Abstract
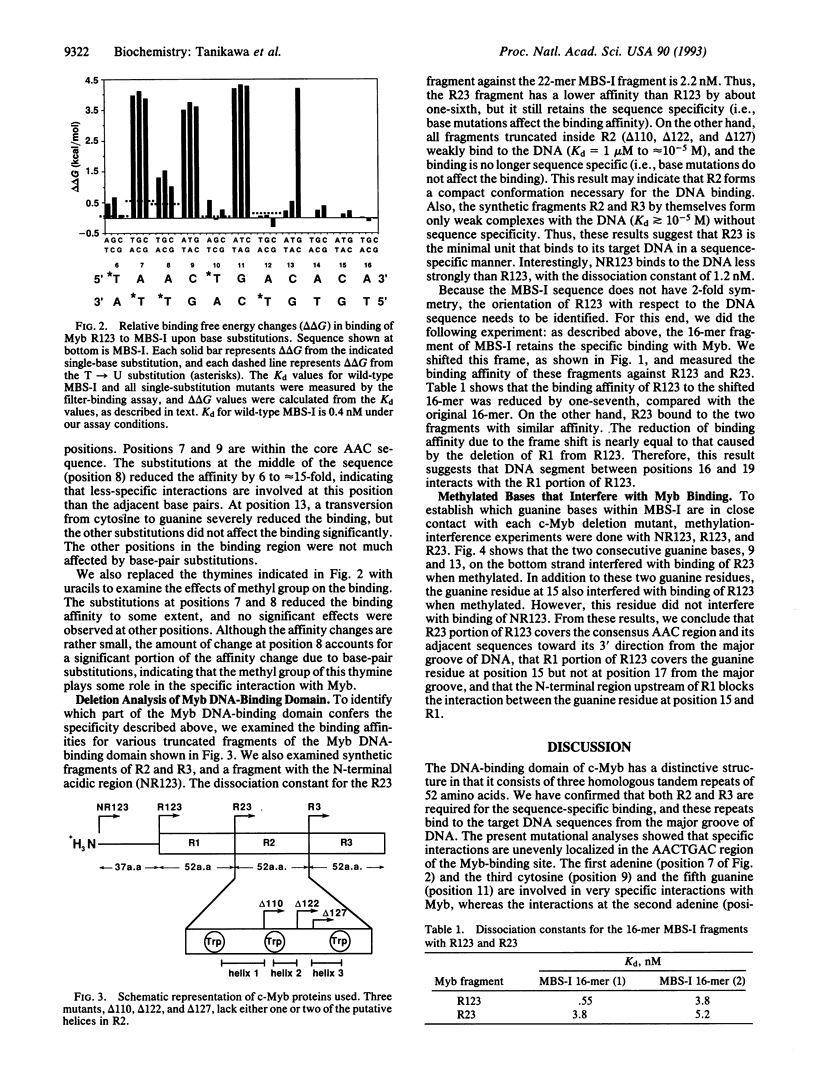
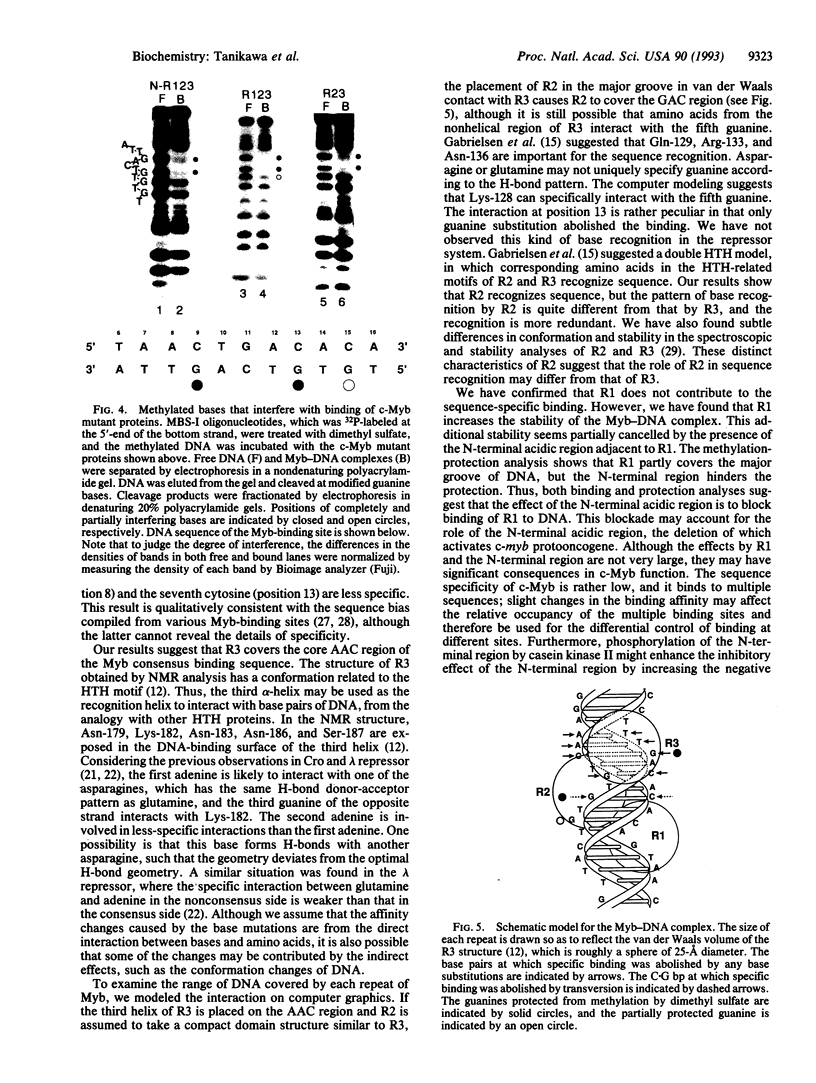
The DNA-binding domain of c-Myb consists of three homologous tandem repeats of 52 amino acids. The structure of the third (C-terminal) repeat obtained by NMR analysis has a conformation related to the helix-turn-helix motif. To identify the role of each repeat in the sequence recognition of DNA, we analyzed specific interactions between c-Myb and DNA by measuring binding affinities for systematic mutants of Myb-binding DNA sites and various truncated c-Myb mutants. We found that specific interactions are localized unevenly in the AACTGAC region in the consensus binding site of c-Myb: The first adenine, third cytosine, and fifth guanine are involved in very specific interactions, in which any base substitutions reduce the binding affinity by > 500-fold. On the other hand, the interaction at the second adenine is less specific, with the affinity reduction in the range of 6- to 15-fold. The seventh cytosine involves a rather peculiar interaction, in which only guanine substitution abolishes the specific binding. The binding analyses, together with the chemical protection analyses, showed that the c-Myb fragment containing the second and third repeats covers the AACTGAC region from the major groove of DNA in such an orientation that the third repeat covers the core AAC sequence. These results suggest that the third repeat recognizes the core AAC sequence very specifically, whereas the second repeat recognizes the GAC sequence in a more redundant manner. The first (N-terminal) repeat, which covers the major groove of DNA only partially, is not significant in the sequence recognition, but it contributes to increase the stability of the Myb-DNA complex. The presence of an N-terminal acidic region upstream of the first repeat, which is important for the activation of c-myb protooncogene, was found to reduce the binding affinity by interfering with the first repeat in binding to DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton I. A., Frampton J. Tryptophans in myb proteins. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):719–719. doi: 10.1038/336719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Specific DNA binding by c-Myb: evidence for a double helix-turn-helix-related motif. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1140–1143. doi: 10.1126/science.1887237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., de Blaquiere J. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA clones of the murine myb proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2003–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K. M., Reakes C. F., Watson R. J. Characterization of the sequence-specific interaction of mouse c-myb protein with DNA. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):161–169. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K. M., Watson R. J. Nucleotide preferences in sequence-specific recognition of DNA by c-myb protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3913–3919. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanei-Ishii C., Sarai A., Sawazaki T., Nakagoshi H., He D. N., Ogata K., Nishimura Y., Ishii S. The tryptophan cluster: a hypothetical structure of the DNA-binding domain of the myb protooncogene product. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19990–19995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Sippel A. E. The highly conserved amino-terminal region of the protein encoded by the v-myb oncogene functions as a DNA-binding domain. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2719–2725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Christenson E., Litchfield D. W., Krebs E. G., Eisenman R. N. Myb DNA binding inhibited by phosphorylation at a site deleted during oncogenic activation. