Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a multifunctional cytokine with distinct functions in angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, vascular permeability, and hematopoiesis. VEGF is a highly conserved, disulfide-bonded dimeric glycoprotein of 34 to 45 kDa produced by several cell types including fibroblasts, neutrophils, endothelial cells, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells, particularly T lymphocytes and macrophages. Six VEGF isoforms are generated as a result of alternative splicing from a single VEGF gene, consisting of 121, 145, 165, 183, 189, or 206 amino acids. VEGF121, VEGF145, and VEGF165 are secreted whereas VEGF183, VEGF189, and VEGF206 are cell membrane-bound. VEGF145 has a key role during the vascularization of the human ovarian follicle and corpus luteum, in the placentation and embryonic periods, and in bone and wound healing, while VEGF165 is the most abundant and biologically active isoform. VEGF has been linked with a number of vascular pathologies including cardiovascular diseases such ischemic heart disease, heart failure, stroke, and diabetes and its related complications. In this review we aimed to present some important roles of VEGF in a number of clinical issues and indicate its involvement in several phenomena from the initial steps of the embryonic period to cardiovascular diseases.
Key Words: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), Vascular pathogenesis
Introduction
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was first characterized as vascular permeability factor (VPF) by Senger et al. (1) in 1983. They reported that this protein promotes extravasation of proteins from tumor-associated blood vessels. VEGF was further characterized in 1989 when two groups independently identified a heparin-binding protein acting as a mitogen specific for endothelial cells. Subsequently, it was revealed that VPF and VEGF are the same protein encoded by a single gene (2, 3). VEGF is a potent mitogen with various functions involved in early stages of embryogenesis to several pathologies through somatic angiogenesis with a unique specificity for vascular endothelial cells (4, 5). In this review we aimed to present some important roles of VEGF in a number of clinical issues and discuss its family, gene, and structure.
VEGF family members, receptors and mode of action
There are five VEGF variants including VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, and placental growth factor, all described in mammals, VEGF-E found in Parapoxviridae, and VEGF-F, also called svVEG-F, for snake venom VEGF found in viper venom, each with structurally similar proteins involved in the regulation and differentiation of the vascular system, particularly in the blood and lymph vessels (4-7). Table 1 shows similarities and differences between the human VEGF family members.
Table 1.
| Gene | Sequence homology | Number of exons | Chromosomal localization | Splice variants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGF-A | 8 | 6p21.1 | 121,145,165*,183*,189*,206* | |
| VEGF-B | 45% homology with VEGF-A | 7 | 11q13 | 183,189,206 |
| VEGF-C | 30% homology with VEGF-A165 | 7 | 4q34 | - |
| VEGF-D | 61% homology with VEGF-C; 31% with VEGF-A165 |
7 | Xp22.31 | - |
| PlGF | 42% homology with VEGF-A | 14q24 | 131,152*,219 |
Splice variants that bind heparin sulfate proteoglycans
Among these subtypes, VEGF-A has a main role in mediating angiogenic effects (4, 6). VEGF-A binds and activates two receptors on the cell membrane of endothelial cells, namely VEGF receptor-1, also known as VEGFR-1 and Flt-1, and VEGF receptor-2, also known as VEGFR-2, FlK-1, and KDR. These receptors regulate physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis (6). VEGFR-2 is mainly associated with pathological angiogenesis, such as vascular network formation in tumors and diabetic retinopathy. VEGFR-1, however, has a dual role; in embryo it has a negative effect on angiogenesis via isolation of VEGF-A, while in adults it has a main influence on monocytes and endothelial cells that stimulate angiogenesis (4, 6, 9).
VEGF-A gene, related isoforms, and proteins
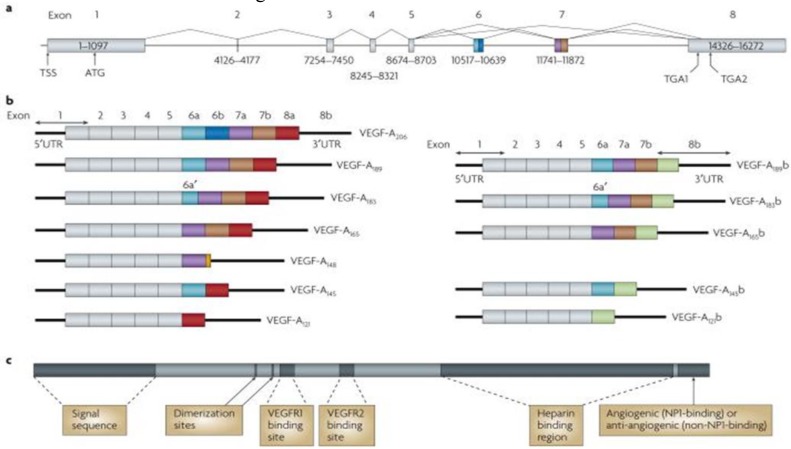
The human VEGF-A gene is organized in eight exons separated by seven introns and is located on chromosome 6p21.1. The coding region spans approximately 14 kb. Alternative exon splicing results in the generation of four isoforms with 121, 165, 189, and 206 amino acids, respectively, after signal sequence cleavage. The four isoforms are referred to as VEGF121, VEGF165, VEGF189, and VEGF206. VEGF165, the predominant isoform, lacks the residues encoded by exon 6, whereas VEGF121 lacks the residues encoded by exons 6 and 7. Less frequent splice variants have been also reported, including VEGF145, VEGF183, VEGF121b, VEGF145b,VEGF165b, and VEGF189b.The variants are reported to have, paradoxically, an inhibitory effect on VEGF induced mitogenesis (6). Figure 1 shows details of the VEGF gene, isoforms, and protein.
