Abstract
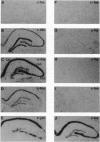
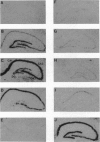
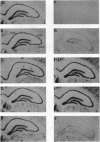
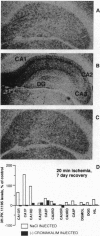
Transient global forebrain ischemia induces in rat brain a large increase of expression of the immediate early genes c-fos and c-jun and of the mRNAs for the 70-kDa heat-shock protein and for the form of the amyloid beta-protein precursor including the Kunitz-type protease-inhibitor domain. At 24 hr after ischemia, this increased expression is particularly observed in regions that are vulnerable to the deleterious effects of ischemia, such as pyramidal cells of the CA1 field in the hippocampus. In an attempt to find conditions which prevent the deleterious effects of ischemia, representatives of three different classes of K+ channel openers, (-)-cromakalim, nicorandil, and pinacidil, were administered both before ischemia and during the reperfusion period. This treatment totally blocked the ischemia-induced expression of the different genes. In addition it markedly protected neuronal cells against degeneration. The mechanism of the neuroprotective effects involves the opening of ATP-sensitive K+ channels since glipizide, a specific blocker of that type of channel, abolished the beneficial effects of K+ channel openers. The various classes of K+ channel openers seem to deserve attention as potential drugs for cerebral ischemia.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Tanzi R. E., Kogure K. Selective induction of Kunitz-type protease inhibitor domain-containing amyloid precursor protein mRNA after persistent focal ischemia in rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Apr 29;125(2):172–174. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90020-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abele A. E., Miller R. J. Potassium channel activators abolish excitotoxicity in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Jul 31;115(2-3):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90454-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allard B., Lazdunski M. Nucleotide diphosphates activate the ATP-sensitive potassium channel in mouse skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Nov;422(2):185–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00370419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer C., ten Bruggencate G. Actions of BRL 34915 (Cromakalim) upon convulsive discharges in guinea pig hippocampal slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;337(4):429–434. doi: 10.1007/BF00169535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amoroso S., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Glucose, sulfonylureas, and neurotransmitter release: role of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):852–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2305257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ari Y. B., Lazdunski M. Galanin protects hippocampal neurons from the functional effects of anoxia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 20;165(2-3):331–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90732-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashford M. L., Sturgess N. C., Trout N. J., Gardner N. J., Hales C. N. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate-sensitive ion channels in neonatal rat cultured central neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Aug;412(3):297–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00582512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ari Y., Krnjević K., Crépel V. Activators of ATP-sensitive K+ channels reduce anoxic depolarization in CA3 hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience. 1990;37(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benavides J., Capdeville C., Dauphin F., Dubois A., Duverger D., Fage D., Gotti B., MacKenzie E. T., Scatton B. The quantification of brain lesions with an omega 3 site ligand: a critical analysis of animal models of cerebral ischaemia and neurodegeneration. Brain Res. 1990 Jul 9;522(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91472-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste H., Drejer J., Schousboe A., Diemer N. H. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1369–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan A., Li H., Pulsinelli W. A. The N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, MK-801, fails to protect against neuronal damage caused by transient, severe forebrain ischemia in adult rats. J Neurosci. 1991 Apr;11(4):1049–1056. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-04-01049.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Gordon M. B., Rubino K. L., Sambucetti L. C. Isolation and characterization of the c-fos(rat) cDNA and analysis of post-translational modification in vitro. Oncogene. 1987;2(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet J. P., Squinto S. P., Bazan N. G. Fos-jun and the primary genomic response in the nervous system. Possible physiological role and pathophysiological significance. Mol Neurobiol. 1990 Spring-Summer;4(1-2):27–55. doi: 10.1007/BF02935584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. Potassium selective ion channels in insulin-secreting cells: physiology, pharmacology and their role in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90012-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G., Weston A. H. Structure-activity relationships of K+ channel openers. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Oct;11(10):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escande D., Cavero I. K+ channel openers and 'natural' cardioprotection. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jul;13(7):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90083-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escande D., Thuringer D., Leguern S., Cavero I. The potassium channel opener cromakalim (BRL 34915) activates ATP-dependent K+ channels in isolated cardiac myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 29;154(2):620–625. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., De Weille J. R., Green R. D., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Lazdunski M. Antidiabetic sulfonylureas control action potential properties in heart cells via high affinity receptors that are linked to ATP-dependent K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7933–7936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandolfo G., Romettino S., Gottesmann C., van Luijtelaar G., Coenen A., Bidard J. N., Lazdunski M. K+ channel openers decrease seizures in genetically epileptic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 11;167(1):181–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90762-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover G. J., Dzwonczyk S., Sleph P. G. Reduction of ischemic damage in isolated rat hearts by the potassium channel opener, RP 52891. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 20;191(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94091-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häusser M. A., de Weille J. R., Lazdunski M. Activation by cromakalim of pre- and post-synaptic ATP-sensitive K+ channels in substantia nigra. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 31;174(2):909–914. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito U., Spatz M., Walker J. T., Jr, Klatzo I. Experimental cerebral ischemia in mongolian gerbils. I. Light microscopic observations. Acta Neuropathol. 1975 Aug 27;32(3):209–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00696570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang C., Haddad G. G. Effect of anoxia on intracellular and extracellular potassium activity in hypoglossal neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Jul;66(1):103–111. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen M. B., Deckert J., Wright D. C., Gehlert D. R. Delayed c-fos proto-oncogene expression in the rat hippocampus induced by transient global cerebral ischemia: an in situ hybridization study. Brain Res. 1989 Apr 10;484(1-2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawagoe J., Abe K., Kogure K. Different thresholds of HSP70 and HSC70 heat shock mRNA induction in post-ischemic gerbil brain. Brain Res. 1992 Dec 25;599(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90391-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontos H. A., Wei E. P. Superoxide production in experimental brain injury. J Neurosurg. 1986 May;64(5):803–807. doi: 10.3171/jns.1986.64.5.0803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Glucose-regulated potassium channels are sweet news for neurobiologists. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourre C., Ben Ari Y., Bernardi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Antidiabetic sulfonylureas: localization of binding sites in the brain and effects on the hyperpolarization induced by anoxia in hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1989 May 1;486(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91288-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourre C., Widmann C., Lazdunski M. Specific hippocampal lesions indicate the presence of sulfonylurea binding sites associated to ATP-sensitive K+ channels both post-synaptically and on mossy fibers. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 1;540(1-2):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90533-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourre C., Widmann C., Lazdunski M. Sulfonylurea binding sites associated with ATP-regulated K+ channels in the central nervous system: autoradiographic analysis of their distribution and ontogenesis, and of their localization in mutant mice cerebellum. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 11;519(1-2):29–43. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90057-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellgård B., Wieloch T. Postischemic blockade of AMPA but not NMDA receptors mitigates neuronal damage in the rat brain following transient severe cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1992 Jan;12(1):2–11. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1992.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D., Attwell D. The release and uptake of excitatory amino acids. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Nov;11(11):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90129-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson C., Bruggencate G. T., Steinberg R., Stöckle H. Calcium modulation in brain extracellular microenvironment demonstrated with ion-selective micropipette. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1287–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak T. S., Jr Localization of 70 kDa stress protein mRNA induction in gerbil brain after ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 May;11(3):432–439. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politi D. M., Rogawski M. A. Glyburide-sensitive K+ channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurons: activation by cromakalim and energy-depleting conditions. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):308–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulsinelli W. A., Brierley J. B. A new model of bilateral hemispheric ischemia in the unanesthetized rat. Stroke. 1979 May-Jun;10(3):267–272. doi: 10.1161/01.str.10.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U. Potassium channel openers: pharmacological and clinical aspects. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1992;6(7):279–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1992.tb00122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., Amoroso S., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. K+ channel openers activate brain sulfonylurea-sensitive K+ channels and block neurosecretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3489–3492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., De Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15840–15844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheardown M. J., Nielsen E. O., Hansen A. J., Jacobsen P., Honoré T. 2,3-Dihydroxy-6-nitro-7-sulfamoyl-benzo(F)quinoxaline: a neuroprotectant for cerebral ischemia. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):571–574. doi: 10.1126/science.2154034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siesjö B. K. Acidosis and ischemic brain damage. Neurochem Pathol. 1988 Jul-Dec;9:31–88. doi: 10.1007/BF03160355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siesjö B. K., Bengtsson F. Calcium fluxes, calcium antagonists, and calcium-related pathology in brain ischemia, hypoglycemia, and spreading depression: a unifying hypothesis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989 Apr;9(2):127–140. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. T., Rash K., Clemens J. A. Amyloid precursor protein accumulates in regions of neurodegeneration following focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Brain Res. 1992 Oct 9;593(1):128–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91274-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takakura S., Susumu T., Satoh H., Mori J., Shiino A., Handa J. Nilvadipine, a new calcium channel blocker, reduces ischemic brain injury in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;56(4):547–550. doi: 10.1254/jjp.56.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., McClatchey A. I., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L., Gusella J. F., Neve R. L. Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):528–530. doi: 10.1038/331528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura Y., Kowall N. W., Beal M. F. Global ischemia induces NMDA receptor-mediated c-fos expression in neurons resistant to injury in gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res. 1991 Mar 1;542(2):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91589-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakita H., Tomimoto H., Akiguchi I., Ohnishi K., Nakamura S., Kimura J. Regional accumulation of amyloid beta/A4 protein precursor in the gerbil brain following transient cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Nov 9;146(2):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90061-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich P. Digital dyslexia. Neural network mimics the effects of stroke. Sci Am. 1991 Oct;265(4):36–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J. Mammalian stress response: cell physiology, structure/function of stress proteins, and implications for medicine and disease. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4):1063–1081. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.4.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel T. C., Joh T. H., Volpe B. T. In situ hybridization analysis of c-fos and c-jun expression in the rat brain following transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res. 1991 Dec 20;567(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90800-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Sasaki H., Dohura K., Goto I., Sakaki Y. Structure and expression of the alternatively-spliced forms of mRNA for the mouse homolog of Alzheimer's disease amyloid beta protein precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 15;158(3):906–912. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92808-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]