Abstract
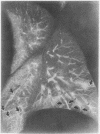
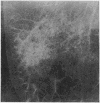
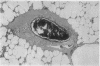
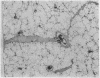
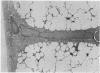
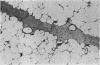
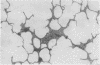
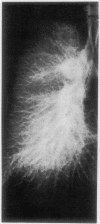
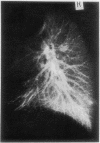
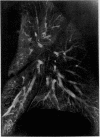
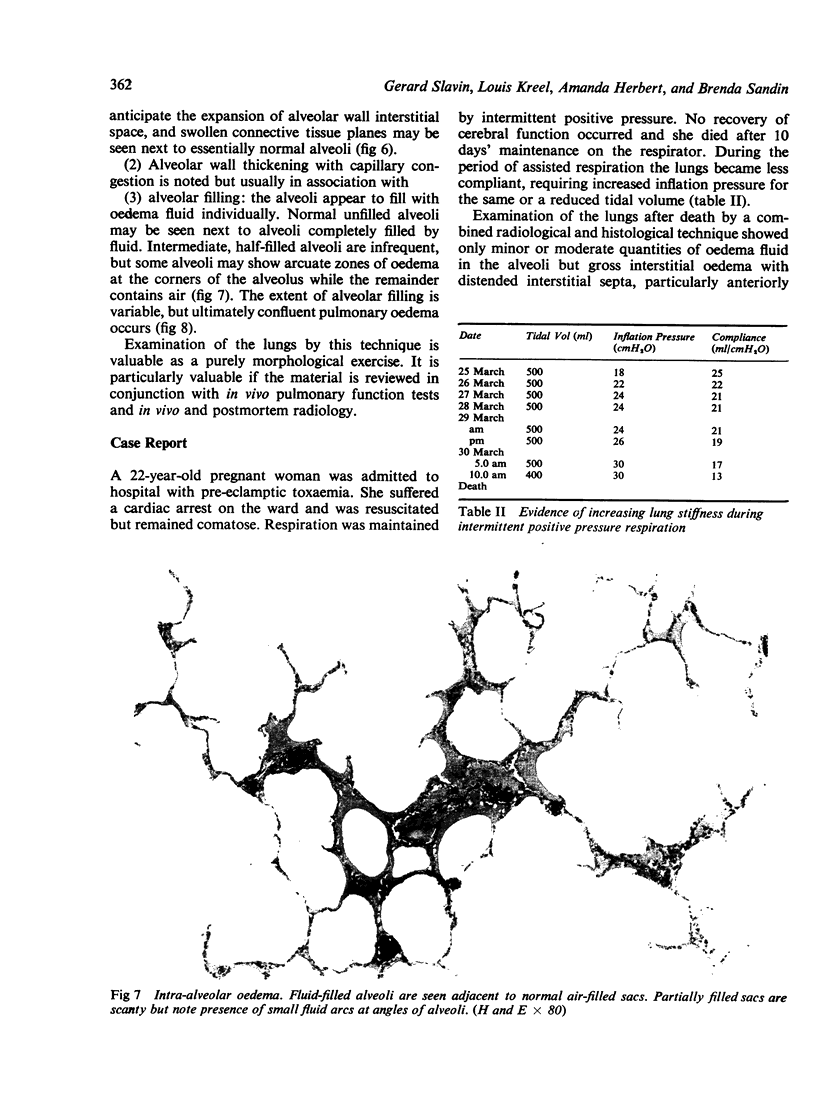
Fixation of lungs at necropsy by inflation with formaldehyde vapour was used in a combined radiological and pathological study of pulmonary oedema. Pulmonary oedema was found in 79% of lungs examined. The earliest phases affect the interstitial tissue with oedematous connective tissue planes and distension of pulmonary lymphatics. These changes may be associated with reduction in the compliance of the lung. Alveolar filling is a late stage in the accumulation of oedema fluid in the lungs.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAMERON G. R. Pulmonary oedema. Br Med J. 1948 May 22;1(4559):965–972. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4559.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell T. S., Levine O. R., Senior R. M., Wiener J., Spiro D., Fishman A. P. Electron microscopic alterations at the alveolar level in pulmonary edema. Circ Res. 1967 Dec;21(6):783–797. doi: 10.1161/01.res.21.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold M. J. Interstitial pulmonary edema. An electron microscopic study of the pathology of staphylococcal enterotoxemia in Rhesus monkeys. Lab Invest. 1967 Jun;16(6):912–924. doi: 10.21236/ad0811615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Miller J., Reid L. Pulmonary oedema induced by ANTU, or by high or low oxygen concentrations in rat--an electron microscopic study. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Aug;53(4):347–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash G., Foley F. D., Langlinais P. C. Pulmonary interstitial edema and hyaline membranes in adult burn patients. Electron microscopic observations. Hum Pathol. 1974 Mar;5(2):149–160. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietra G. G. The lung in shock. Hum Pathol. 1974 Mar;5(2):121–122. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(74)80057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID L. The connective tissue septa in the adult human lung. Thorax. 1959 Jun;14:138–145. doi: 10.1136/thx.14.2.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub N. C., Nagano H., Pearce M. L. Pulmonary edema in dogs, especially the sequence of fluid accumulation in lungs. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Feb;22(2):227–240. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub N. C. Pulmonary edema. Physiol Rev. 1974 Jul;54(3):678–811. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.3.678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub N. C. The pathophysiology of pulmonary edema. Hum Pathol. 1970 Sep;1(3):419–432. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szidon J. P., Pietra G. G., Fishman A. P. The alveolar-capillary membrane and pulmonary edema. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jun 1;286(22):1200–1204. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197206012862208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. M., Slavin G., Kreel L., Callan K., Sandin B. Postmortem inflation and fixation of human lungs. A technique for pathological and radiological correlations. Thorax. 1974 Mar;29(2):189–194. doi: 10.1136/thx.29.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]