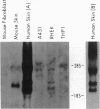
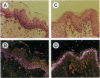
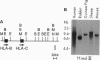Abstract
A gene designated S has been identified in the class I region of the human major histocompatibility complex. The S gene is located 160 kb telomeric of HLA-C. It is expressed at high levels as 2.2-kb and 2.6-kb mRNAs in human skin. No homologous transcripts were detected in other tissues including placenta, liver, spleen, thymus, and brain. In situ hybridization showed that S gene expression was restricted to the differentiating keratinocytes in the granular layer of the epidermis. The predicted amino acid sequence of the S protein was remarkable for its high content of serine, glycine, and proline. There were significant similarities with the amino acid sequences of loricrin, keratin 1, and keratin 10, all major components of the granular-cell layer. The selective expression of the S gene in the granular-cell layer in the epidermis suggests a role in the developmental program of differentiating keratinocytes. Furthermore, in light of the recognized association of psoriasis vulgaris, a disorder of keratinocyte proliferation, with alleles of HLA-C, this gene may contribute primarily to the pathogenesis of this common disorder.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahram S., Arnold D., Bresnahan M., Strominger J. L., Spies T. Two putative subunits of a peptide pump encoded in the human major histocompatibility complex class II region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10094–10098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck S., Hanson I., Kelly A., Pappin D. J., Trowsdale J. A homologue of the Drosophila female sterile homeotic (fsh) gene in the class II region of the human MHC. DNA Seq. 1992;2(4):203–210. doi: 10.3109/10425179209020804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronson S. K., Pei J., Taillon-Miller P., Chorney M. J., Geraghty D. E., Chaplin D. D. Isolation and characterization of yeast artificial chromosome clones linking the HLA-B and HLA-C loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1676–1680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. G., Driscoll J., Monaco J. J. Structural and serological similarity of MHC-linked LMP and proteasome (multicatalytic proteinase) complexes. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):355–357. doi: 10.1038/353355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein B. H., Silverman G. A., Little R. D., Burke D. T., Korsmeyer S. J., Schlessinger D., Olson M. V. Isolation of single-copy human genes from a library of yeast artificial chromosome clones. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1348–1351. doi: 10.1126/science.2544027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. D., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The molecular genetics of components of complement. Adv Immunol. 1986;38:203–244. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Katzman P., Alicot E. M., Koller B. H., Geraghty D. E., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L., Spies T. Linkage map of the human major histocompatibility complex including the tumor necrosis factor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Woods D. E., Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R., Seidman J. G. Molecular map of the murine S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6947–6951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham I., Sargent C. A., Trowsdale J., Campbell R. D. Molecular mapping of the human major histocompatibility complex by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7237–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyk G. M., Kim S. W., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. Exon trapping: a genetic screen to identify candidate transcribed sequences in cloned mammalian genomic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8995–8999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R. L., Green H. Structure and evolution of the human involucrin gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90884-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folz R. J., Gordon J. I. Computer-assisted predictions of signal peptidase processing sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):870–877. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90611-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folz R. J., Gordon J. I. PARA-SITE: a computer algorithm for rapidly analyzing the physical-chemical properties of amino acid sequences at sites of co- and post-translational protein processing. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):175–179. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty D. E., Pei J., Lipsky B., Hansen J. A., Taillon-Miller P., Bronson S. K., Chaplin D. D. Cloning and physical mapping of the HLA class I region spanning the HLA-E-to-HLA-F interval by using yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynne R., Powis S. H., Beck S., Kelly A., Kerr L. A., Trowsdale J. A proteasome-related gene between the two ABC transporter loci in the class II region of the human MHC. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):357–360. doi: 10.1038/353357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Maika S. D., Richardson J. A., Tang J. P., Taurog J. D. Spontaneous inflammatory disease in transgenic rats expressing HLA-B27 and human beta 2m: an animal model of HLA-B27-associated human disorders. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1099–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90512-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson I. M., Poustka A., Trowsdale J. New genes in the class II region of the human major histocompatibility complex. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):417–424. