Abstract
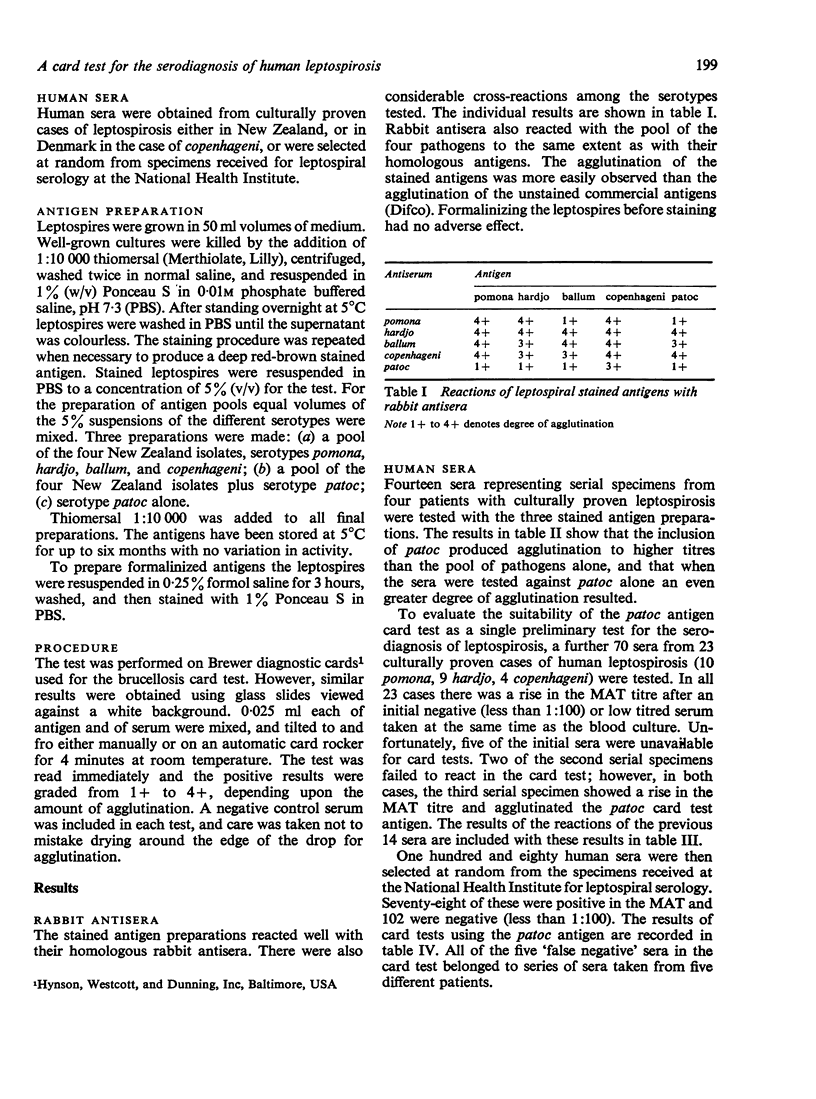
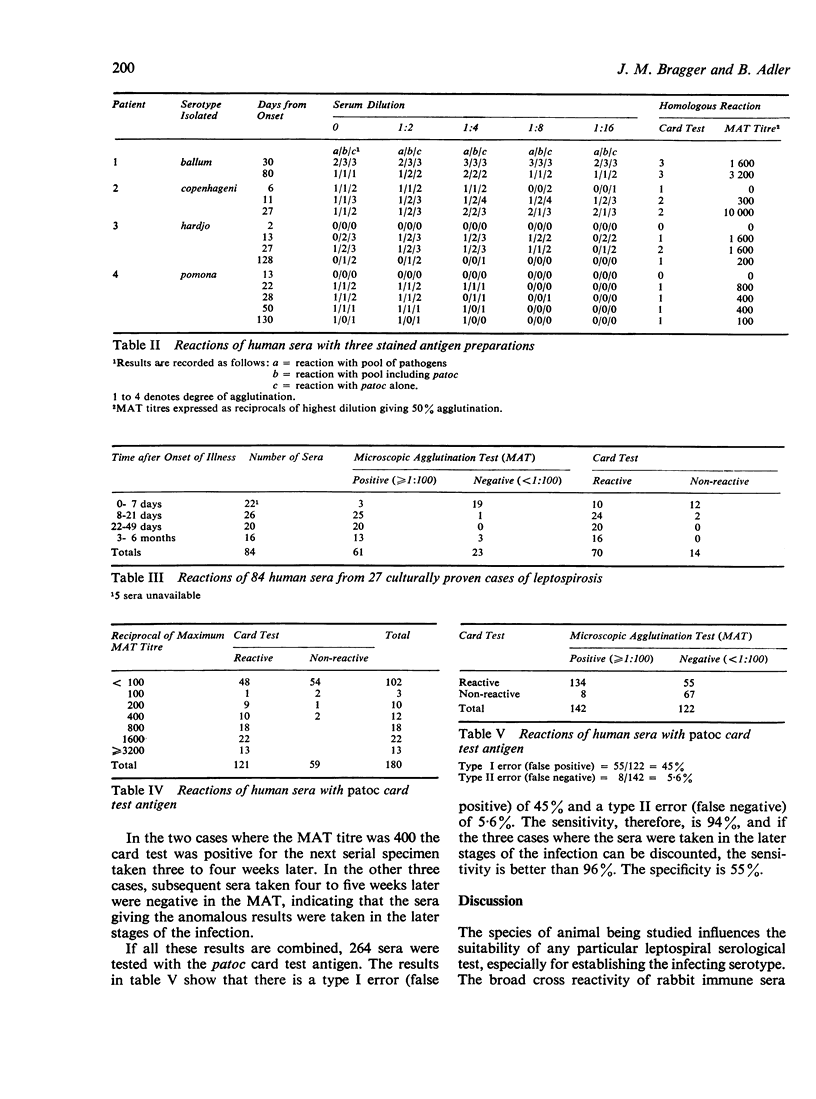
A macroscopic agglutination test for detecting leptospiral antibodies in human sera is described. The test utilizes a stained preparation of non-pathogenic leptospires and is performed on the Brewer diagnostic cards used for bovine brucellosis screening. The agglutination of the stained antigen is more easily observed than the current macroscopic slide test using unstained leptospiral antigens. The non-pathogenic serotype patoc is agglutinated by sera from humans infected with serotypes pomona, hardjo, ballum, and copenhageni with a sensitivity of 94% in comparison with the microscopic agglutination test.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COMBIESCU D., STURDZA N., SEFER M., RADU I. Leptospirenforschungen in Rumänien. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1958 Nov;173(1-2):103–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX C. D., ALEXANDER A. D., MURPHY L. C. Evaluation of the hemolytic test in the serodiagnosis of human leptospirosis. J Infect Dis. 1957 Sep-Oct;101(2):210–218. doi: 10.1093/infdis/101.2.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX C. D. Hemolysis of sheep erythrocytes sensitized with leptospiral extracts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Dec;90(3):610–615. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX C. D. Standardization and stabilization of an extract from Leptospira biflexa and its use in the hemolytic test for leptospirosis. J Infect Dis. 1957 Sep-Oct;101(2):203–209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/101.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christmas B. W., Bragger J. M., Till D. G. Dairy farm fever in New Zealand: isolation of L pomona and L hardjo from a local outbreak. N Z Med J. 1974 May 8;79(514):904–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELIAN M., NICOARA I. THE USE OF LEPTOSPIRA BIFLEXA PATOC ANTIGEN IN FIELD INVESTIGATIONS OF LEPTOSPIROSIS. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;31:359–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faine S., Carter J. N. Natural antibody in mammalian serum reacting with an antigen in some leptospires. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):280–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.280-285.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALTON M. M., POWERS D. K., HALL A. D., CORNELL R. G. A rapid macroscopicslide screening test for the serodiagnosis of leptospirosis. Am J Vet Res. 1958 Apr;19(71):505–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palit A., Gulasekharam J. Genus-specific leptospiral antigen and its possible use in laboratory diagnosis. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jan;26(1):7–16. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palit A., Sharma G. L. Comparison of microscopic agglutination, indirect haemagglutination and complement-fixation tests in rabbit and buffalo-calf hyperimmune sera for detection of leptospiral antibodies. Br Vet J. 1971 Apr;127(4):154–162. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)37632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson A., Boulanger P. Comparison of the Complement-Fixation Test and the Microscopic-Agglutination Test (Agglutination-Lysis) for the Detection of Leptospiral Serogroup Antibodies. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1963 May;27(5):113–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulzer C. R., Jones W. L. Evaluation of a hemagglutination test for human leptospirosis. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):655–657. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.655-657.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torten M., Shenberg E., Van der Hoeden J. The use of immunofluorescence in the diagnosis of human leptospirosis by a genus-specific antigen. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):537–543. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner L. H. Leptospirosis. II. Serology. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1968;62(6):880–899. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(68)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


