Abstract
Purpose:
To evaluate the accuracy of corneal power measurements for intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation after myopic laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK).
Methods:
The study evaluated 45 eyes with a history of myopic LASIK. Corneal power was measured using manual keratometry, automated keratometry, optical biometry, and Scheimflug tomography. Different hypothetical IOL power calculation formulas were performed for each case.
Results:
The steepest mean K value was measured with manual keratometry (37.48 ± 2.86 D) followed by automated keratometry (37.31 ± 2.83 D) then optical biometry (37.06 ± 2.98 D) followed by Scheimflug tomography (36.55 ± 3.08). None of the K values generated by Scheimflug tomography were steeper than the measurements from the other 3 instruments. Using equivalent K reading (EKR) 4 mm with the Double-K SRK/T formula, the refractive outcome generated 97.8% of cases within ± 2 D, 80.0% of cases within ± 1 D, and 42.2% of cases within ± 0.5 D. The best combination of formulas was “Shammas-PL + Double-K SRK/T formula using EKR 4 mm.”
Conclusion:
Scheimflug tomography imaging using the Holladay EKR 4 mm improved the accuracy of IOL power calculation in post-LASIK eyes. The best option is a combination of formulas. We recommended the use the combined “Shammas-PL ± Double-K SRK/T formula using EKR 4 mm”h for optical outcomes.
Keywords: Biometry, Intraocular Lens Calculation, Laser In situ Keratomileusis, Pentacam
INTRODUCTION
The volume of cataract surgeries in eyes after myopic keratorefractive surgery is expected to increase in the coming decades. Although cataract extraction is possible without major technical obstacles, intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation remains challenging.1,2,3,4,5 Determination of lens implant power for a desired postoperative refraction for routine cases requires measurement of two key variables: The average central corneal power and the axial length (AL) of the eye. These measurements are then entered into an appropriate formula.6,7,8,9 Utilizing average K-reading in postlaser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) eyes into standard IOL power calculation formulas results in an overestimation of keratometric diopters, causing an underestimation of IOL power leading to postoperative hyperopia. Furthermore, this subset of patients has extremely high expectations, which makes accurate IOL power calculations, especially critical in cases of refractive lens exchange.1,2,3,4,5
Sources of error in estimating corneal power after excimer laser corneal surgery are due to the fact that current keratometers and topography systems primarily measure the radius of curvature of the anterior surface of the central cornea. Keratometric diopters are derived from this radius of curvature using an effective refractive index that incorrectly uses a single refractive lens model to represent the anterior and posterior corneal surfaces. This effective refractive index is considered valid as long as the radii of the anterior and posterior surfaces of the cornea are proportionate and resemble the model eye. In post-LASIK eyes, the radius of curvature of the anterior surface is considerably increased and the distance between both refractive surfaces is decreased. Therefore, this method of calculating keratometric diopters from the anterior radius of curvature is inaccurate.1,10,11,12,13,14 The current study evaluates the accuracy of different corneal power measurements for IOL power calculation after myopic LASIK.
METHODS
This is a combined prospective and retrospective clinical study that was conducted on 45 eyes with previous myopic LASIK that had undergone successful phacoemulsification cataract surgery. Cases with a complication during cataract surgery that affected IOL position or required enlarging the incision, as well as cases with corneal pathology, for example, corneal opacities, were excluded from the study. This study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. The local ethics committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University, Egypt, approved this study.
Patients underwent keratometry measurements with manual keratometry with the KM-450 Keratometer (Nidek Co. Ltd., Gamagori, Japan), auto-keratometry with the KR-8800 auto-kerato-refractometer (Topcon Corp, Tokyo, Japan), an optical biometer (IOLMaster; Carl Zeiss Meditec, Jena, Germany), and Scheimpflug tomography (Pentacam; Oculus GmBh, Wetzlar, Germany). “IOLMaster with Advance Technology V.5.4” was the software used for the IOLMaster. The software version 1.17r37 was used for the Pentacam (IOLMaster; Carl Zeiss Meditec, Jena, Germany - Pentacam; Oculus GmBh, Wetzlar, Germany). The following K readings were obtained from Pentacam: Sim-k, Holladay equivalent K readings (EKRs) at 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm, 4 mm, 4.5 mm, and true net power. AL was measured with the IOLMaster.
