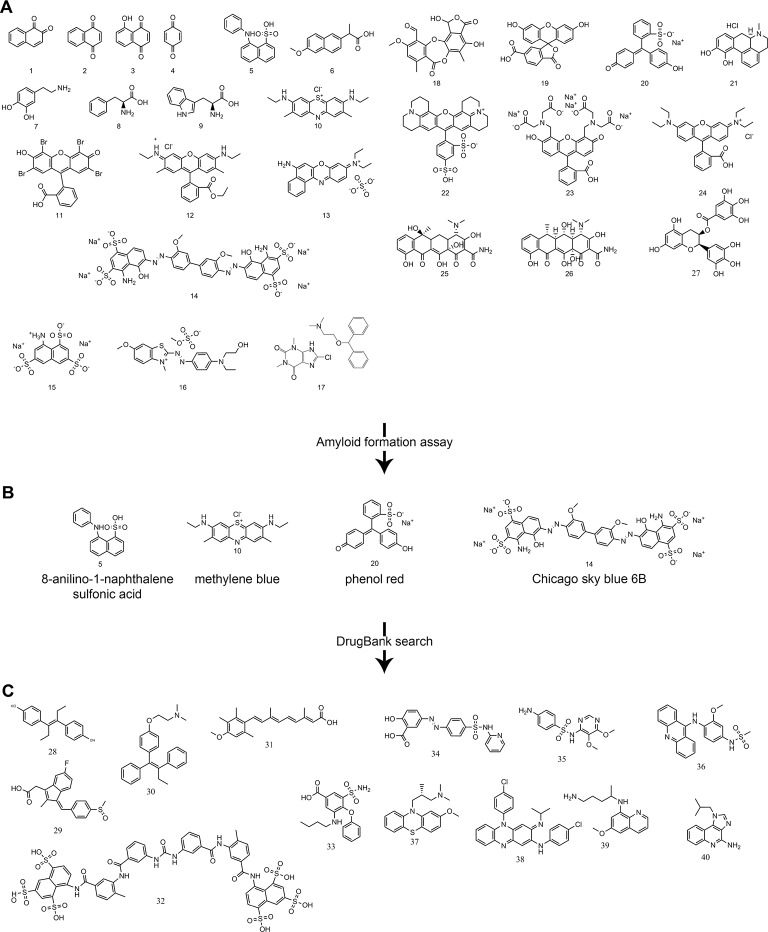
Figure 3. Panel of ligands analyzed with ThT assays and EM for their ability to inhibit VL amyloid formation.
(A) Preliminary molecules screened. 1. 1,2-naphthoquinone. 2. 1,4-naphthoquinone. 3. 5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone. 4. quinone. 5. 8-anilinonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid. 6. methoxy-2-naphthyl-propionic acid. 7. dopamine. 8. L-phenylalanine. 9. L-tryptophan. 10. methylene blue. 11. eosin Y. 12. rhodamine 6G. 13. Basic Blue 12. 14. Chicago Sky Blue 6B. 15. 8-aminonaphthalene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid. 16. Basic Blue 41. 17. dimenhydrinate. 18. stictic acid. 19. 6-carboxyfluorescein. 20. phenol red. 21. R-(-)-apomorphine. 22. sulforhodamine 101. 23. fluorescein methyleneiminodiacetic acid. 24. rhodamine B. 25. tetracycline. 26. doxycycline. 27. (−)-epigallocatechin gallate. (B) Molecules showing an inhibitory effect on the formation of amyloid fibrils during the preliminary screen. (C) Molecules identified in a DrugBank search using the most effective candidates from the preliminary screen and a similarity threshold of 0.3. Search using phenol red: 28. diethylstilbestrol (0.4), 29. sulindac (0.4), 30. tamoxifen (0.4), 31. acitretin (0.4). Search using Chicago Sky Blue 6B: 32. suramin (0.4), 33. Bumetanide (0.3), 34. sulfasalazine (0.3), 35. sulfadoxine (0.3), 36. amsacrine (0.3), 37. methotrimeprazine (0.3). Search using methylene blue: 38. clofazimine (0.3), 39. primaquine (0.3), 40. imiquimod (0.3).