Abstract
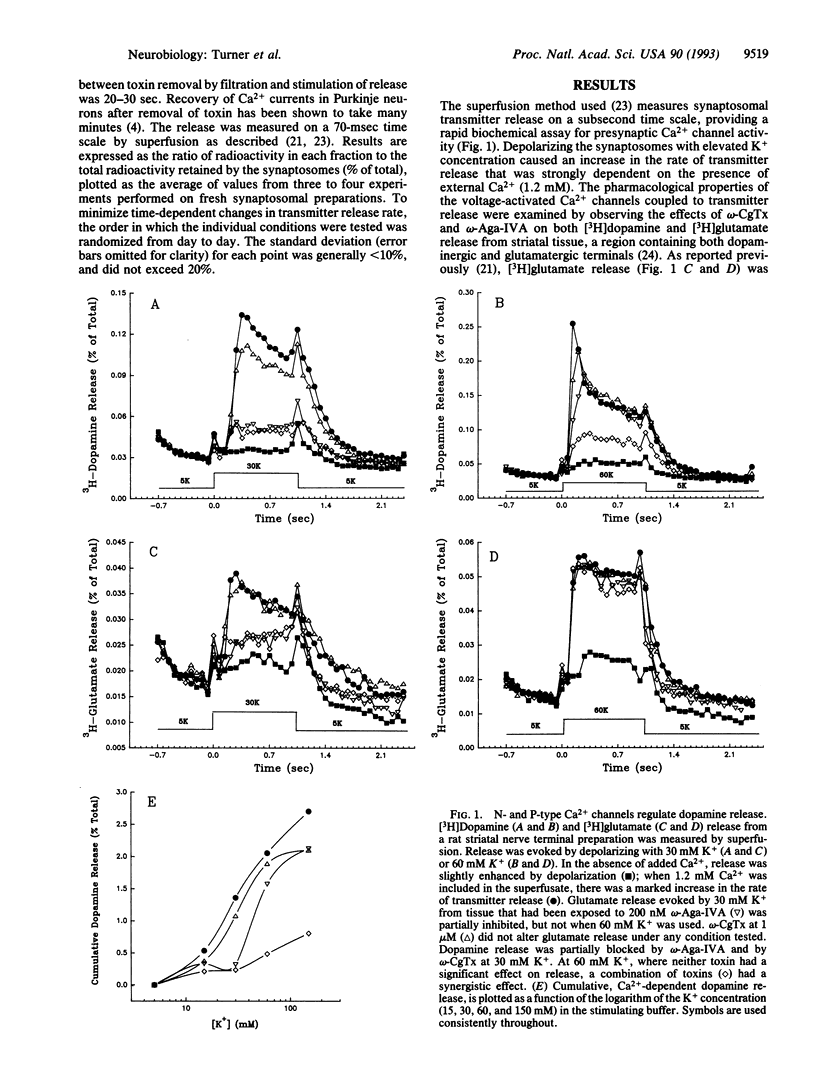
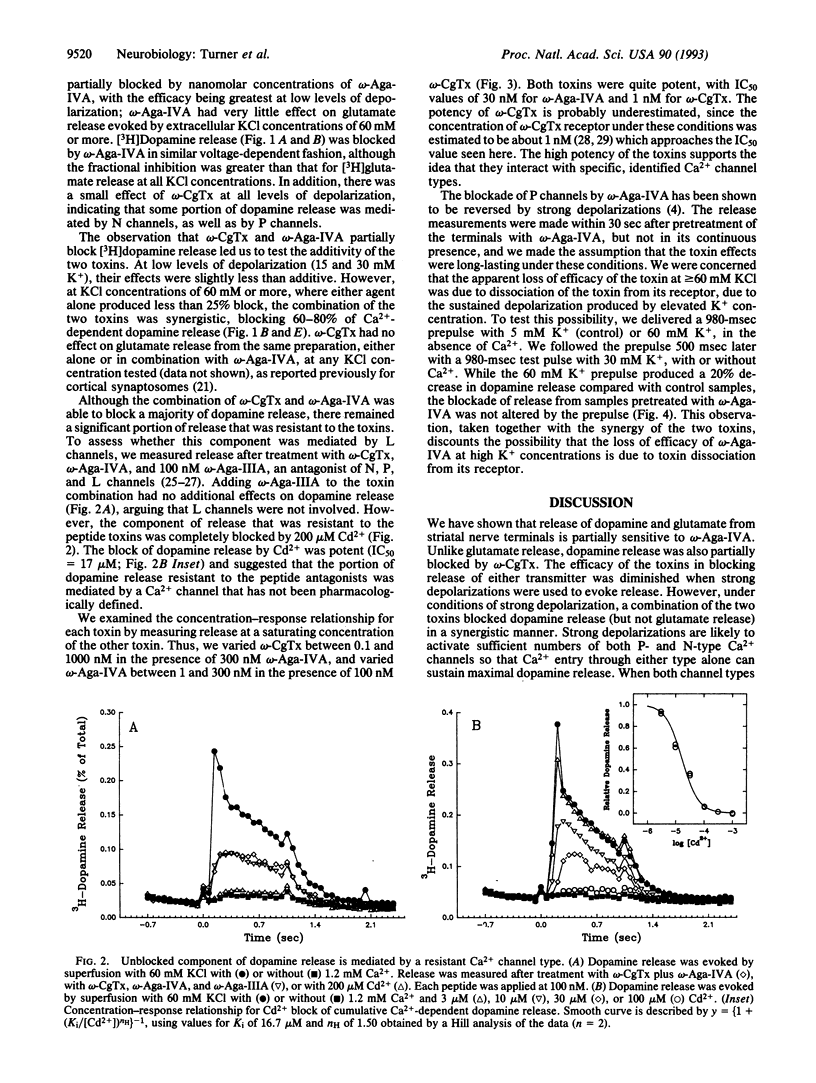
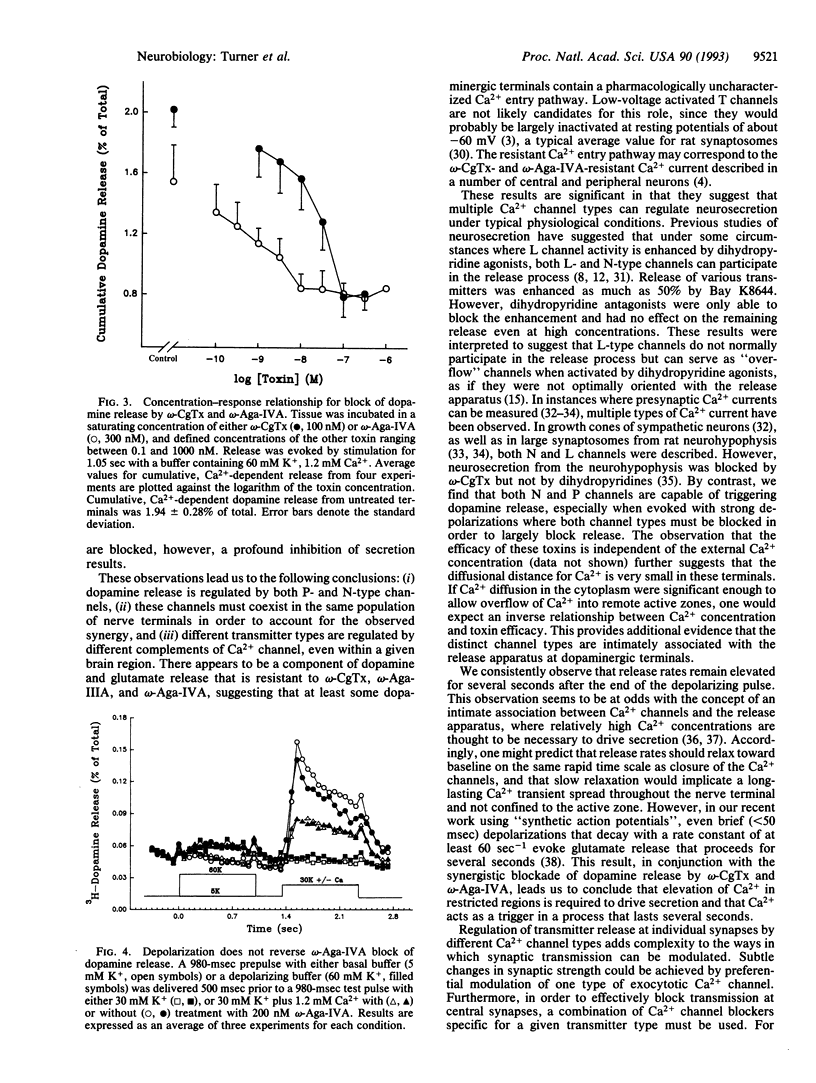
The regulation of excitation-secretion coupling by Ca2+ channels is a fundamental property of the nerve terminal. Peptide toxins that block specific Ca2+ channel types have been used to identify which channels participate in neurotransmitter release. Subsecond measurements of [3H]-glutamate and [3H]dopamine release from rat striatal synaptosomes showed that P-type channels, which are sensitive to the Agelenopsis aperta venom peptide omega-Aga-IVA, trigger the release of both transmitters. Dopamine (but not glutamate) release was also controlled by N-type, omega-conotoxin-sensitive channels. With strong depolarizations, where neither toxin was very effective alone, a combination of omega-Aga-IVA and omega-conotoxin produced a synergistic inhibition of 60-80% of Ca(2+)-dependent dopamine release. The results suggest that multiple Ca2+ channel types coexist to regulate neurosecretion under normal physiological conditions in the majority of nerve terminals. P- and N-type channels coexist in dopaminergic terminals, while P-type and a omega-conotoxin- and omega-Aga-IVA-resistant channel coexist in glutamatergic terminals. Such an arrangement could lend a high degree of flexibility in the regulation of transmitter release under diverse conditions of stimulation and modulation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine G. J., Charlton M. P., Smith S. J. Calcium action in synaptic transmitter release. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:633–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.003221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson M., Carlsson A. Interactions between glutamatergic and monoaminergic systems within the basal ganglia--implications for schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90108-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. J., Ertel E. A., Smith M. M., Venema V. J., Adams M. E., Leibowitz M. D. High affinity block of myocardial L-type calcium channels by the spider toxin omega-Aga-toxin IIIA: advantages over 1,4-dihydropyridines. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;42(6):947–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. H., Dunlap K. Pharmacological discrimination of N-type from L-type calcium current and its selective modulation by transmitters. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):906–914. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00906.