Key Points
PCNSLs and PTLs have a defining genetic signature that differs from other LBCLs and suggests rational targeted therapies.
PCNSLs and PTLs frequently exhibit 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 copy number alterations and translocations, likely genetic bases of immune evasion.
Abstract
Primary central nervous system lymphomas (PCNSLs) and primary testicular lymphomas (PTLs) are extranodal large B-cell lymphomas (LBCLs) with inferior responses to current empiric treatment regimens. To identify targetable genetic features of PCNSL and PTL, we characterized their recurrent somatic mutations, chromosomal rearrangements, copy number alterations (CNAs), and associated driver genes, and compared these comprehensive genetic signatures to those of diffuse LBCL and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBL). These studies identify unique combinations of genetic alterations in discrete LBCL subtypes and subtype-selective bases for targeted therapy. PCNSLs and PTLs frequently exhibit genomic instability, and near-uniform, often biallelic, CDKN2A loss with rare TP53 mutations. PCNSLs and PTLs also use multiple genetic mechanisms to target key genes and pathways and exhibit near-uniform oncogenic Toll-like receptor signaling as a result of MYD88 mutation and/or NFKBIZ amplification, frequent concurrent B-cell receptor pathway activation, and deregulation of BCL6. Of great interest, PCNSLs and PTLs also have frequent 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 CNAs and additional translocations of these loci, structural bases of immune evasion that are shared with PMBL.
Introduction
Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) often involve multiple nodal and extranodal sites. In contrast, large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) subtypes, including primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), primary testicular lymphoma (PTL), and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBL), present as localized masses in extranodal organs.1-4 PCNSLs and PTLs, which both arise in sites that were previously considered to be immune sanctuaries, have inferior responses to therapies.1-6 The defining genetic alterations in PCNSL and PTL and the relationships between these LBCLs, PMBL, and systemic DLBCL are incompletely characterized.
DLBCLs exhibit several types of low-frequency genetic alterations including copy number alterations (CNAs), mutations, and chromosomal rearrangements.7 Certain alterations are more common in transcriptionally defined tumor subtypes. In the cell-of-origin classification, DLBCLs share transcriptional signatures of normal germinal center B-cells (GCBs) or in vitro activated B-cells (ABCs). ABC-type DLBCLs exhibit increased baseline NF-κB activity, more frequent genetic alterations of NF-κB and Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway components including mutations of CARD11 and MYD88 and the proximal B-cell receptor (BCR)-signaling pathway component, CD79B. However, these alterations are only detected in a subset of ABC-type DLBCLs (MYD88, 29%; CD79B, 18%; and CARD11, 10%).8-10 Additional aspects of DLBCL heterogeneity are captured by the consensus clustering classification, which identifies “B-cell receptor,” “Oxidative Phosphorylation,” and “Host Response” subtypes.11-13
Recent genetic analyses of DLBCL underscore the importance of capturing both somatic mutations and CNAs.14 Although only 15% to 20% of DLBCLs have inactivating TP53 mutations, the majority of these tumors exhibit complementary CNAs that decrease p53 activity and perturb cell-cycle regulation.14 DLBCLs with CNA-dependent p53 deficiency and cell-cycle deregulation have increased genomic instability and have a less favorable outcome.14
PMBL is a distinct LBCL subtype that exhibits constitutive NF-κB activation and shares certain clinical and genetic features with classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL).15 We and others identified 9p24.1/CD274(PD-L1)/PDCD1LG2(PD-L2), copy gain, and increased expression of the PD-1 ligands in 65% of PMBLs.16,17 Translocations of PD-L1 and PD-L2 were also reported in PMBL.18,19 Genetic bases of PD-1 ligand overexpression are of particular interest given the role of PD-1 signaling in tumor-immune evasion and the efficacy of PD-1 blockade in other B-cell lymphomas with 9p24.1 copy gain.20-22
PCNSLs primarily arise in elderly patients and present as infiltrative masses of EBV– tumor cells in periventricular white matter.1,4 Additional EBV+ PCNSLs occur in younger immunocompromised patients.1 Reported CNAs include loss of the HLA-loci at 6p21.32 and deletion of CDKN2A in a minority of tumors.5,23-25 Somatic mutations of MYD88, CD79B, and additional less common targets have been described.23,24,26-28
PTLs, which are the most common testicular tumors in elderly men,2 present as focal masses with epididymal and scrotal involvement. At relapse, PTLs often involve additional extranodal sites including the central nervous system (CNS), skin, pleura, and contralateral testis. In previous array comparative genomic hybridization studies, PTLs exhibited frequent loss of the HLA-loci and 19q13 gain.25 Somatic mutations of MYD88 and CD79B of variable frequency have also been reported.29,30
Herein, we comprehensively characterize the genetic features of PCNSL and PTL and compare these tumors with systemic DLBCLs of known transcriptional subtypes and PMBL. The goal was to identify targetable lesions, bases of immune privilege in PCNSL and PTL, and unique combinations of genetic alterations in discrete LBCL subtypes.
Materials and methods
Patients and primary tumor specimens
In accordance with local institutional review board protocols, newly diagnosed fresh-frozen PMBLs, EBV– PCNSLs, and PTLs were obtained from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Massachusetts General Hospital, and University of Freiburg; formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) PTLs and PCNSLs were obtained from the Netherlands Cancer Institute/VU University Medical Center Amsterdam and Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
The discovery cohort includes the aforementioned primary LBCLs (PMBLs, PTLs, and PCNSLs with fresh-frozen tumor specimens) and an additional comparative cohort of previously analyzed primary DLBCL fresh-frozen biopsy specimens.14 The number of discovery cohort samples analyzed for CNAs with high-density single nucleotide polymorphism (HD-SNP) arrays, transcript abundance with Affymetrix arrays, single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) with whole-exome sequencing (WES) of tumors and paired normals or RNA-Seq of tumors only and chromosomal rearrangement by DNA-Seq with a custom designed bait set are indicated in supplemental Figure 1A and supplemental Table 1A-B (available on the Blood Web site). An extension cohort of 43 PTLs, and 43 EBV– and 8 EBV+ PCNSLs from FFPE tissue were evaluated by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for CNAs, qPCR and Sanger sequencing for SNVs, and immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis for protein expression as indicated in supplemental Figure 1B-C, supplemental Table 1C-D, and supplemental Methods.
Results
Recurrent CNAs and candidate driver genes in LBCL subtypes
CNAs.
To define recurrent CNAs in specific LBCL subtypes, we performed HD-SNP analyses of 21 EBV– PCNSLs, 7 PTLs, and 11 PMBLs and evaluated these data with the Genomic Identification of Significant Targets in Cancer (GISTIC) algorithm31 (supplemental Figure 1 and supplemental Tables 1 and 2). Thereafter, we compared the recurrent CNAs in these LBCL subtypes with the previously described CNAs in 180 systemic DLBCLs14 using mirror plots (Figure 1A-B and supplemental Figure 2).
Figure 1.
GISTIC-defined CNAs in LBCL subtypes. (A-B) GISTIC-defined recurrent CNAs (amplification in [A], red; deletions in [B], blue) in 180 primary DLBCLs14 are compared with those in 11 PMBLs (left panel) and 28 PCNSLs/PTLs (right panel) in mirror plots. Chromosome position is on the y-axis, and significance is on the x-axis. The green line denotes q value of 0.25. (C) Frequencies of the 21 GISTIC-defined amplification peaks (top panel, red) and the 26 GISTIC-defined deletion peaks (bottom panel, blue) in the respective LBCL subtypes are plotted as bar graphs. DLBCL-GCB and DLBCL-ABC are subsets of DLBCL-All. CNAs that are more frequent in PTL and PCNSL (a), PTL only (b), PMBL and PTL (c), and PCNSL only (d), respectively, are noted. CNAs that are significantly enriched in PMBL, PCNSL, and/or PTL are boxed (FDR q value < 0.3; see also supplemental Table 2). Top genes by integrative analyses of copy number (CN) and transcript abundance are indicated on the right.
To quantify the relative frequencies of specific CNAs in the LBCL subtypes, we aggregated the HD-SNP array data from all LBCLs and applied the GISTIC algorithm (supplemental Table 3A-D). Subtype-specific differences in the frequency of CNAs were assessed with an enrichment test (Figure 1C and supplemental Table 3E). Copy gains of 3q12.3, 18q21.33, and 19q13.42 and copy losses of 6p21.33, 6q21, and 9p21.3 were significantly more frequent in PCNSL and PTL. Although the frequencies of 18q21.33 and 19q13.42 copy gain were comparable in PCNSL, PTL, and ABC-type DLBCLs, 9p21.3 copy loss was significantly more common and often biallelic in PCNSL and PTL (Figure 1C). Of interest, we found more frequent 9p24.1 copy gain in PTL, as in PMBL (Figure 1C).