The IOLMaster measures corneal radii based on image analysis, in which distances between light reflections on the cornea are measured. Six light spots are projected hexagonally in a 2.3 mm radius on the cornea. The device records the reflection of these spots, measuring the separation of opposite pairs of light spots and calculating the toroidal surface curvature. The mean of 3 measurements was used as the corneal power that was entered into the IOL power calculation formulas.15,16
For the Pentacam, the true net corneal power map uses real anterior curvature, posterior curvature, corneal thickness values, and an accordingly modified refractive index. The true net power is based on the Gaussian optics formula and uses a modified refractive index rather than the real refractive index of air, cornea, and aqueous.5 The simulated keratometry values are calculated by averaging power obtained from the anterior corneal radius measured along the 3.0 mm central ring. The Sim-K is calculated with a keratometric refractive index = 1.3375.17 The Pentacam unit was programed to calculate an EKR (equivalent K), labeled in the Holladay report. The software of the unit evaluates the measurements taken at the central corneal front surface and adjusts them to reflect the difference in the back-surface power of the cornea for the mean of the population.18,19
All cases underwent routine phacoemulsification cataract surgery and foldable IOL implantation in the bag through a clear corneal tunnel incision. The power of the implanted IOL was determined according to the method of calculation preferred by the operating surgeon. The implanted IOL was a hydrophobic acrylic IOL (Acrysof SA60AT, Alcon Surgical Inc., Fort Worth, TX, USA).
The final refraction was obtained one to 4 months after the surgery. Autorefraction with the Topcon KR-8800 auto-kerato-refractometer (Topcon Corp, Tokyo, Japan) was used as a starting point for the examination. Fine adjustment of the refraction was aided by the retinoscopy findings and the Jackson cross-cylinder technique.
The Haigis formula, SRK/T formula, and SRK/T formula with Double-K modification20 were used with all available K readings for each case. The Haigis-L formula21 (available on IOLMaster) was also used. The Shammas No-history method (Shammas modified IOLMaster K readings, where, modified K = 1.14 X K post-LASIK - 6.8) was used in the Shammas-PL formula22 (the formula was entered on an excel sheet by the authors).
Regression analysis of post-LASIK eyes was performed and a regression formula was determined for the commonly used method using IOLMaster K values with SRK/T formula. IOL power was determined by the deduced regression formula and the results were tabulated in a data sheet. Combinations of means of different IOL powers calculated using various formulas were hypothetically calculated and the best outcomes were determined.
The following parameters were used for each formula (as they were stored in the IOLMaster software):
For the hydrophobic acrylic IOL Acrysof SA60AT:
SRK/T formula: A-constant = 118.7
Haigis formula: a0 = 0.091, a1 = 0.231, a2 = 0.179.
For the Double-K modification of SRK/T, an average K value of 43.86 D was used as the prerefractive surgery K value (43.86 D is the default value used with the Web-based American Society of Cataract and Refractive surgery IOL power calculator).
The predictive accuracy of the calculation was analyzed by calculating the refraction prediction error (which equals actual manifest refraction spherical equivalent (MRSE) minus predicted MRSE). Calculation of the mean absolute error (MAE) was performed of the values above. The MAE is derived from the algebraic sum of the absolute values of the errors. The MAE signifies the formula's outcome from emmetropia. In addition, post-MRSE predictions were calculated for ± 0.50 D, ±1.00 D, and ± 2.00 D were derived.
Clinical findings were statistically evaluated using Excel 2007 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) and Statistical Package for the Social Sciences Software version 15.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Means, standard deviations, and ranges were calculated. To check for normal distribution, the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was applied. Comparisons of the means of normally distributed data were performed with the t-test for paired samples and analysis of variance test. Chi-square test and Fisher's exact test were used to compare different frequencies. A P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
This study included 45 post-LASIK eyes. The patients age ranged from 33 to 65 years (mean, 51.27 ± 7.31 years). The mean AL was 28.66 ± 2.78 mm (range, 24.01–33.48 mm). The mean anterior chamber depth measured with the IOLMaster was 3.43 ± 0.35 mm (range 2.74–4.86 mm).