Fig. 1.
Protein and mRNA products of human vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A)(11). a Gene structure of human VEGF-A. VEGF-A spans 16,272 bp of chromosome 6p21.1 and consists of eight exons. Alternate 5′ and 3′ splice site selection in exons 6, 7, and 8 generate multiple isoforms. Exons 6 and 7 encode heparin-binding domains. The transcriptional start site (TSS) and translational start site (ATG) in exon 1 are indicated. Alternative stop codons within exon 8 are also indicated (TGA1 and TGA2). b | Alternative splicing can occur either at the 5′ donor splice site (for example, VEGF-A189 versus VEGF-A206) or the 3′ acceptor splice site (for example, VEGF-A189 versus VEGF-A165). Two mRNA isoform families are generated. The pro-angiogenic isoforms (VEGF-Axxx, left) are generated by proximal splice site (PSS) selection in exon 8 and the anti-angiogenic family (VEGF-Axxxb, right) from exon 8 distal splice site (DSS) choice. Thus, VEGF-A165, formed by PSS selection in exon 8, has VEGF-A165b as its DSS sister isoform, the DSS-selected mRNA encoding a protein of exactly the same length. Exon 6a’ occurs in VEGF-A183 as a result of a conserved alternative splicing donor site in exon 6a and is 18 bp shorter than full-length exon 6a. VEGF-A148 is a truncated isoform splicing from exon 7a into exon 8a out of frame and resulting in a premature stop codon. VEGF-A206b has not yet been identified. c | Protein structure of VEGF-A containing the dimerization sites and binding sites for heparin, VEGF-A receptor 1 (VEGFR1; encoded by exon 3) and VEGFR2 (encoded by exon 4), which are present in all isoforms. The six amino acids at the extreme carboxyl terminus of the protein can be either pro-angiogenic (CDKPRR, encoded by exon 8a) or anti-angiogenic (SLTRKD, encoded by exon 8b). The epitopes recognized by most commercial antibodies are in the region of the VEGF-A receptor-binding domains, present in VEGF-A isoforms of both families. UTR, untranslated region [ Adapted from (11)].
Solution of the crystal structure has shown that VEGF forms an antiparallel homodimer covalently linked by two disulfide bridges (6, 10) (Figure 1). This mode of dimerization is similar to that of the PDGF monomers. VEGF121 is an acidic polypeptide that fails to bind heparin. VEGF189 and VEGF206 are highly basic and bind heparin with high affinity. VEGF121 is a freely diffusible protein. In contrast, VEGF189 and VEGF206 are almost completely sequestered in the extracellular matrix.
VEGF165 has intermediate properties, because it is secreted, but a significant fraction remains bound to the cell surface and extracellular matrix. Several studies suggest that VEGF165 has optimal characteristics of both bioavailability and biological potency (4, 6, 10).
Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis
The formation of the vascular system is a prerequisite for vertebrate embryogenesis and involves two fundamental processes: vasculogenesis, defined as the differentiation of endothelial cell progenitors and their assembly into the primary capillary plexus, and angiogenesis, the sprouting of new capillaries from pre-existing vessels (6).
Vascular system in embryonic period
Induction by fibroblast growth factors of mesoderm during gastrulation leads to blood-forming tissue, including angioblasts and hemopoietic cells, which together constitute the blood islands of the yolk sac. The differentiation of angioblasts from mesoderm and the formation of primitive blood vessels from angioblasts at or near the site of their origin are the two distinct steps during the onset of vascularization that are defined as vasculogenesis. The central role of VEGF in embryonic angiogenesis was illustrated in heterozygote knock-out mice suffering from fatal deficiencies in vascularization (5). Although vasculogenesis occurs mainly during fetal development, recruitment of angioblasts from bone marrow and peripheral blood in response to ischemic insult has been described in adults (12, 13).
Table 2.