Integrative analyses.
To identify the genes perturbed by CNAs, we performed gene expression profiling on all LBCLs with available RNA and a representative subset of DLBCLs.14 Genes within recurrent CNAs that had the most significant association between transcript abundance and copy gain or loss were defined as candidate drivers (supplemental Table 4).14
NFKBIZ, the candidate driver of 3q12.3 copy gain (Figure 1C), encodes IκB-ζ. This atypical IκB family member is induced by TLR signaling32 and coactivates canonical and noncanonical NF-κB pathways.32-34 3q12.3/NFKBIZ copy gain was also detected in a subset of systemic DLBCLs (11% [19/180]) and a larger percentage of ABC-type tumors (24% [13/55]) (Figure 1C and supplemental Figure 3).14
BCL2 was most closely associated with 18q21.33 copy gain, and CDKN2A was most tightly linked with 9p21.3 copy loss (Figure 1C); the peak of 6p21.33 copy loss included the HLA-B and HLA-C loci. PCNSL-selective 3p14.2 copy loss was associated with decreased expression of the tumor suppressor, FHIT (Figure 1C). In PTL, as in PMBL, 9p24.1 copy gain was linked with increased expression of the PD-1 ligand, PD-L2 (Figure 1C).
These data indicate that PCNSL and PTL share certain recurrent CNAs and candidate drivers that are also present in a subset of ABC-type DLBCLs. However, the defining CNA, 9p21.3/CDKN2A copy loss, was significantly more frequent in PCNSLs and PTLs than in ABC-type DLBCLs (71% [20/28] PCNSL/PTL vs 34.5% [19/55] ABC-type DLBCL; P = .0023; supplemental Table 3E). Furthermore, 9p21.3/CDKN2A copy loss was more often biallelic in PCNSL/PTL (50% [14/28] biallelic, 21% [6/28] monoallelic) compared with ABC-type DLBCLs (8% [5/62] biallelic, 26% [16/62] monoallelic; P < .0001).14
Patterns of CNAs and bases of genomic instability in LBCL subtypes
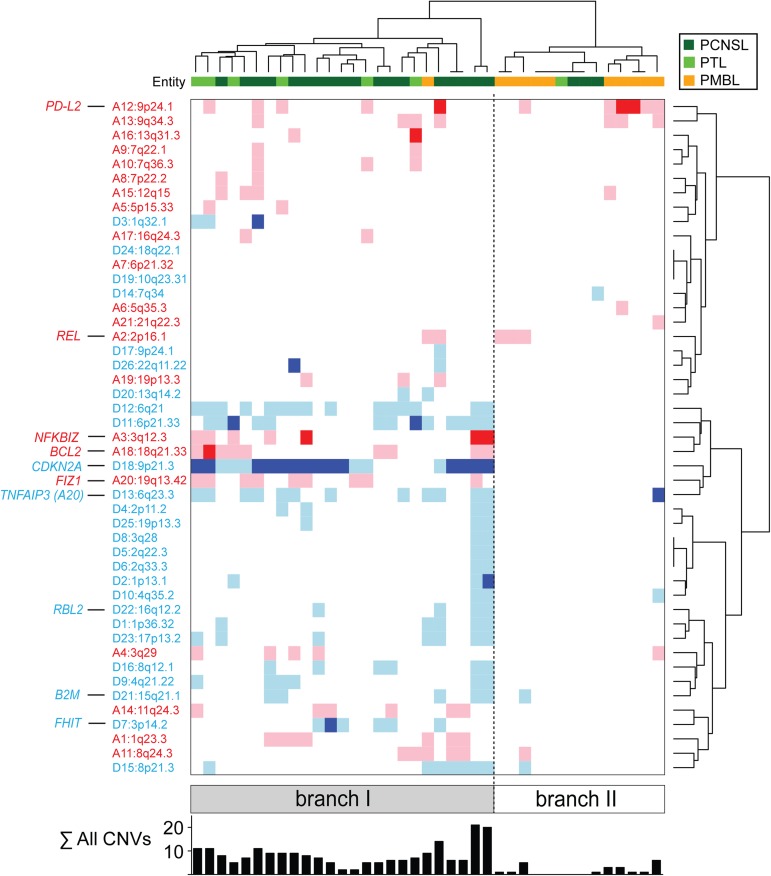
Certain DLBCLs have CNAs of multiple modulators of p53 activity and cell-cycle progression, increased genomic instability, and significantly higher total CNAs.14 To evaluate patterns of CNAs in PCNSL, PTL, and PMBL, we performed unsupervised bihierarchical clustering. The majority of PCNSLs and PTLs were clustered together and characterized by frequent, often biallelic 9p21.3/CDKN2A loss and/or FHIT loss (branch I, Figure 2), These tumors also had increased genomic instability as reflected by significantly higher total CNAs (branch 1 vs branch 2; P < .0001). These findings likely reflect the complementary roles of the CDNK2A gene products, p16INK4A and p19ARF, in p53 and cell-cycle regulation and the link between p53 deficiency, perturbed cell-cycle regulation, and genomic instability.14,35-39 FHIT loss has also been associated with increased genomic instability.40
Figure 2.
PCNSLs, PTLs, and PMBLs clustered by recurrent CNAs. (A) Unsupervised bihierarchical clustering of all 47 GISTIC-defined CNAs (y-axis) in 39 primary LBCLs (21 PCNSLs [dark green], 7 PTLs [light green], 11 PMBLs [orange]; x-axis). Copy gains, red; copy losses, blue; color intensity corresponds to magnitude of CNA. The sum of all GISTIC-defined CNAs per sample is listed below as a bar graph. Top genes by integrative analyses of CN and transcript abundance are indicated on the left.
Almost all PMBLs (10/11), a small number of PCNSLs, and one PTL (4/28) were clustered in a branch with relatively few CNAs (branch II, Figure 2). In contrast to PMBLs, which exhibited 9p24.1/PD-L2 copy gains with few other CNAs (branch II), PTLs and PCNSLs had 9p24.1/PD-L2 copy gains in association with 9p21.3/CDKN2A copy loss and increased genomic instability (branch I, Figure 2).
Chromosomal rearrangements in PCNSL
We next assessed chromosomal rearrangements (including translocations, deletions duplications, and inversions) in 24 PCNSLs using a targeted DNA sequencing approach and a custom bait set covering 49 candidate genetic loci. The resulting data were analyzed with 2 complementary detection algorithms, dRanger/Breakpointer41 and BreaKmer42 (Figure 3A and supplemental Table 5A-C).
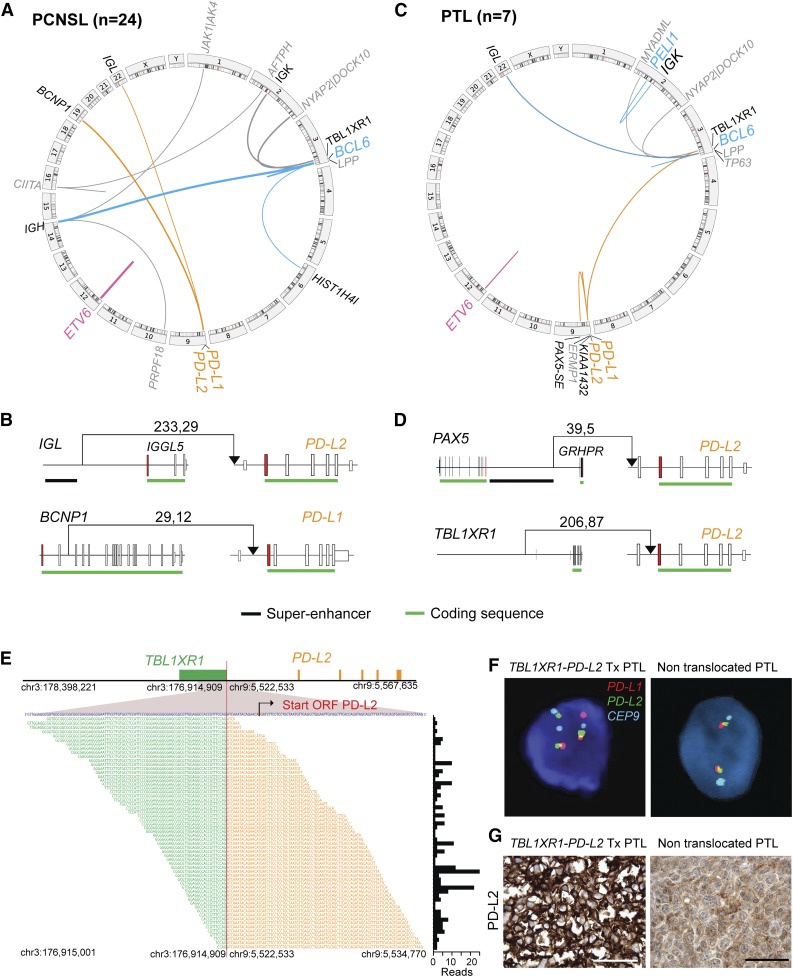
Figure 3.