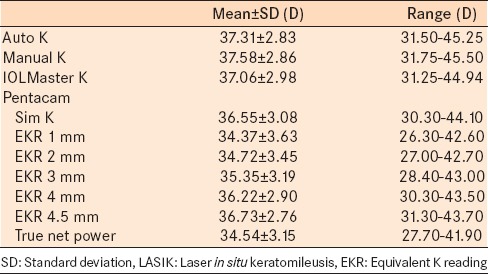
Table 1 presents the mean K values measured by the different methods. The steepest mean K value was measured with manual keratometry (37.48 ± 2.86 D) followed by automated keratometry (37.31 ± 2.83 D) then the IOLMaster mean K value (37.06 ± 2.98 D) [Table 1]. All the K values measured with the Pentacam were flatter than the other 3 units. The flattest mean K values were Holladay EKRs at 1 mm (34.37 ± 3.63 D) and true net power from Pentacam (34.54 ± 3.15 D). The Holladay EKR values increased in steepness from smaller diameters to larger diameters (i.e. EKR at 1 mm was the flattest mean value and then increased progressively to EKR at 4.5 mm which was the steepest mean value).
Table 1.
Keratometry values of the included eyes in post-LASIK group
Using the Haigis formula with different K readings, the results were significantly more accurate with EKR 3 mm and EKR 4 mm (F = 72.093, P < 0.001). The refractive outcome was significantly better using EKR 4 mm compared to EKR 3 mm (97.8% and 95.6% were within ± 2 D and 37.8% and 35.6% were within ± 0.5 D; P < 0.05). Similarly, the MAEs were significantly different between the EKR 3 mm and EKR 4 mm; t = 12.351, P < 0.001 [Table 2].
Table 2.
Refractive outcome of intraocular power calculations using various formulations
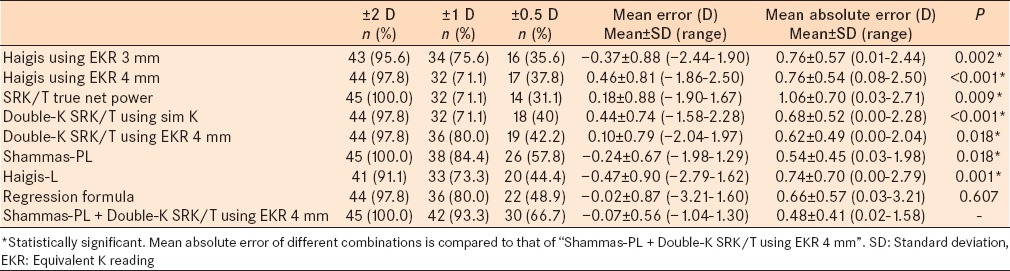
Using the SRK/T formula with different K readings, the true net power gave the best results (F = 43.092, P < 0.001); with 100.0% of cases within ± 2 D, 71.1% within ± 1 D, and 31.1% within ± 0.5 D. The MAE was 1.06 ± 0.70 D [Table 2].
Linear regression analysis was used to deduce the following regression formula [Figure 1 and Table 2] to calculate IOL power using the SRK/T formula and IOLMaster K readings:
Figure 1.
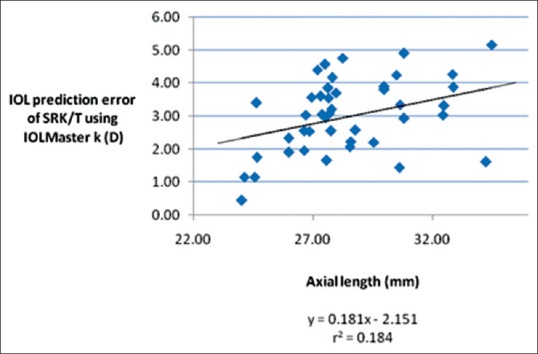
Correlation between the intraocular lens prediction error of the SRK/T formula using IOLMaster keratometry values and axial length
IOL power = SRK/T calculated power using IOLMaster K readings + (0.181 × AL) – 2.151
Using the Double-K SRK/T formula with different K readings, the results were significantly more accurate with EKR 4 mm (F = 88.546, P < 0.001); with 97.8% of cases within ±2 D, 80.0% within ±1 D, and 42.2% within ±0.5 D. The MAE was 0.62 ± 0.49 D [Table 2].