Properties of VEGFs
| Ligand | Isoforms | Receptor | Solubility | Source in adults | Biological activities | Phenotype of knockout mouse |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGF-A | VEGF-A121, VEGF-A165 VEGF-A189, VEGF-A206 (also VEGF-A138/145/162/165b have been described) | VEGFR-1 and R-2, VEGF165 binds to neuroplin-1 and -2, VEGF145 neuroplin-2 | VEGF121 soluble, longer forms bind heparin sulfates with increasing affinity | Almost all vascularized tissues, especially fenestrated and sinusoidal endothelium, up-regulated by ischemia (via HIF-1α) | Vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, vascular homeostasis, vascular permeability, and recruitment of bone marrow-derived cells | Loss of even single VEGF allele leads to embryonic lethality due to impaired vasculogenesis and angiogenesis |
| PlGF | PlGF131 (PlGF-1), PlGF152 (PlGF-2), PlGF203 (PlGF-3) | VEGFR-1, PLGF152 binds neuroplin-1 and -2 | PlGF131 and PlGF203 soluble, PlGF152 binds heparin sulfate | Placenta, thyroid, lung, and goiter | Angiogenesis, monocyte migration, recruitment of bone marrow-derived cells, up-regulation of VEGF-A | Almost-normal phenotype and fertile with minor defects in vascular growth in pathological conditions |
| VEGF-B | VEGF-B167 and VEGF-B186 | VEGF-1 and neuroplin-1 | VEGF-B167 binds heparin sulfates, VEGF186 soluble | Heart, skeletal muscle, and vascular smooth muscle cells | Angiogenesis, recruitment of bone marrow-derived cells | Almost-normal phenotype with minor possible defects: reduced heart size, prolonged PQ-time, impaired recovery from ischemia |
| VEGF-C (VEGF-2) | Unprocessed and proteolytically processed mature forms | VEGF-2, R-3, and neuroplin-2, processing increases receptor affinity | Soluble | Neuroendocrine organs, lung, heart, kidney, and vascular smooth muscle cells | Development of lymphatics and lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis | Lethal because of impaired development of lymphatics |
| VEGF-D | Unprocessed and proteolytically processed mature forms | VEGF-2 and VEGF-3, processing increases receptor affinity | Soluble | Neuroendocrine organs, lung, heart, skeletal muscle, intestine, and vascular smooth muscle cells | Lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis | Normal |
| VEGF-E | --- | VEGF-2 and neuroplin-1 | Soluble | Virus-derived | Angiogenesis | --- |
| VEGF-F | --- | VEGFR-2 | Binds to heparin sulfates | Snake venom | Angiogenesis and vascular permeability | --- |
HIF = hypoxia-inducible factor; PlGF = placental growth factor; VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor
Vasculogenesis steps and angiogenesis forms
Vasculogenesis consists of three major steps: induction of hemangioblasts and angioblasts (mediated mainly through fibroblast growth factor (FGF)), assembly of primordial vessels (mediated mainly by vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor system, VEGF/VEGFR), and transition from vasculogenesis to angiogenesis (9). Angiogenesis represents the development of new vessels from pre-existing vessels. Two forms of angiogenesis have been described: sprouting and non-sprouting angiogenesis or intussusceptive microvascular growth (intussusception) (14). The sprouting process is based on endothelial cell migration, proliferation, and tube formation. Intussusception divides existing vessel lumens by formation and insertion of tissue folds and columns of interstitial tissue into the vessel lumen (14). Physiologic angiogenesis plays an important role in wound and fracture healing, endometrial growth, embryo implantation, and placentation. In contrast, pathologic angiogenesis underlies pathophysiology of the following conditions: tumor growth and metastasis, rheumatoid arthritis, retinopathies, chronic inflammation, and psoriasis (15). Therapeutic angiogenesis, defined as the use of biological agents or bioactive materials to stimulate the growth of new blood vessels, was developed for the treatment of ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and delayed wound healing (16).
Angiogenesis regulatory factors
Several regulatory factors (Table 3) play a role in angiogenesis. Among them, during angiogenesis, VEGF interacts with several other angiogenic factors and plays an important role in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, cell survival, nitric oxide (NO) production, and release of other growth factors (7).
Table 3.
Regulatory factors of angiogenesis
| Protein |
|---|
| a) Angiogenic Factors |
| FGF-β |
| FGF-α |
| Angiogenin |
| Transforming growth factor-α |
| Transforming growth factor-β |
| Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF) |
| Platelet-derived endothelial growth factor |
| Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor |
| Placental growth factor |
| Interleukin-8 |
| Hepatocyte growth factor |
| Proliferin |
| Angiopoietin-1 |
| Leptin |
| hCG human chorionic gonadotropin |
| Estrogens |
| b) Angiostatic factors (natural) |
| Angiostatin |
| Thrompospodin |
| Endostatin |
| Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| Prolactin |
| Thromboxane A2 |
| c) Angiostatic factors (therapeutic) |
| Thalidomide |
| Steroids |
FGF-β = basic fibroblast growth factor; FGF-α = acidic FGF; VPF = vascular permeability factor
Wide implications of VEGF from physiological circumstance to pathological conditions
The ability of VEGF to promote monocyte chemotaxis was the earliest evidence that VEGF can affect blood cells. Subsequently, VEGF was reported to have hematopoietic effects, inducing colony formation by mature subsets of granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells, regulation of osteoclast differentiation, stimulation of surfactant production, and neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects on neuronal and glial cells. Notably, VEGF infusion to adult mice inhibits dendritic cell development, leading to the hypothesis that VEGF facilitates tumor growth by allowing evasion of tumors from the host immune system. Also, VEGF increased production of B cells and the generation of immature myeloid cells. Some studies suggest that VEGF controls hematopoietic stem cells survival during hematopoietic repopulation (17).
