Abstract
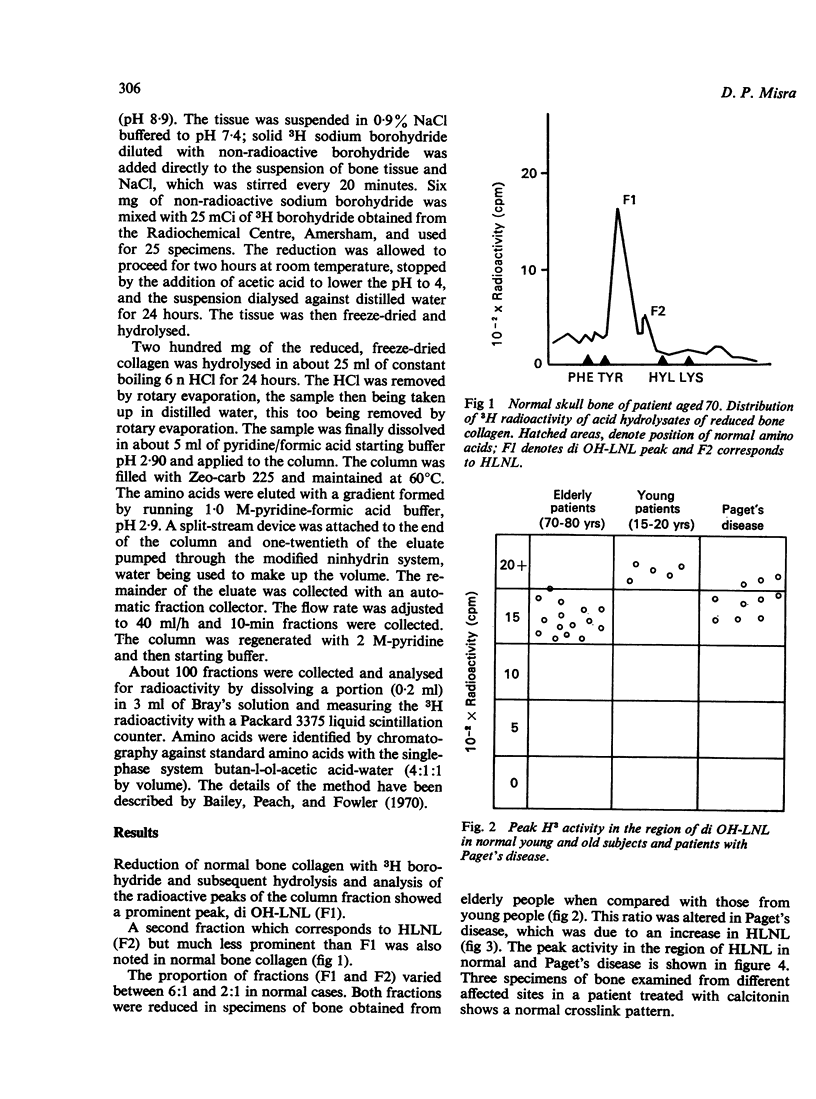
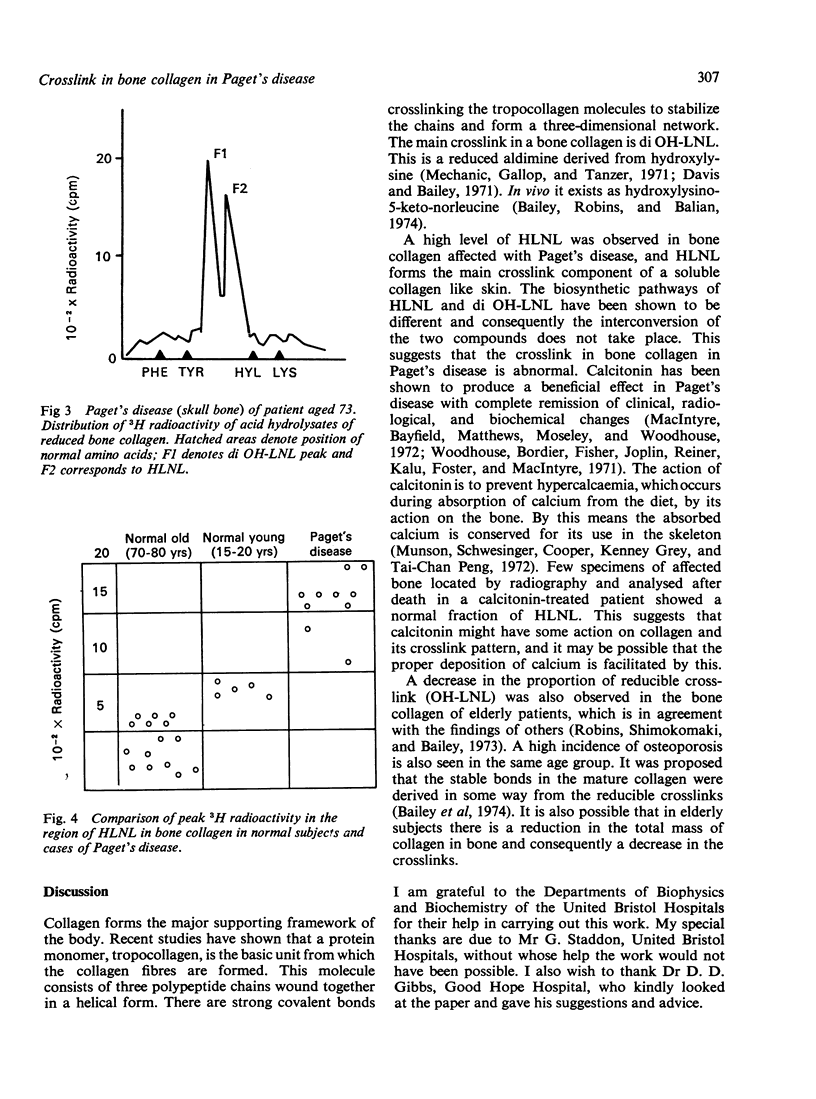
The crosslink in bone collagen was analysed in specimens of bone obtained at necropsy from cases of Paget's disease and compared with normal bone collagen of the same age. The specimens were stored at -20 degrees C before analysis. The predominant crosslink in a normal bone collagen was hydroxylysinohydroxynorleucine (di OH-LNL) (F1), which was designated syndesine in the past; another fraction, hydroxylysinorleucine (HLNL) (F2), musch less prominent than di OH-LNL, was also noted in a normal bone collagen. Both fractions were reduced in bone tissue of advancing age. The peak corresponding to HLNL was considerably increased in Paget's disease. This abnormality was constantly seen in specimens of bone from cases of Paget's disease, but the significance of the finging could not be assessed from the present investigation. Calcitonin has been shown to produce complete remission in Paget's disease and the crosslink pattern was found to be normal in specimens examined froma calcitonin-treated patient. This shows that calcitonin has some effect on the metabolism of collagen and a normal crosslink in such a situation lends support to this idea.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey A. J. Comparative studies on the nature of the crosslinks in the collagen of various fish tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):652–656. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Peach C. M., Fowler L. J. Chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Isolation and characterization of two intermediate intermolecular cross-links in collagen. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):819–831. doi: 10.1042/bj1170819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Robins S. P., Balian G. Biological significance of the intermolecular crosslinks of collagen. Nature. 1974 Sep 13;251(5471):105–109. doi: 10.1038/251105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. R., Bailey A. J. Chemical synthesis of the reduced form of an intermolecular crosslink of collagen: a re-evaluation of the structure of syndesine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 17;45(6):1416–1422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Glimcher M. J. Reducible crosslinks in hydroxylysine-deficient collagens of a heritable disorder of connective tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2594–2598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler L. J., Bailey A. J. Current concepts of the crosslinking in bone collagen. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972;85:193–206. doi: 10.1097/00003086-197206000-00035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechanic G., Gallop P. M., Tanzer M. L. The nature of crosslinking in collagens from mineralized tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):644–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P., Shimokomaki M., Bailey A. J. The chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Age-related changes in the reducible components of intact bovine collagen fibres. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):771–780. doi: 10.1042/bj1310771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhouse N. J., Bordier P., Fisher M., Joplin G. F., Reiner M., Kalu D. N., Foster G. V., MacIntyre I. Human calcitonin in the treatment of Paget's bone disease. Lancet. 1971 Jun 5;1(7710):1139–1143. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91657-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