Using the Haigis-L formula, the MAE was 0.74 ± 0.70 D; with 91.1% of cases within ±2 D, 73.3% within ±1 D, and 44.4% within ±0.5 D. Using Shammas-PL, the MAE was 0.54 ± 0.45 D; with 100% of cases within ±2 D, 84.4% within ±1 D, and 57.8% within ±0.5 D [Table 2].
The data derived from IOLMaster and Pentacam with the Holladay report were used in various combinations using the formulas with statistically significant good results. The mean IOL power with each formula was calculated. To avoid confusion, only the results of the best combinations were shown, which included:
“Shammas-PL + Haigis using EKR 4 mm”
“Shammas-PL + Double-K SRK/T using EKR 4 mm”
“Shammas-PL + SRK/T using true net power.” This combination is useful when using scheimpflug imaging system that does not provide Holladay report, which shows the different Holladay EKRs.
The combinations mentioned above yielded excellent results [Table 3]. Comparison of the number of cases within ±1 D and within ±0.5 D of the five combinations, indicated no statistically significant difference (X2 = 1.823, P = 0.986).
Table 3.
Comparison between different means of combinations of formulas
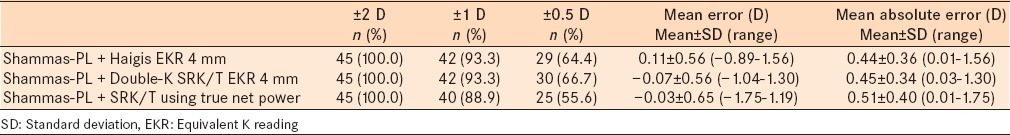
The combinations of the formulas refractive outcome showed strong positive correlation (r > 0.8, P < 0.001) to each other. Comparison of the MAEs of the combinations indicated no significant difference (F = 1.654, P = 0.162). Using multiple paired t-tests to compare the MAEs of the combinations, the combination of “Shammas-PL + Double-K SRK/T formula using EKR 4 mm” resulted in a significantly better outcome than the other combinations (P < 0.004).
Table 2 and Figure 2 present the summary of the formulas and combinations that yielded the best results. Using the Chi-square test to compare the number of cases within ±2 D, within ±1 D, and within ±0.5 D, the result was not statistically significant (X2 = 21.236, P = 0.170). Comparison of the “Shammas-PL + Double-K SRK/T using EKR 4 mm” with other K values individually, indicated statistically significantly better results than Haigis using EKR 3 mm (X2 = 8.420, P = 0.015), Haigis using EKR 4 mm (X2 = 9.319, P = 0.009), SRK/T using true net power (X2 = 13.268, P = 0.001), and Double-K SRK/T using sim K (X2 = 8.544, P = 0.014), but not statistically significantly different from Double-K SRK/T using EKR 4 mm, Shammas-PL formula, Haigis-L formula, or regression formula. Comparison of regression formula with other K values individually was not statistically significantly different (P > 0.05).
Figure 2.