VEGF is also known as vascular permeability factor, based on its ability to induce vascular leakage. The permeability-enhancing activity of this molecule underlies dominant roles in inflammation and other pathological conditions. In accordance with a role in the regulation of vascular permeability, VEGF induces endothelial fenestration in some vascular beds and cultured adrenal endothelial cells (6, 10). Some studies have shown a critical role for nitric oxide (NO) in VEGF-induced vascular permeability, as well as angiogenesis. Fukumura et al. (18) verified the relative contribution of the NO synthase (NOS) isoforms, inducible NOS (iNOS) and endothelial NOS (eNOS), to these processes. Thereby, elevated circulating VEGF has been observed in vascular diseases including ischemic heart disease, heart failure, and stroke, and in various other disorders including diabetes, cognitive decline and dementia, reproductive disorders such as polycystic ovary disease and endometriosis, immunoallergic-inflammatory diseases such as asthma and rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, ophthalmologic disorders such as macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, and several neoplastic diseases (19).
Wound healing
Skin-wound healing starts immediately after injury and consists of three phases: inflammation, proliferation, and maturation. These phases proceed with complicated but well-organized interactions between various tissues and cells. Wounding can destroy blood vessels and create a hypoxic environment because of poor perfusion, and therefore provides an appropriate environment for hypoxia inducible factor alpha stabilization. At the first phase of wounding, induced hypoxia leads to rapid infiltration of inflammatory cells including neutrophils, mast cells, lymphocytes, and macrophages. The formation of granulation tissue, which is necessary for the last phase of wound healing, starts at the wound space approximately four days after injury. Numerous new capillaries endow the new stroma with its granular appearance. Macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells move into the wound space at the same time. Macrophages not only augment inflammatory responses but also secrete VEGF and FGF, eventually promoting angiogenesis (20, 21).
Proangiogenic roles of macrophages in diabetic wounds are similar to those in wounds inflicted by physical injuries. However, severe hypoxia in diabetic wounds often fails to directly trigger effective angiogenesis because of significant cell death under such conditions. As a practical conclusion, the hypoxia inducible factor pathway offers promising therapeutic targets to promote angiogenesis in wounds (20) (1).
Diabetes and its related complication s
Hiroaki Kakizawa et al. (22) reported that plasma VEGF concentrations are higher in diabetic patients who are hospitalized because of poor glycemic control than in healthy subjects. According to them, the increased plasma VEGF concentrations declined along with decreases in fasting plasma glucose and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) as a result of treatment. The significant and independent correlation between plasma VEGF concentrations and HbA1c suggests that chronic hyperglycemia may increase plasma levels of VEGF, and that reduction of high VEGF levels may be possible by improvement of glycemic control (23). Prolonged hyperglycemia activates the sorbitol pathway and induces intracellular anaerobic conditions and hemodynamic change (24). These conditions may facilitate the production of VEGF that may contribute to diabetic vascular complications and arteriosclerosis. Interestingly, the increase in VEGF production has a reverse correlation with the reduction of hyperglycemia. Santilli et al. (25) suggested increased serum VEGF levels as a predicting risk factor for the development of persistent microalbuminuria in young type 1 diabetic patients. Another study indicates that VEGF mRNA and urinary excretion of VEGF are increased in diabetic nephropathy (26).
Most diabetic patients, especially those with poor glycemic control, develop diabetic retinopathy, which remains the major cause of new-onset blindness among diabetic adults. Diabetic retinopathy is characterized by vascular permeability and increased tissue ischemia and angiogenesis.
VEGF has initially drawn much attention as an important mediator of retinal ischemia– associated intraocular neovascularization (4, 6, 10). VEGF is produced from many cell types within the eye and past studies have shown that VEGF levels are markedly elevated in vitreous and aqueous fluids in the eyes of individuals with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). Recently there has been success in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy as well as other ocular vasculopathies with anti-VEGF medication. Bevacizumab (Avastin, Genentech, South San Francisco, CA) is a recombinant, humanized monoclonal anti-VEGF antibody that binds all VEGF isoforms and exerts its neutralizing effect by inhibiting the VEGF–receptor interaction, thus blocking both increased vascular permeability and angiogenesis. The drug was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration initially for intravenous use for metastatic colorectal cancer. Bevacizumab has been administered off label for the treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration and other retinal vascular conditions with encouraging results (6).