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90327-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison G. S., Drabkin H. A., Kao F. T., Hartz J., Hart I. M., Chu E. H., Wu B. J., Morimoto R. I. Chromosomal location of human genes encoding major heat-shock protein HSP70. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Mar;13(2):119–130. doi: 10.1007/BF01534692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohl D., Mehrel T., Lichti U., Turner M. L., Roop D. R., Steinert P. M. Characterization of human loricrin. Structure and function of a new class of epidermal cell envelope proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6626–6636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh S. L., Campbell R. D. Evidence that gene G7a in the human major histocompatibility complex encodes valyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 15;278(Pt 3):809–816. doi: 10.1042/bj2780809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozono H., Bronson S. K., Taillon-Miller P., Moorti M. K., Jamry I., Chaplin D. D. Molecular linkage of the HLA-DR, HLA-DQ, and HLA-DO genes in yeast artificial chromosomes. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90065-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrance S. K., Smith C. L., Srivastava R., Cantor C. R., Weissman S. M. Megabase-scale mapping of the HLA gene complex by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1387–1390. doi: 10.1126/science.3029868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E. Y., Elliott J. F., Cwirla S., Lanier L. L., Davis M. M. Polymerase chain reaction with single-sided specificity: analysis of T cell receptor delta chain. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2463672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrel T., Hohl D., Rothnagel J. A., Longley M. A., Bundman D., Cheng C., Lichti U., Bisher M. E., Steven A. C., Steinert P. M. Identification of a major keratinocyte cell envelope protein, loricrin. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1103–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90073-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Neve R. L., Colletti-Feener C., Bertelson C. J., Kurnit D. M., Kunkel L. M. Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):646–650. doi: 10.1038/323646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., Cho S., Attaya M. Transport protein genes in the murine MHC: possible implications for antigen processing. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1723–1726. doi: 10.1126/science.2270487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. V., Loughney K., Hall B. D. Identification of the yeast DNA sequences that correspond to specific tyrosine-inserting nonsense suppressor loci. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):387–410. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa A., Ohkido M., Inoko H., Ando A., Tsuji K. Specific restriction fragment length polymorphism on the HLA-C region and susceptibility to psoriasis vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Mar;90(3):402–405. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12456500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parimoo S., Patanjali S. R., Shukla H., Chaplin D. D., Weissman S. M. cDNA selection: efficient PCR approach for the selection of cDNAs encoded in large chromosomal DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9623–9627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser I. W., Stenmark K. R., Suthar M., Crouch E. C., Mecham R. P., Parks W. C. Regional heterogeneity of elastin and collagen gene expression in intralobar arteries in response to hypoxic pulmonary hypertension as demonstrated by in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1073–1088. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Campbell R. D. Identification of multiple HTF-island associated genes in the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Trowsdale J., Campbell R. D. Human major histocompatibility complex contains genes for the major heat shock protein HSP70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1968–1972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer J., Kinjo M., Fürstenberger G., Winter H. Sequential expression of mRNA-encoded keratin sets in neonatal mouse epidermis: basal cells with properties of terminally differentiating cells. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90311-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Strominger J. L. Human major histocompatibility complex contains a minimum of 19 genes between the complement cluster and HLA-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8955–8958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Morton C. C., Nedospasov S. A., Fiers W., Pious D., Strominger J. L. Genes for the tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta are linked to the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8699–8702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Hanson I., Mockridge I., Beck S., Townsend A., Kelly A. Sequences encoded in the class II region of the MHC related to the 'ABC' superfamily of transporters. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):741–744. doi: 10.1038/348741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Chaplin D. D., Weis J. H., Dupont B., New M. I., Seidman J. G. Two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes are located in the murine S region. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):465–467. doi: 10.1038/312465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Werkmeister J., New M. I., Dupont B. Steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency and the major histocompatibility complex. Hum Immunol. 1986 Apr;15(4):404–415. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. B., Gavel Y., von Heijne G. Amino acid distributions around O-linked glycosylation sites. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):529–534. doi: 10.1042/bj2750529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]