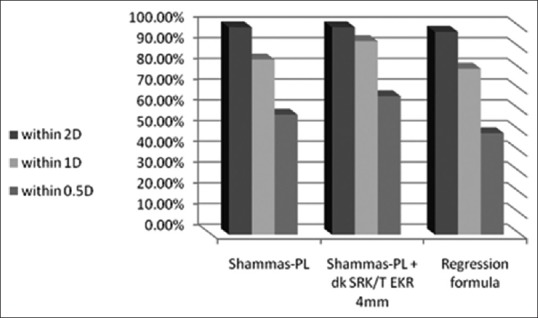
Refractive outcome of intraocular lens power calculations using the most accurate formulas
Comparison of the different MAEs indicated a statistically significant difference (F = 17.737, P < 0.001). The different MAEs were compared to the MAE for the “Shammas-PL + Double-K SRK/T using EKR 4 mm” and was statistically significant different except for “the regression formula” (t = 0.519, P = 0.607). The MAE of the regression formula was compared to that of the other formulas and was found to be statistically significantly different (P < 0.025) except for “Double-K SRK/T using EKR 4 mm” (t = 0.851, P = 0.399) and “Shammas-PL + Double-K SRK/T using EKR 4 mm” [Table 2].
DISCUSSION
Patients who have undergone previous excimer laser refractive surgery have high expectations with regards to the visual outcome after cataract surgery. Despite numerous methods for IOL power calculation, the postoperative refractive errors are less predictable in these patients compared to those who have not undergone refractive surgery. Unpredictable results are most likely due to inaccurate measurements of the corneal power following keratorefractive surgery (in addition to the error in estimation of ELP by third generation formulas, e.g., SRK/T).1,20,23,24
The major problem noted in literature on IOL power calculation after corneal refractive surgery was the relatively small number of patients included in the studies. For example, Masket and Masket25 included 30 eyes, Latkany et al.26 included 21 eyes, Shammas and Shammas22 included 15 eyes, and Aramberri20 included 9 cases. Some newer studies included larger number of eyes, for example, Haigis21 included 187 eyes retrospectively (the author mentioned some limitations including that the patient selection may have been biased toward better results and lack of additional data on patient age, BCVA, and time between cataract surgery and refraction). In addition, the exact role of the many K values reported in the Holladay report was not properly evaluated.
In the present study, K readings measured by different instruments were used to calculate IOL power after myopic LASIK. The manual K and automated K readings were steeper than that measured by the IOLMaster and, therefore, their use in IOL power calculation formulas would have resulted in postoperative hyperopia. The Holladay EKRs showed a gradual transition from flattest at 1 mm to steepest at 4.5 mm. Variable possibilities of incorporating those K values into IOL power calculation were considered in the current study. The true net power yielded one of the flattest K values that nearly approached EKR 1 mm. The mean sim-K value was slightly flatter than the IOLMaster K values. Tang et al.19 reported that the Holladay EKR at 4.5 mm measured a steeper corneal power than true corneal power based on paraxial optics and surgical outcome data.
In the present study, when calculating postrefractive surgery IOL power with the IOLMaster only, the Shammas-PL formula presented the best refractive outcome. The absolute IOL prediction error was 0.77 ± 0.65 D, with 100.0% of cases within ±2D, 84.4% of cases within ±1 D, and 57.8% of cases within ±0.5 D. Shammas and Shammas23 showed that using the Shammas modified K values yielded the best results with the Shammas-PL formula (mean absolute IOL prediction error 0.55 ±0.31 D, with 93.3% of cases within ±1 D) and the Holladay 2 formula (mean absolute IOL prediction error 0.55 ± 0.41 D, with 93.3% of cases within ±1 D).
Another alternative with the IOLMaster only is the Haigis-L formula. However, this formula yielded less accurate results than the Shammas-PL formula (ME was −0.47 ± 0.90 D; range, −2.79 – 1.62 D; 91.1% of cases were within ±2 D; 73.3% of cases were within ± 1 D; and 44.4% of cases were within ±0.5 D). Haigis20 published better results for the Haigis-L formula in his series of 186 eyes (ME was −0.04 ± 0.70 D; range, −2.30 to ±2.40 D; 98.4% of cases were within ±2 D; 84.0% of cases were within ±1 D; and 61.0% of cases were within ±0.5 D).
Regression analysis was used to deduce a formula to modify the IOL power calculated with the SRK/T formula using the IOLMaster K value. The goal of this modification was to provide a simple method to calculate the postrefractive surgery IOL power without the need for the Pentacam. The outcome of the regression formula was better than the Haigis-L formula, but worse than the Shammas-PL formula. There was no statistically significant difference from the mean of the combination of “Shammas-PL + Double-K SRK/T formula using EKR 4 mm”. However, R2 = 0.184 indicated a weak correlation for the prediction formula.
