Abstract
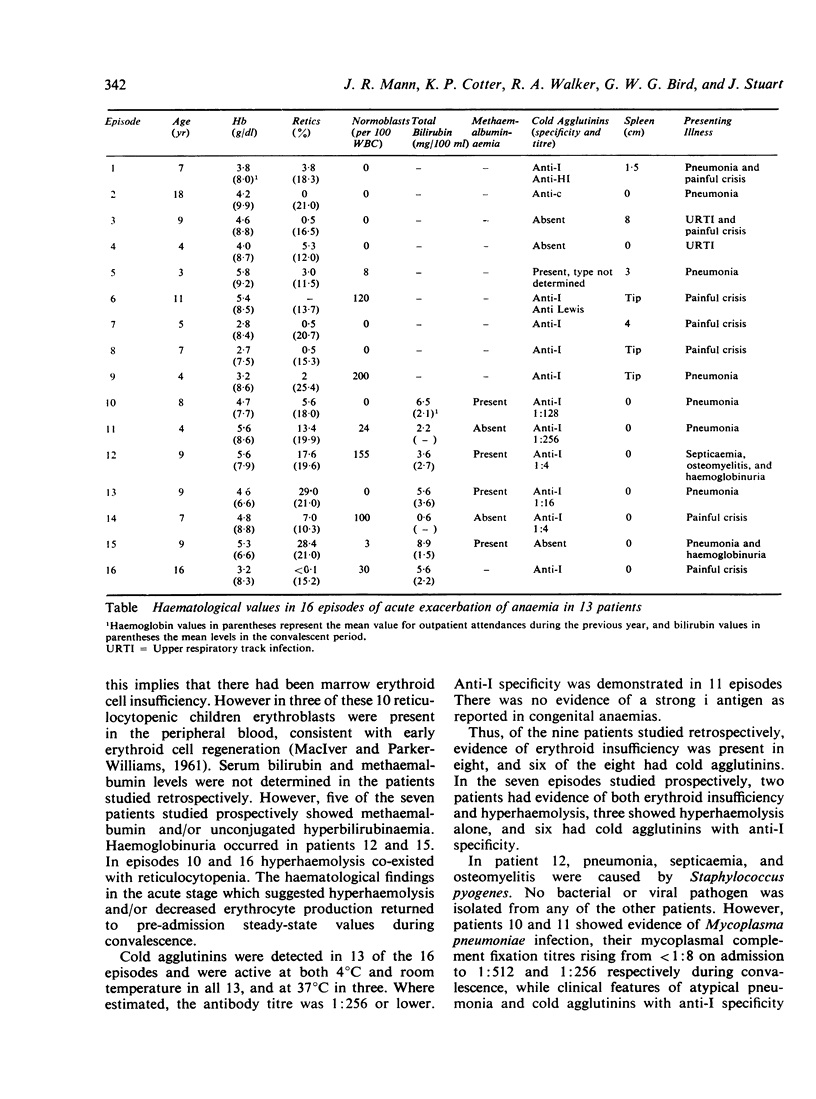
Sixteen episodes of acute anaemia necessitating urgent blood transfusion have been investigated in 13 children with sickle cell anaemia. In five out of seven episodes there was evidence of increased haemolysis while in 10 out of 16 episodes a profound fall in reticulocyte count indicated marrow erythroid cell failure. Cold agglutinins active at room temperature were detected in 13 episodes, and anti-I specificity was demonstrated in 11. Warmed blood of homologous ABO and Rhesus groups was administered without complication despite difficulty with cross-matching. The exacerbation of anaemia was not due to folate lack, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency or splenic sequestration, and an infectious agent appeared responsible. The degree of anaemia in homozygous sickle cell disease is usually constant during asymptomatic periods. An episode of sudden profound anaemia (anaemic crisis) may, however, result from marrow hypoplasia, an exacerbation of haemolysis, splenic sequestration, or folate deficiency.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURCHMORE J. W., BUCKLE R. M., LEHMANN H., JENKINS W. J. Agglutinating-sickling arterial thrombosis. An unusual case of sickle-cell haemoglobin-C-disease. Lancet. 1962 Nov 17;2(7264):1008–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92699-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURCHMORE J. W., BUCKLE R. M., LEHMANN H., JENKINS W. J. Agglutinating-sickling arterial thrombosis. An unusual case of sickle-cell haemoglobin-C-disease. Lancet. 1962 Nov 17;2(7264):1008–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92699-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett-Connor E. Acute pulmonary disease and sickle cell anemia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Aug;104(2):159–165. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.2.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G. W., Wingham J. Anti-I autoantibody acting preferentially in albumin. Br J Haematol. 1973 Aug;25(2):280–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARMOT G., REYNAUD R., BERGOT J. CRYOGLOBULINAEMIA AND COLD AGGLUTININS IN PAINFUL CRISES OF SICKLE-CELL ANAEMIA. Lancet. 1963 Sep 14;2(7307):540–540. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92638-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARNEY E., MILLER G. RETICULOCYTOPENIA IN SICKLE CELL DISEASE. APLASTIC EPISODES IN THE COURSE OF SICKLE CELL DISEASE IN CHILDREN. Am J Dis Child. 1964 May;107:450–455. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1964.02080060452004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNOFF A. I. The human hemoglobins in health and disease. N Engl J Med. 1955 Sep 1;253(9):365–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195509012530905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIGGS L. W. The crisis in sickle cell anemia; hematologic studies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1956 Oct;26(10):1109–1118. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/26.10.