Chromosomal rearrangements in PCNSL and PTL. (A,C) Detected chromosomal rearrangements in 24 PCNSL (A) and 7 PTL (C) are summarized as circos plots. Structural alterations involving certain partners are highlighted; BCL6, blue; ETV6, pink; PD-1 ligands, orange. Partners of color-coded alterations are black, all other alterations are gray. Frequency of events is indicated by line thickness. (B,D) Chromosomal rearrangements involving PD-L1 or PD-L2 are plotted in their genomic context. Exons are visualized as boxes, ATG-containing exon are in red, the coding region is underlined in green, and previously identified super-enhancers in DLBCLs43 are underlined in black. The number of supporting reads (split reads, read pairs) is indicated above each translocation. (E) TBL1XR1-PD-L2 fusion as validated by RNA-Seq. Chromosomal breakpoint is depicted by the red line. Start codon of PD-L2 is indicated in red within the contig of the RNA-Seq reads. The translocation involves only the regulatory elements of TBL1XR1 and does not affect the open reading frame (ORF) of PD-L2. Individual supporting reads are shown in the lower panel, with frequencies as a bar graph on the right. (F) FISH assays of PTLs with the PD-L2 translocation (left panel) or with wild-type PD-L2 (right panel). PD-L1 in red, PD-L2 in green, and centromeric probe (CEP9) in aqua. (G) IHC of PD-L2 expression in the translocated PTL (left panel) and a PTL with wild-type PD-L2 (right panel). The scale bar represents 100 μm.
BCL6.
The most frequent chromosomal rearrangements deregulated BCL6 by juxtaposing the IgH super-enhancer43 or 5′HIST1H4I regulatory elements to the BCL6 5′-untranslated region (5′UTR) (17% [4/24]) (Figure 3A and supplemental Figure 4). In 2 cases, deletions proximal to the 5′UTR of BCL6 removed the regulatory elements, transcriptional start side, and first 5 exons of the BCL6-adjacent LPP gene (supplemental Figure 4C). This alteration may decrease the abundance of the LPP-intragenic miR-28, a reported tumor suppressor that is frequently downregulated in aggressive lymphomas.44
ETV6.
Thirteen percent (3/24) of the PCNSLs had inactivating alterations of ETV6, deletions of exon 2 or exons 2-5 that altered the reading frame (Figure 3A and supplemental Figure 4B). ETV6 encodes a transcriptional repressor perturbed by translocations, whole-gene deletions, or somatic mutations in multiple hematopoietic malignancies.45 However, selective exon deletions that alter the ETV6 reading frame were previously undescribed.
PD-L1/PD-L2.
Of note, 13% (3/24) of PCNSLs had previously unidentified translocations involving the PD-1 ligand loci (Figure 3A). These included the juxtaposition of the Igλ super-enhancer proximal to the PD-L2 5′UTR or translocation of BCNP1 (FAM129C)46 regulatory elements proximal to the PD-L1 start codon (Figure 3B and supplemental Figure 4). An additional PCNSL had an inactivating translocation of CIITA, the master transcription factor regulating MHC class II expression (Figure 3A).
Chromosomal rearrangements in PTL
Using the same approach, we analyzed chromosomal rearrangements in 7 PTLs from the discovery cohort.
BCL6.
Two PTLs had translocations that deregulated BCL6-juxtaposition of the Igλ super-enhancer proximal to BCL6 5′UTR and the first reported translocation of the Igκ super-enhancer to the 5′ regulatory elements of PELI1 (Figure 3C and supplemental Figure 4A). PELI1 encodes the E3 ubiquitin ligase, Pellino1, which stabilizes BCL6 via K63 polyubiquitination and promotes B-cell lymphomagenesis in a murine model.47 As in PCNSL, one PTL had a deletion proximal to BCL6 that removed the transcriptional start side and first 5 exons of LPP (supplemental Figure 4C).
ETV6.
One PTL had an inactivating alteration of ETV6 that disrupts the coding sequence (Figure 3C and supplemental Figure 4B).
PD-L2.
Two PTLs had novel translocations involving PD-L2. In one case, the translocation juxtaposed the recently described PAX5 super-enhancer43 to the PD-L2 5′UTR (Figure 3C-D and supplemental Table 5C). In another, the translocation placed the 5′ regulatory elements of TBL1XL1 proximal to the first coding exon of PD-L2 (Figure 3C-D and supplemental Figure 4E). These findings were confirmed using RNA-Seq and the QueryFuse algorithm48 and a split-apart FISH assay (Figure 3E-F). The PTL with the TBL1XR1-PD-L2 translocation also had increased PD-L2 expression (Figure 3G).
Recurrent somatic mutations in PCNSL
We next evaluated the PCNSLs for recurrent somatic mutations by performing WES on the subset of PCNSLs with available paired normal specimens (5 samples) and prioritizing the alterations with the MutSig2CV algorithm49 (supplemental Figures 5 and 6 and supplemental Table 5D-F). To increase sample size, we performed RNA-Seq on an additional 9 PCNSLs and assessed the frequency of WES-detected mutations in the combined cohort (supplemental Table 5G-H). Eighty-six percent (12/14) of the analyzed PCNSLs exhibited oncogenic gain-of-function mutations in MYD88 (MYD88L265P); 64% (9/14) had missense mutations in the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif domain of CD79B and 29% (4/14) had missense mutations in the coiled-coil domain of CARD11 (Figure 4A and supplemental Figure 7). These data indicate that canonical MYD88 and CD79B mutations are more frequent in PCNSLs than in previously reported ABC-type DLBCLs (MYD88, 29%8; CD79B, 18%9).
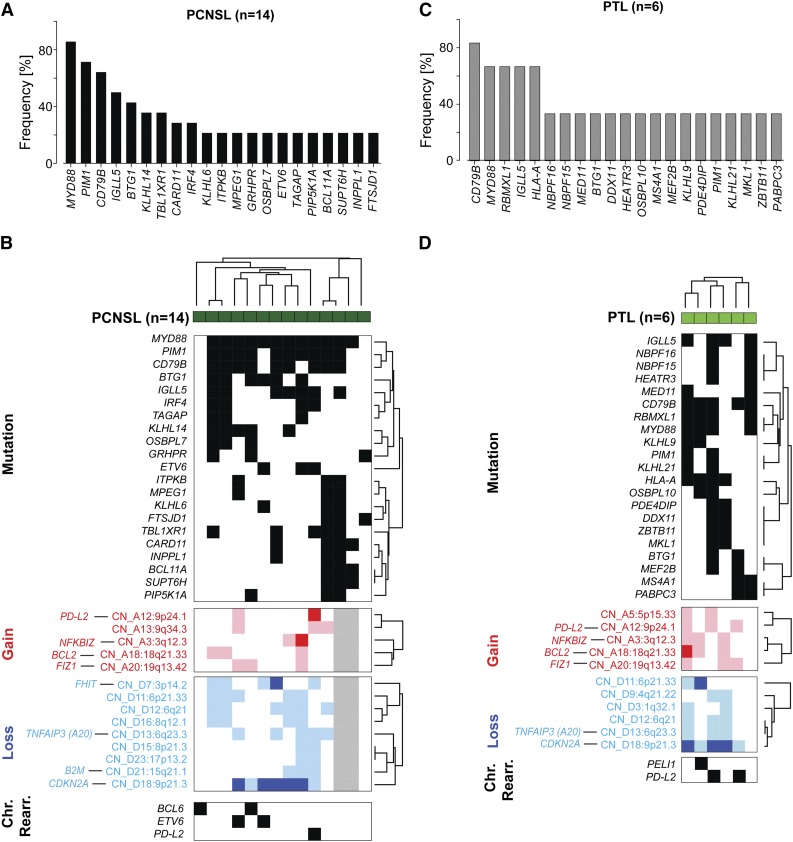
Figure 4.