Data from Pentacam without the Holladay report improved the accuracy of IOL power calculation after keratorefractive surgery. SRK/T formula using true net power yielded good results (100.0% of cases were within ±2 D, 71.1% of cases were within ±1 D, and 31.1% of cases were within ± 0.5 D), which were inferior than the results published by Kim et al.5 using the same formula (93% of cases were within ±1 D, 70% of cases were within ± 0.5 D). The combination of “Shammas-PL + SRK/T using true net power” yielded excellent results (100.0% of cases were within ±2 D, 88.9% of cases were within ±1 D, and 55.6% of cases were within ±0.5 D), which was better than the Shammas-PL formula alone. However, an important limitation is the lack of IOL constant optimization. The true net power and sim-K from Pentacam require different optimized constants in virgin eyes and also in post-LASIK eyes.
Another issue that arose was, whether the use of Holladay EKRs improves the accuracy of IOL power calculations after keratorefractive surgery. Tang et al.25 reported that the Holladay EKR was inaccurate in IOL power calculation in virgin corneas and in those with a history of LASIK, PRK, or RK using current IOL power calculation formulas. However, Masket and Masket25 only used EKR at 4.5 mm. In this study, we attempted to address this more thoroughly using EKR at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 4.5 mm.
The most accurate EKR with the Haigis formula was EKR 4 mm (the refractive outcome was modest, with 97.8% of cases within ±2 D, 71.1% of cases within ±1 D, and 37.8% of cases within ±0.5 D). The most accurate EKR with the Double-K SRK/T formula was also EKR 4 mm (the refractive outcome was good, with 97.8% of cases within ±2 D, 80.0% of cases within ±1 D, and 42.2% of cases within ±0.5 D). The results of SRK/T using different Holladay EKR were less satisfactory. None of the Holladay EKR values showed a better outcome than that of true net power using the SRK/T formula.
The concept of using multiple formulas to improve the accuracy for IOL calculations after myopic LASIK has been published, albeit with older generation formulas.27 It was found that the means of combinations of formulas yielded excellent results that were better than any single formula alone (100.0% of cases within ±2 D, ≥88.9% of cases within ±1 D, and ≥55.6% of cases within ±0.5 D). The best combination was “Shammas-PL ± Double-K SRK/T using EKR 4 mm” (100.0% of cases were within ±2 D, 93.3% of cases were within ±1 D, and 66.7% of cases were within ±0.5 D).
In conclusion, we recommended the Shammas-PL formula or the simple regression formula “IOL power = SRK/T calculated power using IOLMaster K readings + (0.181 × AL) –2.151” when using the IOLMaster alone (both are better than using Haigis-L formula incorporated in the IOLMaster software). When using the Pentacam without the Holladay report, the combination of “Shammas-PL + SRK/T formula using true net power” yielded the best results. When using Pentacam with Holladay report, we recommend the combination of “Shammas-PL + Double-K SRK/T formula using EKR 4 mm.”