Hypertension
VEGF-A is highly expressed by renal glomerular epithelial cells (podocytes) and plays an important role in the formation of the glomeruli during development (27), but curiously is also highly expressed within the adult glomerulus despite little or no angiogenesis occurring beyond development. VEGF isoform expression in glomeruli is heterogeneous. Individual human glomeruli express one, two, or all three of these (VEGF121, VEGF165, VEGF189) main isoforms at the mRNA level. VEGF189 and VEGF165 are most predominantly found in the renal glomerulus. Minor VEGF mRNA splice variants (VEGF206, VEGF183, VEGF148, and VEGF145) have also been reported, but are less well characterized than the three main isoforms (28).
Obesity and metabolic syndrome
Adipose tissue is considered as the largest endocrine gland because it produces free fatty acids, hormones, growth factors, and cytokines such as leptin, adiponectin, resistin, VEGF, insulin growth factor (IGF-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) (29). Epidemiological studies show that the visceral fat accumulation ”the predominant driving force behind the metabolic syndrome MetS “ (30) is the most important determining factor for VEGF circulating levels. During embryogenesis, adipose tissue development is spatially and temporally associated with microvessel growth. In developing embryos, the formation of primitive fat organs occurs at the perivascular site (29). Endothelial cells isolated from different adipose tissues differ in their proliferative capacity, which suggests that adipocytes play both guidance and maintenance roles in vascular development. A recent study suggests that adipocytes and their accompanying endothelial cells might share a common progenitor that could differentiate into adipocytes or endothelial lineages depending upon exposure to different environments (29) (145). Accumulating evidence shows that capillary endothelial cells communicate with adipocytes via paracrine signaling pathways, extracellular components, and direct cell-cell interactions (31).
Adipose tissue has been long known to promote wound healing and revascularize ischemic tissues including myocardium (31). These findings suggest that adipose tissue produces angiogenic molecules (31). Experimental angiogenesis assays show that conditioned media obtained from preadipocytes and tissue homogenates from omentum or subcutaneous fat induce angiogenesis in chick chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) and mouse cornea (31). It seems that bone marrow-derived circulating endothelial precursor cells do not significantly participate in adipose neovascularization, although these cells are known to contribute to neovascularization in other tissues. For instance, VEGF is a potent chemoattractant for inflammatory cells and contributes to mobilization of bone marrow-derived circulating endothelial precursor cells, which are involved in tumor neovascularization. Interestingly, expression levels of VEGF are only moderately up-regulated in growing adipose tissue although VEGF is a main angiogenic factor in omentum (29).
In rapidly extending adipose tissue, hypoxia is another important factor for vascular growth and remodeling. In response to hypoxia, adipose tissues produce hypoxia inducible factor 1a– induced angiogenic factors such as VEGF, leptin, TNF-α, and PAI-1, which regulate angiogenesis and vasculogenesis (32). Thus it is reasonable to speculate that expansion of adipose tissue is associated with local hypoxia, which contributes to angiogenesis by induction of a number of growth factors.
Leptin is an adipocyte-derived hormone that regulates food intake and energy homeostasis. Functional impairment of leptin leads to severe obesity, diabetes, and infertility. Interestingly, leptin is also defined as a potent angiogenic factor. In addition to its direct angiogenic activity, leptin up-regulates VEGF mRNA expression via activation of the Jak/Stat3 signaling pathway (33). Among all adipose tissues examined in the body, omentum expresses the highest level of VEGF (29). Localization studies have shown that adipocytes are the primary source of VEGF, which may act as an angiogenic and vascular survival factor for the omental vasculature. Additionally, adipose- infiltrated inflammatory cells and adipose stromal cells also significantly contribute to VEGF production (29). Anatomically, visceral adipose tissue, which is the main indicator of waist circumference, is present mainly in the mesentery and omentum, and drains directly through the portal circulation to the liver (34).
Several documents indicate that serum VEGF concentrations are positively correlated with body mass index (BMI) and visceral obesity (35, 36). Michaela Loebig et al. (37) reported a positive correlation between plasma VEGF concentrations and BMI over a large range of BMI groups in a healthy population. They also demonstrated significantly higher concentrations of plasma VEGF in obese subjects than in normal and low weight individuals.
Lian-Yu Lin et al. (38), in their proposed model, demonstrated that obesity directs to an inflammatory process, which could be the precursor of MetS components including insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.
Gaby Kressel et al. (39) investigated the relationship between vascular and systemic markers of low-grade inflammation such as high sensitive c-reactive protein (hs-CRP ), soluble vascular adhesion molecule 1(sVCAM-1), soluble intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), plasminogen activating inhibitor-1(PAI-1), fibrinogen, and cardiovascular traditional risk factors and the MetS.