Somatic mutations and patterns of genetic alterations in PCNSL and PTL. (A) Frequency of mutations in PCNSLs (mutations initially identified by WES in 5 tumor/normal pairs and subsequently assessed in 9 additional tumors without paired normals by RNA-Seq). See also supplemental Table 5D-H. Only genes mutated in at least 20% (3 patients) are shown. (B) Mutations occurring in at least 20% (3/14) of PCNSL samples (dark green) are plotted in a black-and-white–coded matrix (x-axis, samples; y-axis, mutations; black, mutation present; white, mutation absent) and clustered bihierarchically. CNAs in these PCNSLs are visualized as a color-coded heat map below; copy gain, red; copy loss, blue; not available, gray; color intensity corresponds to magnitude of CNA. Top genes by integrative analyses of CN and transcript abundance are indicated on the left, y-axis. Chromosomal rearrangements of BCL6, ETV6, or PD-L2 are added below. (C) Frequency of mutations in 6 PTLs as assessed by RNA-Seq. Only mutations present in at least 2 patients are shown (supplemental Table 5I, full list). SNVs were filtered for known SNPs; only SNVs previously deposited in COSMIC or reported to be mutated in DLBCLs/PCNSLs are shown. (D) Mutations present in at least 2 PTLs (y-axis) are plotted in a black-and-white–coded matrix as in (B) and clustered bihierarchically. CNAs in these PTLs are visualized as a color-coded heat map below, and selected chromosomal rearrangements modifying BCL6 (PELI1) and PD-L2 are added at the bottom.
PCNSLs also exhibited frequent (71% [10/14]) missense mutations in the kinase domain of PIM1, a known target of aberrant somatic hypermutation (Figure 4A and supplemental Figure 7D). In addition, 29% (4/14) of the evaluated PCNSLs had mutations in IRF4. The encoded IRF4 transcription factor, which regulates germinal center exit, class switch recombination, and plasma cell development is also expressed in ABC-type DLBCLs (Figure 4A and supplemental Figure 7).50
Twenty-one percent (3/14) of PCNSLs exhibited mutations of ETV6 (Figure 4A and supplemental Figure 7D), which was also perturbed by inactivating deletions of coding exons (Figure 3A and supplemental Figure 4). PCNSLs also had mutations of BTG1 (43% [6/14]) and TBL1XR1 (36% [5/14]), transcriptional cofactors that regulate ETV6 activity (Figure 4A and supplemental Figure 7D).51 Of interest, TBL1XR1 also modulates TLR/MYD88 signaling by increasing clearance of NCor/SMRT transcriptional corepressors from certain TLR/MYD88 target genes.52
Patterns of genetic alterations in PCNSLs
After defining recurrent mutations, chromosomal rearrangements, and CNAs in PCNSL, we assessed the patterns of alterations in individual tumors. Mutations and CNAs that occurred in ≥20% (3/14) of tumors were included and chromosomal rearrangements were added (Figure 4B). In these PCNSLs, all CD79B mutations occurred in the context of MYD88 mutations. Similarly, the less frequent CARD11 mutations all occurred in MYD88 mutation-positive PCNSLs, three of which had concurrent CD79B mutations. PCNSLs with copy loss of TNFAIP3 also had concurrent CD79B and MYD88 mutations. In the analyzed PCNSLs, MYD88 mutations also occurred in association with additional potential modulators of TLR signaling such as NFKBIZ copy gains (Figure 4B). Furthermore, these PCNSLs often had mutations and/or exon deletions of ETV6, and/or mutations of the transcriptional cofactors BTG1 and TBL1XR1.
The majority of PCNSLs also had evidence of genomic instability as reflected by CDKN2A and/or FHIT loss and multiple additional CNAs (Figure 2 and 4B). However, PCNSLs had infrequent TP53 mutations (7% [1/14]), likely because CDKN2A deregulates the same pathway upstream of TP53.14,53
Recurrent mutations in PTL
Given the shared genetic features of PCNSL and PTL (Figures 1-3), we next evaluated the spectrum of mutations in the series of available PTLs. In the absence of paired germline DNA samples, we performed RNA-Seq on 6 PTLs and identified SNVs after filtering out known SNPs (Figure 4C and supplemental Table 5I). In these PTLs, we focused on genes that were mutated in our WES PCNSL cohort or systemic DLBCLs, or those that were previously deposited in the COSMIC database.54-58 Like the PCNSLs, the PTLs had frequent CD79B and MYD88 mutations and additional mutations of PIM1 and BTG1 (Figure 4C). Mutations of MEF2B, a transcriptional activator and regulator of BCL6 expression,59 were also identified (Figure 4C and supplemental Figure 7D). MEF2B alterations were previously reported in ∼8% of systemic DLBCLs of the ABC and GCB subtypes.59
Patterns of genetic alterations in PTL
As in the PCNSLs, CD79B and MYD88 mutations were largely concurrent in the PTLs; PIM1, BTG1, and MEF2B alterations were detected within this subset of CD79B/MYD88-mutated tumors (Figure 4D). The aforementioned mutations occurred in the setting of frequent, often biallelic, CDKN2A copy loss, TNFAIP3 copy loss, and NFKBIZ copy gain. In addition, PTLs had multiple bases of deregulating BCL6 including mutations of MEF2B and translocations of Igλ-PEL1 (Figure 4D) and Igλ-BCL6 (Figure 3C).
Validation of recurrent CNAs in a PTL extension cohort
Given the small size of our discovery PTL cohort, we obtained an additional 43 FFPE PTLs to evaluate specific recurrent CNAs and SNVs (supplemental Figure 8 and supplemental Table 1C-D). We established qPCR assays for the most significant CNAs/driver genes using DNA from informative LBCL cell lines and normal lymphoid cells as controls (supplemental Table 6). CDKN2A integrity was assessed with 3 independent probe sets that covered exons coding for p16INK4A and p19ARF (supplemental Figure 8A-B). Mono- or biallelic loss of the full CDKN2A locus was detected in ∼81% (35/43) of tumors (supplemental Figure 8A). Frequent copy gain of 18q21.33/BCL2 (47% [20/43]) and 19q13.42/FIZ1 (70% [30/43]) were also confirmed (supplemental Figure 8C-D).
Functional consequences of 3q12.3/NFKBIZ copy gain and near-uniform oncogenic TLR signaling in PTL and PCNSL
In the PTL extension cohort, 44% of these tumors also had 3q12.3/NFKBIZ copy gain (Figure 5A, left panel). Similar to the PTL discovery cohort (Figure 4C), 79% (34/43) of the PTL extension series had MYD88L265P mutations (Figure 5B, left panel, and supplemental Table 6A). Thirty-eight percent (13/34) of PTLs with MYD88 mutations also had NFKBIZ copy gains; in addition, 5 of 9 tumors with wild-type MYD88 had NFKBIZ copy gains (Figure 5B, left panel).
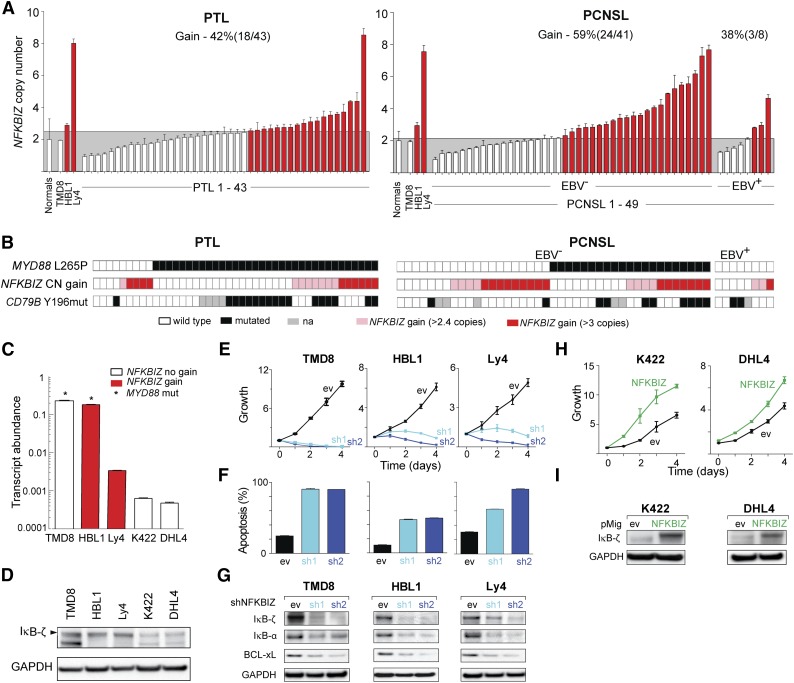
Figure 5.
