka G., Garsky V., Perry H., Bacchetti S., Colonno R., Stein R. B. Oligopeptides inhibit the ribonucleotide reductase of herpes simplex virus by causing subunit separation. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):270–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90421-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund P., Sjöberg B. M., Eklund H. Three-dimensional structure of the free radical protein of ribonucleotide reductase. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):593–598. doi: 10.1038/345593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradis H., Gaudreau P., Brazeau P., Langelier Y. Mechanism of inhibition of herpes simplex virus (HSV) ribonucleotide reductase by a nonapeptide corresponding to the carboxyl terminus of its subunit 2. Specific binding of a photoaffinity analog, [4'- azido-Phe6] HSV H2-6(6-15), to subunit 1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16045–16050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavloff N., Rivard D., Masson S., Shen S. H., Mes-Masson A. M. Sequence analysis of the large and small subunits of human ribonucleotide reductase. DNA Seq. 1992;2(4):227–234. doi: 10.3109/10425179209020807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack Y., Katzen A. L., Spira D. T., Golenser J. The genome of Plasmodium falciparum. I: DNA base composition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):539–546. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. E., Spector T. Acyclovir: mechanism of antiviral action and potentiation by ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors. Adv Pharmacol. 1991;22:1–27. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H., Wang Z. M., Nickbarg E. B., McLarney S., Naidoo N., Schoenberger O. L., Johnson J. L., Cooperman B. S. Cloning, expression, purification, and biological activity of recombinant native and variant human alpha 1-antichymotrypsins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1199–1207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scovill J. P., Klayman D. L., Franchino C. F. 2-Acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazones. 4. Complexes with transition metals as antimalarial and antileukemic agents. J Med Chem. 1982 Oct;25(10):1261–1264. doi: 10.1021/jm00352a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabaugh M., Roseman N., Davis R., Mathews C. Vaccinia virus-encoded ribonucleotide reductase: sequence conservation of the gene for the small subunit and its amplification in hydroxyurea-resistant mutants. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.519-527.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snewin V. A., England S. M., Sims P. F., Hyde J. E. Characterisation of the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthetase gene from human malaria parasites highly resistant to pyrimethamine. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbe J. Ribonucleotide reductases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1990;63:349–419. doi: 10.1002/9780470123096.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbe J. Ribonucleotide reductases: amazing and confusing. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5329–5332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Parashar A., Hooks M., Rubin H. Perturbation of red cell membrane structure during intracellular maturation of Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):102–104. doi: 10.1126/science.3006251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander M., Thelander L. Molecular cloning and expression of the functional gene encoding the M2 subunit of mouse ribonucleotide reductase: a new dominant marker gene. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2475–2479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08383.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volbeda A., Hol W. G. Pseudo 2-fold symmetry in the copper-binding domain of arthropodan haemocyanins. Possible implications for the evolution of oxygen transport proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):531–546. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90499-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Feng T. L., Barton D. E., Thelander L., Lewis W. H., Srinivasan P. R., Francke U. Ribonucleotide reductase M2 subunit sequences mapped to four different chromosomal sites in humans and mice: functional locus identified by its amplification in hydroxyurea-resistant cell lines. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):77–86. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F. D., Spanevello R. A., Celiker I., Hirschmann R., Rubin H., Cooperman B. S. The carboxyl terminus heptapeptide of the R2 subunit of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase inhibits enzyme activity and can be used to purify the R1 subunit. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 15;272(1-2):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80449-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]