It seems that the study of the association of circulating VEGF with MetS in human samples has only recently begun; therefore, documentable reports in this field are scarce (40-43). However, a few reports have shown an association of circulating VEGF with the MetS, as well as with a number of its components (40, 41). Some evidence indicates the associations of some single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with MetS via a genome-wide association study (44) and candidate gene approach (45, 46). It is not yet clear whether the elevated VEGF level is a deleterious factor or a physiologic/negative feedback response to prevent the progress of ischemia in metabolic linked ischemia as well as MetS.
Atherosclerosis
From endothelial dysfunction to plaque rupture, VEGF directly and indirectly attracts inflammatory cells into the intima in various stages of atherogenesis. Human monocytes express the receptor VEGFR-1 (flt-1), and administration of VEGF has been shown to significantly increase the number of mature macrophages in the arterial endothelium within weeks. This accumulation of macrophages was associated with increased total plaque size. VEGF primes endothelial cells to secrete increased amounts of E-selectin, an adhesion molecule necessary for trans-epithelial migration of leukocytes. Endothelial cells ‘‘pretreated’’ with VEGF also produce significantly higher amounts of tissue factor after TNF-α exposure than cells exposed to TNF-α alone. If the plaque contents later become exposed, the accumulation of tissue factor could increase the risk of a thrombotic event. Not surprisingly then, serum VEGF level has been shown to predict adverse cardiac events in patients with known atherosclerosis (47). For example, men with unstable angina and serum VEGF concentrations ≥0.3 pg/L were 2.5 times more likely to die of myocardial infarction within six months of cardiac event than those with serum VEGF levels <0.3 pg/L (48).
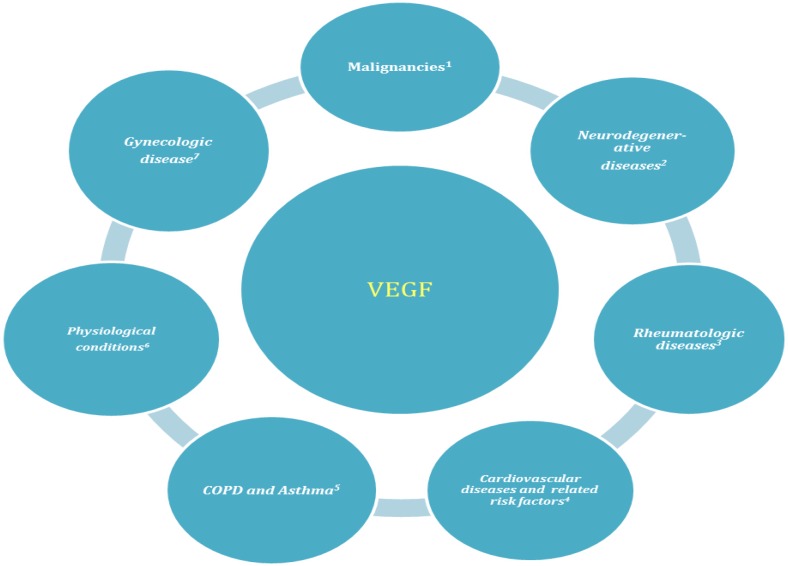
Fig. 2.
VEGF involved in several physiological and pathological conditions
1) Breast, colorectal, prostate, gastric, esophageal, hepatic, ovarian cancers, and hematologic malignancies. 2) Alzheimer, multiple sclerosis, age related macular degeneration. 3) Rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Behjat disease and systemic sclerosis. 4) Hypertension, obesity, diabetes type 2 (diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy), hyperlipidemia, MetS. 5) Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. 6) Response to ovulation, placentation, embryonic development, wound and bone fracture healing. 7) Pre-eclampsia, endometriosis.
herosclerosis, localized hypoxia and oxidative stress in the vessel wall accelerates activation of HIF-1a and expression of VEGF (49). Subsequent intra-plaque angiogenesis leads to neovascularization of the plaque vasavasorum, leaky capillaries, hemorrhage, and progression to a vulnerable plaque phenotype.
VEGF plays an important role in this cascade by not only stimulating the formation of new intra-plaque capillaries, but also attracting macrophages and T lymphocytes into the subintimal space (49, 50).
These cells further produce pro-angiogenic factors such as IL-8, TNF-a, IL-17, and more VEGF (50). When fragile new intra-plaque capillaries bleed, macrophages phagocytize the lipid-rich debris, become foam cells, and eventually add to the plaque’s necrotic core (50-52). Taken together, the contribution of VEGF to athergenesis has been challenged.