Functional consequences of 3q12.3/NFKBIZ copy gain and IκB-ζ overexpression. (A) CN of 3q12.3/NFKBIZ in 43 PTLs (left panel) and 49 PCNSLs (41 EBV– and 8 EBV+, right panel) from the extension cohorts. Normals include 5 tonsils and 5 reactive lymph nodes. The upper 95% confidence interval of the normals was used as a threshold for copy gain. Indicated cell lines with known NFKBIZ CNs were used as controls. Cases with copy gain are shown in red. Error bars reflect standard deviation. (B) Cosegregation of genetic alterations in the TLR pathway (MYD88 mutations [upper panel; black, L265P; white, no L265P], NFKBIZ copy gain [middle panel; copy gain, red; color intensity corresponds to magnitude of copy gain]) and BCR pathway (CD79B mutations [lower panel; black, missense mutations affecting Y196; white, no exon 5 mutations; gray, not available]) in the 43 PTL samples (left panel), and 49 PCNSL cases (right panel; 41 EBV– and 8 EBV+). (C) IκB-ζ encoded by NFKBIZ locus transcript abundance in representative DLBCL cell lines. Asterisks indicate cell lines with MYD88L265P mutation. (D) IκB-ζ protein abundance in indicated cell lines. Full-length IκB-ζ is indicated with an arrowhead. Note that TMD8 has a heterozygous deletion of 159 base pairs, resulting in a shorter, fully functional IκB-ζ protein.32 The membrane was reprobed for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as loading control. (E-F) Proliferation (E) and apoptosis (F) after knockdown of IκB-ζ (sh1 and sh2, 2 independent IκB-ζ hairpins; ev, control) in representative DLBCL cell lines with increased IκB-ζ transcript abundance resulting from NFKBIZ gain only (Ly4), MYD88 mutation only (TMD8), or both (HBL1). (G) Efficacy of knockdown of IκB-ζ and downstream targets was determined by immunoblot. (H) Proliferation after enforced expression of IκB-ζ in cell lines with low IκB-ζ transcript levels (DHL4 and K422). (I) Efficacy of IκB-ζ overexpression was determined by immunoblot.
We also assessed the 3q12.3/NFKBIZ locus in an extension cohort of PCNSLs including 41 EBV– and 8 EBV+ tumors; 59% (24/41) of EBV– PCNSLs and 38% (3/8) of EBV+ PCNSLs had 3q12.3/NFKBIZ copy gain (Figure 5A, right panel). In the EBV– PCNSL extension cohort, 83% of tumors had 3q12.3/NFKBIZ copy gain, MYD88L265P mutations, or both alterations (Figure 5B, right panel). Interestingly, none of the 8 EBV+ PCNSL cases had an oncogenic MYD88L265P mutation. Taken together, these data suggest that NFKBIZ copy gain or viral infection may serve as additional and/or alternative oncogenic modulators of the MYD88/TLR signaling pathway.
We next assessed the functional consequences of NFKBIZ copy gain using a panel of informative LBCL cell lines with known NFKBIZ CN and MYD88 mutational status (Figure 5C). Cell lines with wild-type MYD88 and no NFKBIZ copy gain (K422, DHL4) had the lowest IκB-ζ transcript and protein levels, whereas cell lines with MYD88 mutation alone (TMD8), MYD88 mutation, and NFKBIZ copy gain (HBL1), or NFKBIZ copy gain alone, (Ly4) had more abundant IκB-ζ transcripts and protein (Figure 5C-D). In the 3 LBCL cell lines with high baseline IκB-ζ expression (TMD8, HBL1, Ly4), IκB-ζ depletion significantly decreased cellular proliferation, induced apoptosis, and reduced expression of the IκB-ζ target genes, IκB-α and BCL-xL (Figure 5E-G).32 In LBCL cell lines with low baseline IκB-ζ transcript levels (K422, DHL4), enforced expression of IκB-ζ conferred a growth advantage (Figure 5H-I). These genetic and functional analyses define NFKBIZ copy gain as an alternative oncogenic TLR signaling mechanism in LBCL.
Concurrent alterations of TLR and BCR signaling pathway components in PTL and PCNSL
Recent data suggest that TLR/MYD88 activation may directly augment BCR-mediated survival signals60,61 in addition to modulating NF-κB. The frequent co-occurrence of MYD88 and CD79B mutations in the initial PTL and EBV– PCNSL series (Figure 4B,D) prompted us to evaluate CD79B hotspot mutations in both extension cohorts. Forty-four percent (17/39) of evaluable PTLs had CD79BY196 mutations, almost all (16/17) of which occurred in tumors with MYD88L265P alterations (Figure 5B, left panel). In the extension cohort of EBV– PCNSLs, 28% (10/36) had CD79BY196 mutations, 80% (8/10) in association with MYD88L265P (Figure 5B, right panel). Both EBV– PCNSLs and PTLs were significantly more likely to have co-occurring CD79B and MYD88 mutations than systemic DLBCLs or the ABC DLBCL subset (supplemental Table 6C).
9p24.1 copy gain and PD-1 ligand expression in PTL and PCNSL
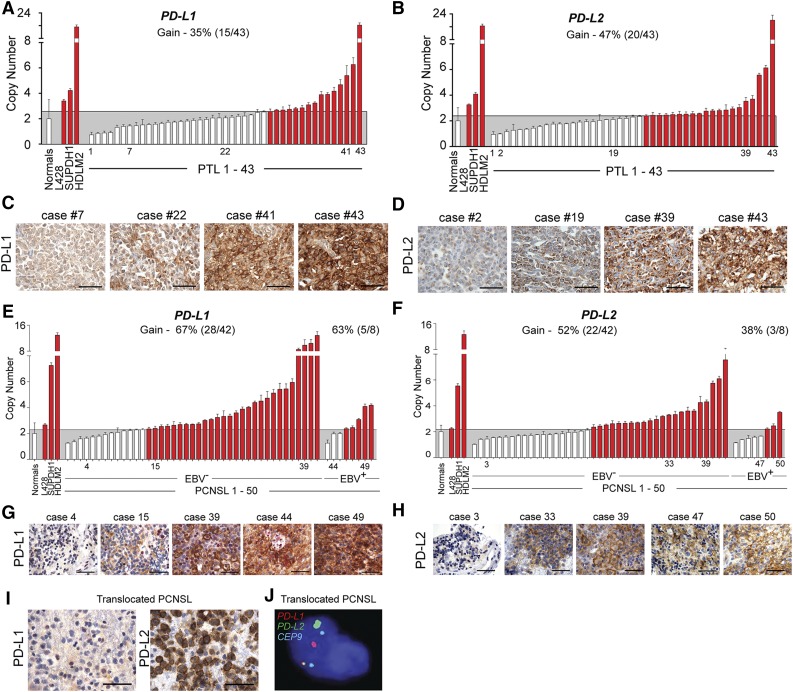
A shared genetic feature of PMBLs and the PTL discovery cohort was frequent 9p24.1 copy gain; several EBV– PCNSLs also had this alteration (Figure 1). PTLs in the extension cohort also exhibited frequent 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 copy gain by ligand-specific qPCR (Figure 6A-B) and CN-associated expression of these ligands by IHC (Figure 6C-D). Using tissue microarrays of the same PTLs, we also identified tumor-infiltrating T cells that expressed the PD-1 receptor (supplemental Figure 9A-B).
Figure 6.
Genetic alterations of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in PTL and PCNSL. (A) CNs of PD-L1 in 43 PTL cases from the extension cohort. Normals include 5 tonsils and 5 reactive lymph nodes. The upper 95% confidence interval of the normals was used as a threshold for CN gain in the PTLs. Indicated cHL cell lines with known PD-L1 copy gain were used as controls. Cases with copy gain are highlighted in red. Error bars reflect standard deviation. (C) PD-L1 protein expression in indicated cases from (A). The scale bar represents 100 μm. (B) CNs of PD-L2 in 43 PTL cases from extension cohort. Controls are as in (A). (D) PD-L2 protein expression in indicated cases from (B). (E) CNs of PD-L1 in 50 PCSNL cases (42 EBV– and 8 EBV+) from the extension cohort. Details are as in (A). (F) CNs of PD-L2 in 50 PCSNL cases (42 EBV– and 8 EBV+) from extension cohort. Controls are as in (A). (G) PD-L1 protein expression in indicated cases from (E). The scale bar represents 100 μm. (H) PD-L2 protein expression in indicated cases from (F). (I) PD-L1 (left panel) and PD-L2 (right panel) of the PCNSL case with wild-type PD-L1/2 CN. (J) Split-apart FISH assay of the PCNSL in (I). PD-L1 in red, PD-L2 in green and centromeric probe (CEP9) in aqua.
Bases of PD-1 ligand deregulation in PCNSL
We similarly evaluated the PD-L1/PD-L2 loci in the extension cohort of 42 EBV– PCNSLs and 8 EBV+ PCNSLs. In the larger EBV– PCNSL series, the majority of tumors exhibited 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 copy gain (67% [28/42]) and CN-associated increased expression of these ligands (Figure 6E-H). We also identified a copy-neutral case with discordant low-level PD-L1 and high-level PD-L2 protein expression and used the split-apart PD-L1/PD-L2 FISH assay to detect a chromosomal rearrangement that selectively deregulated PD-L2 (Figure 6I-J).