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bhopi J, editor. United Kingdom: Taylor and Francis; 2005. IOL power calculation in special situations. In: Evidenced Based Approach in Cataract Surgery; pp. 61–5. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fang JP, Hill W, Wang L, Chang V, Koch DD. Advanced intraocular lens power calculations. In: Kohnen T, Koch DD, editors. Cataract and Refractive Surgery. Germany: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2006. pp. 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rosa N, Capasso L, Lanza M, Borrelli M. Clinical results of a corneal radius correcting factor in calculating intraocular lens power after corneal refractive surgery. J Refract Surg. 2009;25:599–603. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20090610-05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Koch DD, Wang L. Calculating IOL power in eyes that have had refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003;29:2039–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2003.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kim SW, Kim EK, Cho BJ, Kim SW, Song KY, Kim TI. Use of the pentacam true net corneal power for intraocular lens calculation in eyes after refractive corneal surgery. J Refract Surg. 2009;25:285–9. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20090301-08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Coombs A, Gartry D. Cataract surgery. In: Lightman S, editor. Fundamentals of Clinical Ophthalmology. London: BMJ Books; 2003. pp. 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hoffer KJ. Calculating intraocular lens power after refractive corneal surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:500–1. doi: 10.1001/archopht.120.4.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Koch DD, Wang L. IOL Calculations following keratorefractive surgery. In: Fine I, Packer M, Hoffman R, editors. Refractive Lens Surgery. Germany: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg; 2005. pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Arce CG, Soriano ES, Weisenthal RW, Hamilton SM, Rocha KM, Alzamora JB, et al. Calculation of intraocular lens power using Orbscan II quantitative area topography after corneal refractive surgery. J Refract Surg. 2009;25:1061–74. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20091117-05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chen S, Hu FR. Correlation between refractive and measured corneal power changes after myopic excimer laser photorefractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002;28:603–10. doi: 10.1016/s0886-3350(01)01323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gobbi PG, Carones F, Brancato R. Keratometric index, videokeratography, and refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998;24:202–11. doi: 10.1016/s0886-3350(98)80201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Patel S, Alió JL, Pérez-Santonja JJ. Refractive index change in bovine and human corneal stroma before and after lasik: A study of untreated and re-treated corneas implicating stromal hydration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45:3523–30. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Patel S, Alio JL, Perez-Santonja JJ. A model to explain the difference between changes in refraction and central ocular surface power after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Refract Surg. 2000;16:330–5. doi: 10.3928/1081-597X-20000501-06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Holladay JT. Cataract surgery in patients with previous keratorefractive surgery (RK, PRK, and LASIK) Ophthalmic Pract. 1997;15:238–44. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fowler CW. Assessment of toroidal surfaces by the measurement of curvature in three fixed meridians. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1989;9:79–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-1313.1989.tb00812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang JK, Hu CY, Chang SW. Intraocular lens power calculation using the IOLMaster and various formulas in eyes with long axial length. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:262–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2007.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Reuland MS, Reuland AJ, Nishi Y, Auffarth GU. Corneal radii and anterior chamber depth measurements using the IOLmaster versus the Pentacam. J Refract Surg. 2007;23:368–73. doi: 10.3928/1081-597X-20070401-09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shammas HJ, Hoffer KJ, Shammas MC. Scheimpflug photography keratometry readings for routine intraocular lens power calculation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35:330–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2008.10.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tang Q, Hoffer KJ, Olson MD, Miller KM. Accuracy of Scheimpflug Holladay equivalent keratometry readings after corneal refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35:1198–203. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2009.02.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Aramberri J. Intraocular lens power calculation after corneal refractive surgery: Double-K method. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003;29:2063–8. doi: 10.1016/s0886-3350(03)00957-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Haigis W. Intraocular lens calculation after refractive surgery for myopia: Haigis-L formula. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:1658–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2008.06.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shammas HJ, Shammas MC. No-history method of intraocular lens power calculation for cataract surgery after myopic laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:31–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2006.08.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Camellin M, Calossi A. A new formula for intraocular lens power calculation after refractive corneal surgery. J Refract Surg. 2006;22:187–99. doi: 10.3928/1081-597X-20060201-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jarade EF, Abi Nader FC, Tabbara KF. Intraocular lens power calculation following LASIK: Determination of the new effective index of refraction. J Refract Surg. 2006;22:75–80. doi: 10.3928/1081-597X-20060101-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Masket S, Masket SE. Simple regression formula for intraocular lens power adjustment in eyes requiring cataract surgery after excimer laser photoablation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006;32:430–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2005.12.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Latkany RA, Chokshi AR, Speaker MG, Abramson J, Soloway BD, Yu G. Intraocular lens calculations after refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31:562–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2004.06.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Randleman JB, Foster JB, Loupe DN, Song CD, Stulting RD. Intraocular lens power calculations after refractive surgery: Consensus-K technique. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:1892–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2007.06.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