References
- 1.Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983 Feb;219(4587):983–5. doi: 10.1126/science.6823562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Keck PJ, Hauser SD, Krivi G, Sanzo K, Warren T, Feder J, et al. Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science. 1989 Dec;246(4935):1309–12. doi: 10.1126/science.2479987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec;246(4935):1306–9. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Azimi-Nezhad M, Stathopoulou MG, Bonnefond A, Rancier M, Saleh A, Lamont J, Fitzgerald P, et al. Associations of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) with adhesion and inflammation molecules in a healthy population. Cytokine. 2013 Feb;61(2):602–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.10.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Muller YA, Li B, Christinger HW, Wells JA, Cunningham BC, de Vos AM. Vascular endothelial growth factor: crystal structure and functional mapping of the kinase domain receptor binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jul;94(14):7192–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.14.7192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003 Jun;9(6):669–76. doi: 10.1038/nm0603-669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Thanigaimani S, Kichenadasse G, Mangoni AA. The emerging role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in vascular homeostasis: lessons from recent trials with anti-VEGF drugs. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2011 May;9(3):358–80. doi: 10.2174/157016111795495503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tammela T, Enholm B, Alitalo K, Paavonen K. The biology of vascular endothelial growth factors. Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Feb;15;65(3):550–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Flamme I, Frolich T, Risau W. Molecular mechanisms of vasculogenesis and embryonic angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 1997 Nov;173(2):206–10. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199711)173:2<206::AID-JCP22>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev. 2004 Aug;25(4):581–611. doi: 10.1210/er.2003-0027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Harper SJ, Bates DO. VEGF-A splicing: the key to anti-angiogenic therapeutics? . Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(11):880–7. doi: 10.1038/nrc2505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Risau W, Flamme I. Vasculogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:73–91. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.11.110195.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Takahashi T, Kalka C, Masuda H, Chen D, Silver M, Kearney M, et al. Ischemia- and cytokine-induced mobilization of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells for neovascularization. Nat Med. 1999 Apr;5(4):434–8. doi: 10.1038/7434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Folkman J, Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun;267(16):10931–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1995 Jan;1(1):27–31. doi: 10.1038/nm0195-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hockel M, Schlenger K, Doctrow S, Kissel T, Vaupel P. Therapeutic angiogenesis. Arch Surg. 1993 Apr;128(4):423–9. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420160061009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gerber HP, Malik AK, Solar GP, Sherman D, Liang XH, Meng G, et al. VEGF regulates haematopoietic stem cell survival by an internal autocrine loop mechanism. Nature. 2002 Jun;417(6892):954–8. doi: 10.1038/nature00821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fukumura D, Gohongi T, Kadambi A, Izumi Y, Ang J, Yun CO, et al. Predominant role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb;98(5):2604–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.041359198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Debette S, Visvikis-Siest S, Chen MH, Ndiaye NC, Song C, Destefano A, et al. Identification of cis- and trans-acting genetic variants explaining up to half the variation in circulating vascular endothelial growth factor levels. Circ Res. 2011 Aug;109(5):554–63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fong GH. Mechanisms of adaptive angiogenesis to tissue hypoxia. Angiogenesis. 2008 Mar;11(2):121–40. doi: 10.1007/s10456-008-9107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kondo T, Ishida Y. Molecular pathology of wound healing. Forensic Sci Int. 2010 Dec;203(1-3):93–8. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2010.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kakizawa H, Itoh M, Itoh Y, Imamura S, Ishiwata Y, Matsumoto T, et al. The relationship between glycemic control and plasma vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelin-1 concentration in diabetic patients. Metabolism. 2004 May;53(5):550–5. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2003.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zorena K, Mysliwska J, Mysliwiec M, Rybarczyk-Kapturska K, Malinowska E, Wisniewski P, et al. Association between vascular endothelial growth factor and hypertension in children and adolescents type I diabetes mellitus. J Hum Hypertens. 2010 Nov;24(11):755–62. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2010.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tsilibary EC. Microvascular basement membranes in diabetes mellitus. J Pathol. 2003 Jul;200(4):537–46. doi: 10.1002/path.1439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Santilli F, Spagnoli A, Mohn A, Tumini S, Verrotti A, Cipollone F, et al. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor serum concentrations may help to identify patients with onset of type 1 diabetes during childhood at risk for developing persistent microalbuminuria. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001 Aug;86(8):3871–6. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.8.7752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Murata T, Nagai R, Ishibashi T, Inomuta H, Ikeda K, Horiuchi S. The relationship between accumulation of advanced glycation end products and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human diabetic retinas. Diabetologia. 1997 Jul;40(7):764–9. doi: 10.1007/s001250050747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wakelin SJ, Marson L, Howie SE, Garden J, Lamb JR, Forsythe JL. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the kidney in health and disease. Nephron Physiol. 2004;98(3):73–9. doi: 10.1159/000080686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Foster RR, Hole R, Anderson K, Satchell SC, Coward RJ, Mathieson PW, et al. Functional evidence that vascular endothelial growth factor may act as an autocrine factor on human podocytes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003 Jun;284(6):F1263–F1273. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00276.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cao Y. Angiogenesis modulates adipogenesis and obesity. J Clin Invest. 2007 Sep;117(9):2362–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI32239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Grundy SM. Metabolic syndrome: a multiplex cardiovascular risk factor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Feb;92(2):399–404. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sun K, Kusminski CM, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue remodeling and obesity. J Clin Invest . 2011;1217(6):2094–2101. doi: 10.1172/JCI45887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fitzpatrick TE, Graham CH. Stimulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in immortalized human trophoblast cells cultured under low levels of oxygen. Exp Cell Res. 1998 Nov;245(1):155–62. doi: 10.1006/excr.1998.4240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Suganami E, Takagi H, Ohashi H, Suzuma K, Suzuma I, Oh H, et al. Leptin stimulates ischemia-induced retinal neovascularization: possible role of vascular endothelial growth factor expressed in retinal endothelial cells. Diabetes. 2004 Sep;53(9):2443–8. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.9.2443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ibrahim MM. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: structural and functional differences. Obes Rev. 2010 Jan;11(1):11–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Miyazawa-Hoshimoto S, Takahashi K, Bujo H, Hashimoto N, Saito Y. Elevated serum vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with visceral fat accumulation in human obese subjects. Diabetologia. 2003 Nov;46(11):1483–8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-003-1221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Silha JV, Krsek M, Sucharda P, Murphy LJ. Angiogenic factors are elevated in overweight and obese individuals. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005 Nov;29(11):1308–14. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Loebig M, Klement J, Schmoller A, Betz S, Heuck N, Schweiger U, et al. Evidence for a relationship between VEGF and BMI independent of insulin sensitivity by glucose clamp procedure in a homogenous group healthy young men. PLoS One. 2010 Sep;5(9):e12610. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lin LY, Kuo HK, Li HY, Hwang JJ, Lin JW. Confirming a biological pathway in the metabolic syndrome--insight from the NHANES 1999-2002. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008 Dec;16(12):2676–81. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kressel G, Trunz B, Bub A, Hulsmann O, Wolters M, Lichtinghagen R, et al. Systemic and vascular markers of inflammation in relation to metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in adults with elevated atherosclerosis risk. Atherosclerosis. 2009 Jan;202(1):263–71. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jialal I, Fadini GP, Pollock K, Devaraj S. Circulating levels of endothelial progenitor cell mobilizing factors in the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2010 Dec;106(11):1606–8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.07.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lieb W, Safa R, Benjamin EJ, Xanthakis V, Yin X, Sullivan LM, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor, its soluble receptor, and hepatocyte growth factor: clinical and genetic correlates and association with vascular function. Eur Heart J. 2009 May;30(9):1121–7. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tarantino G, Lobello R, Scopacasa F, Contaldo F, Pasanisi F, Cirillo M, et al. The contribution of omental adipose tissue to adipokine concentrations in patients with the metabolic syndrome. Clin Invest Med. 2007;30(5):E192–E199. doi: 10.25011/cim.v30i5.2895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wada H, Satoh N, Kitaoka S, Ono K, Morimoto T, Kawamura T, et al. Soluble VEGF receptor-2 is increased in sera of subjects with metabolic syndrome in association with insulin resistance. Atherosclerosis. 2010 Feb;208(2):512–7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.07.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zabaneh D, Mackay IJ. Genome-wide linkage scan on estimated breeding values for a quantitative trait. BMC Genet. 2003 Dec;4 (Suppl 1):S61. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-4-S1-S61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kraja AT, Vaidya D, Pankow JS, Goodarzi MO, Assimes TL, Kullo IJ, et al. A bivariate genome-wide approach to metabolic syndrome: STAMPEED consortium. Diabetes. 2011 Apr;60(4):1329–39. doi: 10.2337/db10-1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Povel CM, Boer JM, Reiling E, Feskens EJ. Genetic variants and the metabolic syndrome: a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2011 Nov;12(11):952–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Armstrong AW, Voyles SV, Armstrong EJ, Fuller EN, Rutledge JC. Angiogenesis and oxidative stress: common mechanisms linking psoriasis with atherosclerosis. J Dermatol Sci. 2011 Jul;63(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2011.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Heeschen C, Dimmeler S, Hamm CW, Boersma E, Zeiher AM, Simoons ML. Prognostic significance of angiogenic growth factor serum levels in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2003 Feb;4;107(4):524–30. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000048183.37648.1a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Holm PW, Slart RH, Zeebregts CJ, Hillebrands JL, Tio RA. Atherosclerotic plaque development and instability: a dual role for VEGF. Ann Med. 2009;41(4):257–64. doi: 10.1080/07853890802516507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Armstrong AW, Voyles SV, Armstrong EJ, Fuller EN, Rutledge JC. Angiogenesis and oxidative stress: common mechanisms linking psoriasis with atherosclerosis. J Dermatol Sci. 2011 Jul;63(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2011.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Celletti FL, Waugh JM, Amabile PG, Brendolan A, Hilfiker PR, Dake MD. Vascular endothelial growth factor enhances atherosclerotic plaque progression. Nat Med. 2001 Apr;7(4):425–9. doi: 10.1038/86490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Stannard AK, Khurana R, Evans IM, Sofra V, Holmes DI, Zachary I. Vascular endothelial growth factor synergistically enhances induction of E-selectin by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007 Mar;27(3):494–502. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000255309.38699.6c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]