In the EBV+ PCNSLs, we noted largely CN-independent high-level expression of PD-L1 and PD-L216,62,63 (Figure 6E-H). Compared with EBV– PCNSLs, EBV+ tumors had lower-level PD-L1/PD-L2 copy gain, consistent with an additional viral mechanism of PD-1 ligand upregulation in these tumors (Figure 6E-F).
These data extend the molecular similarities in PCNSL and PTL to include 2 genetic bases of PD-1 ligand overexpression, copy gain, and chromosomal translocation, and implicate EBV infection as an additional mechanism of PD-1 ligand upregulation in PCNSLs.
Discussion
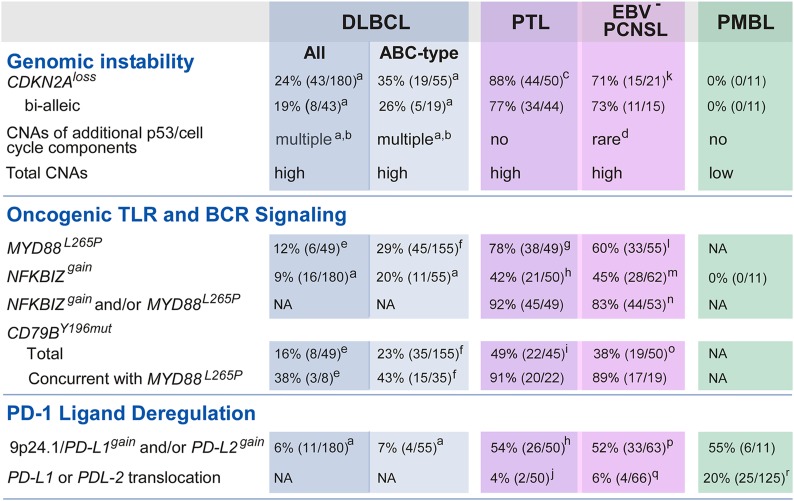
We have defined recurrent mutations, chromosomal rearrangements, CNAs, and associated driver genes in PCNSL and PTL and compared these comprehensive genetic signatures with those of systemic DLBCL and PMBL. These analyses revealed new genetic features, unique combinations of alterations, and a distinctive signature of near-uniform oncogenic TLR signaling with frequent concurrent BCR activation and genomic instability in PCNSL and PTL (Figure 7). The studies also identified specific genetic bases of deregulated PD-1 ligand expression and likely immune evasion in PCNSL and PTL (Figure 7). Most importantly, several of these genetic alterations are amenable to targeted therapy.
Figure 7.
Unique combinations of structural alterations in discrete LBCL subtypes. Frequency of specific genetic alterations modulating “Genomic Instability,” “Oncogenic TLR and BCR Signaling,” and “PD-1 Ligand Deregulation” in DLBCL all, DLBCL ABC-type, PTL, EBV– PCNSL, and PMBL are noted. a, Raw data previously published in reference 14. b, CNAs include the following alterations: MDM2gain, MDM4gain, CDK2gain, CDK4gain, CDK6gain, RB1loss, RBL2loss, TP53loss, KDM6Bloss, RPL26loss, BCL2L12gain, RFWD2gain, CCND3gain. c, CDKN2A CN data were available for 50 PTL (7 discovery + 43 extension). d, Only RBL2loss. e, As reported in reference 54. f, As reported in reference 8. g, MYD88L265P mutation status was available from 49 PTL (7 discovery + 42 extension). h, CN data for NFKBIZ and 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 loci were available from 50 PTL (7 discovery + 43 extension). i, CD79BY196mut mutation status in 45 PTL (7 discovery + 38 extension). j, 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 translocation data were from 50 PTL (7 discovery + 43 extension). k, CDKN2A CN data were available for 21 EBV– PCNSL (discovery only). l, MYD88L265P mutation status was available from 55 EBV– PCNSL (14 discovery + 41 extension). m, CN data for NFKBIZ locus were available from 62 EBV– PCNSL (21 discovery + 41 extension). n, NFKBIZ CN data and MYD88L265P mutation status were available for 53 EBV– PCNSL (12 discovery + 41 extension). o, CD79BY196mut mutation status was available from 50 EBV– PCNSL (12 discovery + 38 extension). p, 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 CN data were from 63 EBV– PCNSL (21 discovery + 42 extension). q, 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 translocation data were from 66 EBV– PCNSL (24 discovery + 42 extension). r, as reported in reference 19.
Incidence and bases of genomic instability in the LBCL subtypes
Comparative analyses of CNAs in the LBCL subtypes revealed distinct differences in incidence and bases of genomic instability in these lymphomas. In contrast to the majority of systemic DLBCLs, PCNSLs, and PTLs, PMBLs have relatively few CNAs (Figure 7). The paucity of CNAs, other than 2p16.1 and 9p24.1 copy gain, distinguish PMBLs from the additional evaluated LBCLs. PMBLs also lack genetic alterations known to either induce or tolerate genomic instability including CNAs of CDKN2A, RB1, or TP53 (Figure 7).14,35-39
Our analyses further suggest that systemic DLBCLs, PCNSLs, and PTLs use different mechanisms to tolerate or induce genomic instability. Systemic DLBCLs primarily exhibit genomic instability in the setting of multiple low-frequency CNAs of p53/cell-cycle components and additional TP53 somatic mutations (Figure 7).14 In contrast, PCNSLs and PTLs rarely have TP53 mutations but frequently perturb the p53 pathway via upstream, often biallelic, CDKN2A loss (Figure 7). As a consequence, PCNSLs and PTLs may be candidates for MDM2/4 inhibitors that augment wild-type p53 activity64 and CDK-blockade.14
Near-uniform oncogenic TLR signaling in PCNSL and PTL
We found oncogenic MYD88L265P mutations and/or NFKBIZ copy gain to be near-universal genetic features of EBV– PCNSL and PTL; both alterations were significantly more common in these lymphomas than in ABC-type DLBCLs (Figure 7).8 IκB-ζ transcription is induced by MYD88 mutations32 or NFKBIZ amplification, and IκB-ζ depletion is lethal in each setting, suggesting that IκB-ζ is an essential intermediary in oncogenic TLR signaling. NFKBIZ copy gain also represents an alternative and/or complementary structural basis for increased TLR activity in PTL and PCNSL (Figure 7).
Genetic alterations that complement oncogenic TLR signaling in PCNSL and PTL
Recent murine studies suggest that the consequences of enforced MYD88L265P expression in normal B cells depend on additional complementary genetic alterations.65 Although MYD88L265P increased cellular proliferation and activated NF-κB in antigen-exposed murine B cells, these effects were rapidly countered by TNFAIP3 induction and BIM-dependent apoptosis.65 In this model, TNFAIP3 inactivation or enforced BCL2 expression was required to sustain MYD88L265P-dependent signaling.65 These findings are of particular interest because PCNSLs and PTLs frequently exhibit TNFAIP3 copy loss and/or BCL2 copy gain in association with MYD88L265P and/or NFKBIZ copy gain (Figure 4). The identification of these complementary genetic alterations required concurrent analyses of mutations, CNAs, and associated driver genes.
Concurrent oncogenic TLR signaling and BCR activation in PCNSL and PTL
In our series of PCNSLs and PTLs, CD79B mutations primarily occurred in the context of oncogenic TLR signaling. The high incidence of concurrent CD79B and MYD88 mutations is an additional distinguishing feature of PCNSLs and PTLs compared with the more heterogeneous group of ABC-type DLBCLs (Figure 7). Given the near-universal genetic alterations of TLR and BCR signaling in PCNSL and PTL, these tumors may be particularly vulnerable to targeted inhibition of pathway components such as IRAK1/4, IRF4, and/or BTK.9,66 However, a subset of PCNSLs exhibits activating CARD11 mutations in association with MYD88L265P and CD79B mutations, which may limit the efficacy of proximal BCR pathway inhibitors.9
Recent studies highlight the complementary roles of BCR- and TLR-signaling in virus-driven B-cell activation, B-cell–intrinsic autoimmunity, and BCR-dependent survival.60,61 In addition, both MYD88L265P and CARD11 mutations promote the breakdown of TLR and B-cell tolerance to self-antigens.65,67 These observations are of note because candidate autoantigens were recently identified in PCNSL.68,69
Additional bases of tumor immune evasion in PTL and PCNSL—copy gain or translocation of PD-L1 and/or PD-L2, and viral induction of PD-1 ligands
Our genetic analyses confirmed previously proposed mechanisms of tumor-immune escape: copy loss of 6p21.33 and the associated HLA loci, deletion of 15q21.1/B2M, and chromosomal rearrangement of CIITA.18,24,25,70
Strikingly, we also found 9p24.1 copy gain and increased expression of the PD-1 ligands in >50% of PTLs and EBV– PCNSLs (Figure 7). In addition, we identified 4 EBV– PCNSLs and 2 PTLs with chromosomal translocations that selectively deregulated PD-L1 or PD-L2. In several tumors, proximal regulatory elements of other genes (TBL1XR1 and BCNP1) replaced the endogenous PD-L1 or PD-L2 promoter. In additional tumors, strong enhancer elements of IgH or PAX543 were juxtaposed to the intact endogenous PD-L2 promoter. The TBL1XR1-PD-L2 translocation both increased the expression of PD-L2 and inactivated TBL1XR1. Given the additional identified mutations in TBL1XR1 (Figure 3 and supplemental Figure 6),23,26,27 we postulate that TBL1XR1 is a tumor suppressor in LBCLs.