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes C. R., Chaplin H., Jr An enhancing effect of albumin on the determination of cold hemagglutinins. Vox Sang. 1971 Jan;20(1):46–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb01799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers J. F. Clinical aspects of infection with Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Proc R Soc Med. 1968 Dec 12;61(12):1325–1330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS M. E., SCOTT R. B., BAIRD R. L. Studies in sickle cell anemia. XVI. Sudden death during sickle cell anemia crises in young children. J Pediatr. 1960 Jan;56:30–38. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(60)80285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONSSON U., ROATH O. S., KIRKPATRICK C. I. Nutritional megaloblastic anemia associated with sickle cell states. Blood. 1959 May;14(5):535–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIKIN S. L. The aplastic crisis of sickle-cell disease; occurrence in several members of families within a short period of time. AMA J Dis Child. 1957 Feb;93(2):128–139. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1957.02060040130005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDENBAUM J., KLIPSTEIN F. A. FOLIC ACID DEFICIENCY IN SICKLE-CELL ANEMIA. N Engl J Med. 1963 Oct 24;269:875–882. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196310242691701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACIVER J. E., PARKER-WILLIAMS E. J. The aplastic crisis in sickle-cell anaemia. Lancet. 1961 May 20;1(7186):1086–1089. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACIVER J. E., WENT L. N. Sickle-cell anaemia complicated by megaloblastic anaemia of infancy. Br Med J. 1960 Mar 12;1(5175):775–779. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5175.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGucken R. B. Bilateral gangrene of the fat in a Nigerian infant. Lancet. 1972 Apr 15;1(7755):852–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90843-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noah N. D. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in the United Kingdom--1967-73. Br Med J. 1974 Jun 8;2(5918):544–546. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5918.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER K., MOTULSKY A. G., WILE S. A. Aplastic crisis in sickle cell anemia; a study of its mechanism and its relationship to other types of hemolytic crises. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 May;35(5):721–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeler R. A., Metzger W., Mufson M. A. Diplococcus pneumoniae infections in children with sickle cell anemia. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jan;123(1):8–10. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110070058003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman S. T., Bartlett J., Clyde W. A., Jr, Ayoub E. M. The unusual severity of Mycoplasmal pneumonia in children with sickle-cell disease. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jul 27;287(4):164–167. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197207272870403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT C. S., GARDNER E., Jr A study of the role of acute infections in precipitating crises in chronic hemolytic states. Ann Intern Med. 1960 Mar;52:530–537. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-52-3-530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