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley D. J., Lickert M., Lupp A., Osswald H. Distribution of [125I]omega-conotoxin GVIA and [3H]isradipine binding sites in the central nervous system of rats of different ages. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 11;93(2-3):318–323. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley D. J., Lupp A., Hertting G., Osswald H. Omega-conotoxin GVIA and pharmacological modulation of hippocampal noradrenaline release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 29;148(2):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90572-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herdon H., Nahorski S. R. Investigations of the roles of dihydropyridine and omega-conotoxin-sensitive calcium channels in mediating depolarisation-evoked endogenous dopamine release from striatal slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;340(1):36–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00169204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirning L. D., Fox A. P., McCleskey E. W., Olivera B. M., Thayer S. A., Miller R. J., Tsien R. W. Dominant role of N-type Ca2+ channels in evoked release of norepinephrine from sympathetic neurons. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):57–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2447647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne A. L., Kemp J. A. The effect of omega-conotoxin GVIA on synaptic transmission within the nucleus accumbens and hippocampus of the rat in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;103(3):1733–1739. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya H., Sawada S., Yamamoto C. Synthetic omega-conotoxin blocks synaptic transmission in the hippocampus in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Aug 15;91(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. M., Yoshikami D. A venom peptide with a novel presynaptic blocking action. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):282–284. doi: 10.1038/308282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Petrov A. V., Smirnov S. V., Nowycky M. C. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity induced by excitatory amino acids includes changes in sensitivity to the calcium channel blocker, omega-conotoxin. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jul 31;102(2-3):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos J. R., Nowycky M. C. Two types of calcium channels coexist in peptide-releasing vertebrate nerve terminals. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1419–1426. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Poenie M., Reuter H., Tsien R. Y., Tsien R. W. Spatial distribution of calcium channels and cytosolic calcium transients in growth cones and cell bodies of sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2398–2402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Lin J. W., Cherksey B. Blocking and isolation of a calcium channel from neurons in mammals and cephalopods utilizing a toxin fraction (FTX) from funnel-web spider poison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1689–1693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. Microdomains of high calcium concentration in a presynaptic terminal. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1350109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marqueze B., Martin-Moutot N., Levêque C., Couraud F. Characterization of the omega-conotoxin-binding molecule in rat brain synaptosomes and cultured neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;34(2):87–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Nicholls D. G. The bioenergetics of neurotransmitter release. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 13;1059(3):243–264. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemiss D. N., Spedding M. A functional correlate for the dihydropyridine binding site in rat brain. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):94–96. doi: 10.1038/314094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):46–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2432656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Adams M. E., Bean B. P. P-type calcium channels in rat central and peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90223-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Venema V. J., Adams M. E., Bean B. P. Inhibition of N- and L-type Ca2+ channels by the spider venom toxin omega-Aga-IIIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6628–6631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Venema V. J., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Bean B. P., Adams M. E. P-type calcium channels blocked by the spider toxin omega-Aga-IVA. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):827–829. doi: 10.1038/355827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogul D. J., Fox A. P. Evidence for multiple types of Ca2+ channels in acutely isolated hippocampal CA3 neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:259–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obaid A. L., Flores R., Salzberg B. M. Calcium channels that are required for secretion from intact nerve terminals of vertebrates are sensitive to omega-conotoxin and relatively insensitive to dihydropyridines. Optical studies with and without voltage-sensitive dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Apr;93(4):715–729. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.4.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perney T. M., Hirning L. D., Leeman S. E., Miller R. J. Multiple calcium channels mediate neurotransmitter release from peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6656–6659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan L. J., Sah D. W., Bean B. P. Ca2+ channels in rat central and peripheral neurons: high-threshold current resistant to dihydropyridine blockers and omega-conotoxin. Neuron. 1991 Feb;6(2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds I. J., Wagner J. A., Snyder S. H., Thayer S. A., Olivera B. M., Miller R. J. Brain voltage-sensitive calcium channel subtypes differentiated by omega-conotoxin fraction GVIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8804–8807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suszkiw J. B., Murawsky M. M., Shi M. Further characterization of phasic calcium influx in rat cerebrocortical synaptosomes: inferences regarding calcium channel type(s) in nerve endings. J Neurochem. 1989 Apr;52(4):1260–1269. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb01874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Adams M. E., Dunlap K. Calcium channels coupled to glutamate release identified by omega-Aga-IVA. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):310–313. doi: 10.1126/science.1357749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner T. J., Pearce L. B., Goldin S. M. A superfusion system designed to measure release of radiolabeled neurotransmitters on a subsecond time scale. Anal Biochem. 1989 Apr;178(1):8–16. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90347-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema V. J., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Hathaway G. M., Adams M. E. Antagonism of synaptosomal calcium channels by subtypes of omega-agatoxins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2610–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Treistman S. N., Lemos J. R. Two types of high-threshold calcium currents inhibited by omega-conotoxin in nerve terminals of rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:181–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S., Fogelson A. L. Relationship between transmitter release and presynaptic calcium influx when calcium enters through discrete channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3032–3036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