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):517–522. doi: 10.1038/344517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagoshi H., Nagase T., Kanei-Ishii C., Ueno Y., Ishii S. Binding of the c-myb proto-oncogene product to the simian virus 40 enhancer stimulates transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3479–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagoshi H., Nagase T., Ueno Y., Ishii S. Transcriptional trans-repression by the c-myb proto-oncogene product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7315–7324. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Marknell A., Graf T. The v-myb oncogene product binds to and activates the promyelocyte-specific mim-1 gene. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1115–1125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90767-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina Y., Nakagoshi H., Imamoto F., Gonda T. J., Ishii S. Trans-activation by the c-myb proto-oncogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):107–117. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Hojo H., Aimoto S., Nakai T., Nakamura H., Sarai A., Ishii S., Nishimura Y. Solution structure of a DNA-binding unit of Myb: a helix-turn-helix-related motif with conserved tryptophans forming a hydrophobic core. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6428–6432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer E., Humphries E. H. RAV-1 insertional mutagenesis: disruption of the c-myb locus and development of avian B-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1630–1640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1630-1640.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. G., Ishii S., Nishina Y., Soe G., Gonda T. J. Characterization of alternate and truncated forms of murine c-myb proteins. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(4):259–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikumar P., Murali R., Reddy E. P. Role of tryptophan repeats and flanking amino acids in Myb-DNA interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8452–8456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Nagase T., Nakagoshi H., Gonda T. J., Ishii S. Delineation of three functional domains of the transcriptional activator encoded by the c-myb protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5758–5762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarai A., Takeda Y. Lambda repressor recognizes the approximately 2-fold symmetric half-operator sequences asymmetrically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6513–6517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarai A., Uedaira H., Morii H., Yasukawa T., Ogata K., Nishimura Y., Ishii S. Thermal stability of the DNA-binding domain of the Myb oncoprotein. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 3;32(30):7759–7764. doi: 10.1021/bi00081a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Potter M., Mushinski J. F. Two modes of c-myb activation in virus-induced mouse myeloid tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):380–392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L. The myb oncogene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 1;1032(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(90)90011-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Sarai A., Rivera V. M. Analysis of the sequence-specific interactions between Cro repressor and operator DNA by systematic base substitution experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):439–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Bishop J. M. Transcriptional activation by the v-myb oncogene and its cellular progenitor, c-myb. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K. Extension of the DNA binding consensus of the chicken c-Myb and v-Myb proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3043–3049. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]