Abstract
To investigate further the role of hepatitis B antigen (HBs Ag) and specific immune complexes in polyarteritis, sera from 55 histologically confirmed cases were tested for the presence of hepatitis B antigen-associated particles and hepatitis B-antibody (anti HBs) by solid phase radio-immunoassay, electron microscopy, and passive haemagglutination. Results of these findings have been correlated with the clinical course of the disease.
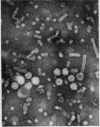
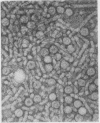
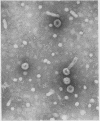
HBs Ag was detected in 30 patients (54·5%) and anti HBs in 13/45 (28%). Subtyping in 20 patients revealed that 11 were Y and 9 D. Thirty-seven cases (69%) demonstrated either HBs Ag or anti HBs and 5/45 (11%) had both. Electron microscopic examination showed 20 nm spherical and tubular particles in sera of 20/27 patients with 42 nm particles in 11 cases and clumped particles in 12 (60%).
No correlation was found between detection of immune complexes and liver disease whereas the presence of coexisting hepatitis B antigen and antibody or aggregated particles was restricted to cases of active vasculitis. Seroconversion or the presence of hepatitis B antibody alone was associated with improved prognosis. Circulating hepatitis B antigen antibody complexes may be responsible for vasculitis or polyarteritis but do not appear to be pathogenic for the liver.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D. Individual morphological variations seen in Australia antigen positive sera. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Apr;123(4):303–309. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110100035013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. Immune complexes in hepatitis. Lancet. 1969 Nov 8;2(7628):983–986. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert E., Isselbacher K. J., Schur P. H. The pathogenesis of arthritis associated with viral hepatitis. Complement-component studies. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 22;285(4):185–189. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107222850401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A. L., Kaplan M. M., Benz W. C., Sidel J. S., Wolff H. J. Polyarteritis associated with Australia antigen-positive hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jan;62(1):105–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Koffler D. Immune complex disease in experimental animals and man. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):185–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couleru O., German A., Bousquet O., Sarrazin A. Immune complexes in large particles of Australia antigen in polyarteritis. Lancet. 1972 Feb 19;1(7747):445–446. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90904-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Fox R. A., Sherlock S. Cellular immunity and hepatitis-associated, Australia antigen liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Apr 1;1(7753):723–726. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Brodin A., Steinberg D., Vernace S., Yang C. P., Paronetto F. Periarteritis nodosa, Australia antigen and lymphatic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 6;286(1):14–17. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201062860103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocke D. J., Hsu K., Morgan C., Bombardieri S., Lockshin M., Christian C. L. Association between polyarteritis and Australia antigen. Lancet. 1970 Dec 5;2(7684):1149–1153. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocke D. J., Hsu K., Morgan C., Bombardieri S., Lockshin M., Christian C. L. Vasculitis in association with Australia antigen. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):330s–336s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knieser M. R., Jenis E. H., Lowenthal D. T., Bancroft W. H., Burns W., Shalhoub R. Pathogenesis of renal disease associated with viral hepatitis. Arch Pathol. 1974 Apr;97(4):193–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F. Clinical immune complex disease. Manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus and hepatitis B virus infection. Medicine (Baltimore) 1973 Sep;52(5):419–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander J. J., Alter H. J., Purcell R. H. Frequency of antibody to hepatitis-associated antigen as measured by a new radioimmunoassay technique. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1166–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L. Editorial: Subtypes of hepatitis B antigen: clinical relevance? Ann Intern Med. 1973 Dec;79(6):894–896. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-6-894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini G. A., Strohmeyer G., Sodomann C. P. Die Panarteriitis nodosa bei chronischer Hepatitis mit australia-Antigen-Nachweis. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1972 Apr 21;97(16):642–645. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1107413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowoslawski A., Krawczyński K., Brzosko W. J., Madaliński K. Tissue localization of Australia antigen immune complexes in acute and chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. Am J Pathol. 1972 Jul;68(1):31–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Mackay I. R. Relation between Australia antigen and autoimmune hepatitis. Lancet. 1972 May 27;1(7761):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Brotman B., Jass D., Ikram H. Specificity of the direct solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of hepatitis-B antigen. Lancet. 1973 Jun 16;1(7816):1346–1350. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Trepo C. Role of immune complexes involving SH antigen in pathogenesis of chronic active hepatitis and polyarteritis nodosa. Lancet. 1971 Jun 26;1(7713):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91883-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepo C. G., Thivolet J., Prince A. M. Australia antigen and polyarteritis nodosa. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Apr;123(4):390–392. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110100122046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepo C., Thivolet J. Antigène australien, hépatite à virus et périartérite noueuse. Presse Med. 1970 Aug 29;78(36):1575–1575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepo C., Thivolet J. Hepatitis associated antigen and periarteritis nodosa (PAN). Vox Sang. 1970 Sep-Oct;19(3):410–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepo C., Thivolet J., Lambert R. Four cases of periarteritis nodosa associated with persistant Australia antigen. Digestion. 1972;5(2):100–107. doi: 10.1159/000197180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepo C., Trepo D., Ortiz J. P., Monier J. C., Sepetjian M. L'antigène de l'hépatite B (Ag HB ou Ag Australia). Intérêt clinique de sa détection par un dosage radio-immunologique (D.R.I.) en phase solide. Nouv Presse Med. 1973 Oct 6;2(35):2339–2340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepo C. Virus de l'hépatite B et périartérite noueuse. Nouv Presse Med. 1972 Jul 8;1(28):1879–1881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff M. Viruses and the connective tissue diseases. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Dec;75(6):951–958. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-6-951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]