Our combined genetic and IHC analyses suggest that tumors with discordant PD-L1 or PD-L2 expression and copy-neutral 9p24.1 status may harbor chromosomal rearrangements of PD-L1 or PD-L2. The frequent genetic alterations of PD-L2 also suggest that it may be preferable to target the PD-1 receptor rather than PD-L1.
Genetic alterations of 9p24.1 and associated overexpression of the PD-1 ligands have now been described in 4 lymphoid malignancies—cHL, PMBL, PTL, and PCNSL (Figure 7,16,19). In EBV+ PCNSL, as in other EBV+ lymphoid malignancies, viral infection is an additional mechanism of PD-1 ligand overexpression.62,63 The emerging data indicate that lymphoid malignancies with unique molecular signatures use common genetic mechanisms to increase the expression of PD-1 ligands (Figure 7). Given the demonstrated activity of PD-1 blockade in other lymphomas with 9p24.1 alterations,22 this targeted therapy should also be considered in PTL and PCNSL. With respect to PCNSL, recent and ongoing clinical trials support the use of immunomodulatory antibodies in tumors involving the CNS71 (www.clinicaltrials.gov, NCT02017717, NCT02311920, NCT02313272, NCT02311582).
Multiple genetic bases of target and pathway deregulation
Comprehensive analyses of CNAs, chromosomal rearrangements, and mutations revealed multiple mechanisms of target and pathway deregulation in PCNSL and PTL. For example, ETV6 was altered by somatic mutations or exon deletion and TBL1XR1 was perturbed by inactivating chromosomal translocations or somatic mutations. In addition, BCL6 was deregulated by mutations of MEF2B, chromosomal translocations of BCL6 with immunoglobulin or nonimmunoglobulin regulatory elements, and a novel translocation of PELI1, which encodes an E3 ligase that stabilizes the BCL6 protein.47
Unique combinations of structural alterations in discrete LBCL subtypes
By comparing the comprehensive molecular signatures of PTL and PCNSL with those of systemic DLBCL and PMBLs, we identified unique combinations of genetic features in discrete LBCL subtypes (Figure 7). For example, PCNSLs, PTLs, and PMBLs exhibit frequent genetic alterations and overexpression of the PD-1 ligands, whereas DLBCLs rarely have these features. Only a subset of transcriptionally defined ABC-type DLBCLs exhibit alterations of MYD88 or NFKBIZ, whereas these are near-uniform genetic features of PCNSL and PTL. Although the majority of DLBCLs, PCNSLs, and PTLs exhibit increased genomic instability, as assessed by total CNAs, the genetic bases differ—multiple CNAs of p53/cell-cycle pathway components and TP53 somatic mutations in DLBCL vs frequent, often biallelic, CDKN2A copy loss and rare TP53 alterations in PCNSL and PTL (Figure 7).14 In contrast, PMBLs have a paucity of CNAs.
Furthermore, the defining genetic features of PCNSL and PTL—near-uniform oncogenic TLR signaling, concurrent BCR activation, CDKN2A deficiency with wild-type p53, and PD-1–mediated immune evasion—suggest multiple targeted therapies that warrant clinical investigation.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute grant R01 CA161026 and an LLS Translational Research Award (M.A.S.), a Claudia Adams Barr Program in Basic Cancer Research (B.C.), National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases grant PO1 AI056299 (G.J.F.), and the Slim Initiative for Genomic Medicine, a project funded by the Carlos Slim Foundation in Mexico (Broad).
Footnotes
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: B.C. and M.G.M.R. designed research, performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; C.S., Y.T., R.P.A., L.Z., A.J.D., M.D.D., D.G., G.G., and S.M. analyzed data; A.R.T., E.S.J., F.F., G.S.P., A.H.L., K.L.L., J.A.F., G.J.F., P.v.H., T.R.G., S.J.R., and D.d.J. performed research and analyzed data; D.M.M., G.L., G.I., E.A.L., H.H.S., H.H., and M.A. performed research; and M.A.S. designed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: G.J.F. has patents and receives royalties on the PD-1 pathway from Amplimmune, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers-Squibb (BMS), EDM-Serrono, Merck, Roche, and Novartis. M.A.S. has received research funding from BMS and served on advisory boards for BMS and Merck. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Margaret Shipp, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, 450 Brookline Ave, Boston, MA 02115; e-mail: margaret_shipp@dfci.harvard.edu.
References
- 1.Rubenstein JL, Gupta NK, Mannis GN, Lamarre AK, Treseler P. How I treat CNS lymphomas. Blood. 2013;122(14):2318–2330. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-06-453084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cheah CY, Wirth A, Seymour JF. Primary testicular lymphoma. Blood. 2014;123(4):486–493. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-10-530659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Horne MJ, Adeniran AJ. Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the testis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135(10):1363–1367. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2010-0158-RS. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Deckert M, Montesinos-Rongen M, Brunn A, Siebert R. Systems biology of primary CNS lymphoma: from genetic aberrations to modeling in mice. Acta Neuropathol. 2014;127(2):175–188. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Riemersma SA, Jordanova ES, Schop RF, et al. Extensive genetic alterations of the HLA region, including homozygous deletions of HLA class II genes in B-cell lymphomas arising in immune-privileged sites. Blood. 2000;96(10):3569–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Deng L, Xu-Monette ZY, Loghavi S, et al. Primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma displays distinct clinical and biological features for treatment failure in rituximab era: a report from the International PTL Consortium. Leukemia. 2013 doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.237. 10.1038/leu.2015.237 [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Basso K, Dalla-Favera R. Germinal centres and B cell lymphomagenesis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(3):172–184. doi: 10.1038/nri3814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ngo VN, Young RM, Schmitz R, et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature. 2011;470(7332):115–119. doi: 10.1038/nature09671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Davis RE, Ngo VN, Lenz G, et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature. 2010;463(7277):88–92. doi: 10.1038/nature08638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lenz G, Davis RE, Ngo VN, et al. Oncogenic CARD11 mutations in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Science. 2008;319(5870):1676–1679. doi: 10.1126/science.1153629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Monti S, Savage KJ, Kutok JL, et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood. 2005;105(5):1851–1861. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Caro P, Kishan AU, Norberg E, et al. Metabolic signatures uncover distinct targets in molecular subsets of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;22(4):547–560. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.08.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen L, Monti S, Juszczynski P, et al. SYK inhibition modulates distinct PI3K/AKT- dependent survival pathways and cholesterol biosynthesis in diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Cancer Cell. 2013;23(6):826–838. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Monti S, Chapuy B, Takeyama K, et al. Integrative analysis reveals an outcome-associated and targetable pattern of p53 and cell cycle deregulation in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;22(3):359–372. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.07.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Steidl C, Gascoyne RD. The molecular pathogenesis of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2011;118(10):2659–2669. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-05-326538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Green MR, Monti S, Rodig SJ, et al. Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2010;116(17):3268–3277. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-282780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rui L, Emre NC, Kruhlak MJ, et al. Cooperative epigenetic modulation by cancer amplicon genes. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(6):590–605. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.11.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Steidl C, Shah SP, Woolcock BW, et al. MHC class II transactivator CIITA is a recurrent gene fusion partner in lymphoid cancers. Nature. 2011;471(7338):377–381. doi: 10.1038/nature09754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Twa DD, Chan FC, Ben-Neriah S, et al. Genomic rearrangements involving programmed death ligands are recurrent in primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2014;123(13):2062–2065. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-10-535443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pardoll DM. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(4):252–264. doi: 10.1038/nrc3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:677–704. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I, et al. PD-1 Blockade with Nivolumab in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(4):311–319. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gonzalez-Aguilar A, Idbaih A, Boisselier B, et al. Recurrent mutations of MYD88 and TBL1XR1 in primary central nervous system lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(19):5203–5211. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Braggio E, McPhail ER, Macon W, et al. Primary central nervous system lymphomas: a validation study of array-based comparative genomic hybridization in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor specimens. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(13):4245–4253. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Booman M, Szuhai K, Rosenwald A, et al. Genomic alterations and gene expression in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of immune-privileged sites: the importance of apoptosis and immunomodulatory pathways. J Pathol. 2008;216(2):209–217. doi: 10.1002/path.2399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bruno A, Boisselier B, Labreche K, et al. Mutational analysis of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2014;5(13):5065–5075. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vater I, Montesinos-Rongen M, Schlesner M, et al. The mutational pattern of primary lymphoma of the central nervous system determined by whole-exome sequencing. Leukemia. 2015;29(3):677–685. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Braggio E, Van Wier S, Ojha J, et al. Genome-wide analysis uncovers novel recurrent alterations in primary central nervous system lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(17):3986–3994. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kraan W, van Keimpema M, Horlings HM, et al. High prevalence of oncogenic MYD88 and CD79B mutations in primary testicular diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2014;28(3):719–720. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Oishi N, Kondo T, Nakazawa T, et al. High prevalence of the MYD88 mutation in testicular lymphoma: Immunohistochemical and genetic analyses. Pathol Int. 2015;65(10):528–535. doi: 10.1111/pin.12336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Beroukhim R, Getz G, Nghiemphu L, et al. Assessing the significance of chromosomal aberrations in cancer: methodology and application to glioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(50):20007–20012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710052104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nogai H, Wenzel SS, Hailfinger S, et al. IκB-ζ controls the constitutive NF-κB target gene network and survival of ABC DLBCL. Blood. 2013;122(13):2242–2250. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-06-508028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yamamoto M, Yamazaki S, Uematsu S, et al. Regulation of Toll/IL-1-receptor-mediated gene expression by the inducible nuclear protein IkappaBzeta. Nature. 2004;430(6996):218–222. doi: 10.1038/nature02738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Krappmann D. Shaping oncogenic NF-κB activity in the nucleus. Blood. 2013;122(13):2146–2147. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-08-516864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hernando E, Nahlé Z, Juan G, et al. Rb inactivation promotes genomic instability by uncoupling cell cycle progression from mitotic control. Nature. 2004;430(7001):797–802. doi: 10.1038/nature02820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang L, He G, Zhang P, Wang X, Jiang M, Yu L. Interplay between MDM2, MDMX, Pirh2 and COP1: the negative regulators of p53. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(1):229–236. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Thompson SL, Compton DA. Proliferation of aneuploid human cells is limited by a p53-dependent mechanism. J Cell Biol. 2010;188(3):369–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200905057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(3):153–166. doi: 10.1038/nrc2602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shlien A, Tabori U, Marshall CR, et al. Excessive genomic DNA copy number variation in the Li-Fraumeni cancer predisposition syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(32):11264–11269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802970105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Karras JR, Paisie CA, Huebner K. Replicative Stress and the FHIT Gene: Roles in Tumor Suppression, Genome Stability and Prevention of Carcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel) 2014;6(2):1208–1219. doi: 10.3390/cancers6021208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Drier Y, Lawrence MS, Carter SL, et al. Somatic rearrangements across cancer reveal classes of samples with distinct patterns of DNA breakage and rearrangement-induced hypermutability. Genome Res. 2013;23(2):228–235. doi: 10.1101/gr.141382.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Abo RP, Ducar M, Garcia EP, et al. BreaKmer: detection of structural variation in targeted massively parallel sequencing data using kmers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(3):e19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chapuy B, McKeown MR, Lin CY, et al. Discovery and characterization of super-enhancer-associated dependencies in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2013;24(6):777–790. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schneider C, Setty M, Holmes AB, et al. MicroRNA 28 controls cell proliferation and is down-regulated in B-cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(22):8185–8190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1322466111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.De Braekeleer E, Douet-Guilbert N, Morel F, Le Bris MJ, Basinko A, De Braekeleer M. ETV6 fusion genes in hematological malignancies: a review. Leuk Res. 2012;36(8):945–961. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2012.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Boyd RS, Adam PJ, Patel S, et al. Proteomic analysis of the cell-surface membrane in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: identification of two novel proteins, BCNP1 and MIG2B. Leukemia. 2003;17(8):1605–1612. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Park HY, Go H, Song HR, et al. Pellino 1 promotes lymphomagenesis by deregulating BCL6 polyubiquitination. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(11):4976–4988. doi: 10.1172/JCI75667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tan Y, Chapuy B, Shipp M, Monti S. FusionQuery: a novel tool for gene-specific fusion detection. International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology (ISMB), July 11-15, 2014, N06. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Polak P, et al. Mutational heterogeneity in cancer and the search for new cancer-associated genes. Nature. 2013;499(7457):214–218. doi: 10.1038/nature12213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.De Silva NS, Simonetti G, Heise N, Klein U. The diverse roles of IRF4 in late germinal center B-cell differentiation. Immunol Rev. 2012;247(1):73–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2012.01113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tijchon E, Havinga J, van Leeuwen FN, Scheijen B. B-lineage transcription factors and cooperating gene lesions required for leukemia development. Leukemia. 2013;27(3):541–552. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Huang W, Ghisletti S, Perissi V, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK. Transcriptional integration of TLR2 and TLR4 signaling at the NCoR derepression checkpoint. Mol Cell. 2009;35(1):48–57. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.05.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gil J, Peters G. Regulation of the INK4b-ARF-INK4a tumour suppressor locus: all for one or one for all. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(9):667–677. doi: 10.1038/nrm1987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lohr JG, Stojanov P, Lawrence MS, et al. Discovery and prioritization of somatic mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) by whole-exome sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(10):3879–3884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121343109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhang J, Grubor V, Love CL, et al. Genetic heterogeneity of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(4):1398–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205299110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pasqualucci L, Trifonov V, Fabbri G, et al. Analysis of the coding genome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nat Genet. 2011;43(9):830–837. doi: 10.1038/ng.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Morin RD, Mendez-Lago M, Mungall AJ, et al. Frequent mutation of histone-modifying genes in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Nature. 2011;476(7360):298–303. doi: 10.1038/nature10351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Morin RD, Mungall K, Pleasance E, et al. Mutational and structural analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using whole-genome sequencing. Blood. 2013;122(7):1256–1265. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-483727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ying CY, Dominguez-Sola D, Fabi M, et al. MEF2B mutations lead to deregulated expression of the oncogene BCL6 in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat Immunol. 2013;14(10):1084–1092. doi: 10.1038/ni.2688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Jabara HH, McDonald DR, Janssen E, et al. DOCK8 functions as an adaptor that links TLR-MyD88 signaling to B cell activation. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(6):612–620. doi: 10.1038/ni.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rawlings DJ, Schwartz MA, Jackson SW, Meyer-Bahlburg A. Integration of B cell responses through Toll-like receptors and antigen receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12(4):282–294. doi: 10.1038/nri3190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Green MR, Rodig S, Juszczynski P, et al. Constitutive AP-1 activity and EBV infection induce PD-L1 in Hodgkin lymphomas and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders: implications for targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(6):1611–1618. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chen BJ, Chapuy B, Ouyang J, et al. PD-L1 expression is characteristic of a subset of aggressive B-cell lymphomas and virus-associated malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(13):3462–3473. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chang YS, Graves B, Guerlavais V, et al. Stapled α-helical peptide drug development: a potent dual inhibitor of MDM2 and MDMX for p53-dependent cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(36):E3445–E3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303002110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wang JQ, Jeelall YS, Beutler B, Horikawa K, Goodnow CC. Consequences of the recurrent MYD88(L265P) somatic mutation for B cell tolerance. J Exp Med. 2014;211(3):413–426. doi: 10.1084/jem.20131424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yang Y, Shaffer AL, III, Emre NC, et al. Exploiting synthetic lethality for the therapy of ABC diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(6):723–737. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.05.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Jeelall YS, Wang JQ, Law HD, et al. Human lymphoma mutations reveal CARD11 as the switch between self-antigen-induced B cell death or proliferation and autoantibody production. J Exp Med. 2012;209(11):1907–1917. doi: 10.1084/jem.20112744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Thurner L, Kemele M, Fadle N, et al. Postranslationally modified proteins in the central nervous system (CNS) are the dominant antigenic target/stimulus of the B-cell receptor (BCR) in primary CNS lymphomas (PCNSL) providing strong evidence for the role of chronic autoantigenic stimulation as an early step in the pathogenesis of aggressive B-cell lymphomas [abstract]. Blood. 2014;124(21) Abstract 142. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Trepel M, Müller F, Illerhaus G, Glatzel M, Binder M, Spies E. B-cell receptors of primary central nervous system lymphoma recognize antigens in the brain [abstract]. Blood. 2014;124(21) Abstract 3003. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Green MR, Kihira S, Liu CL, et al. Mutations in early follicular lymphoma progenitors are associated with suppressed antigen presentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(10):E1116–E1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1501199112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Margolin K, Ernstoff MS, Hamid O, et al. Ipilimumab in patients with melanoma and brain metastases: an open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(5):459–465. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]