Abstract
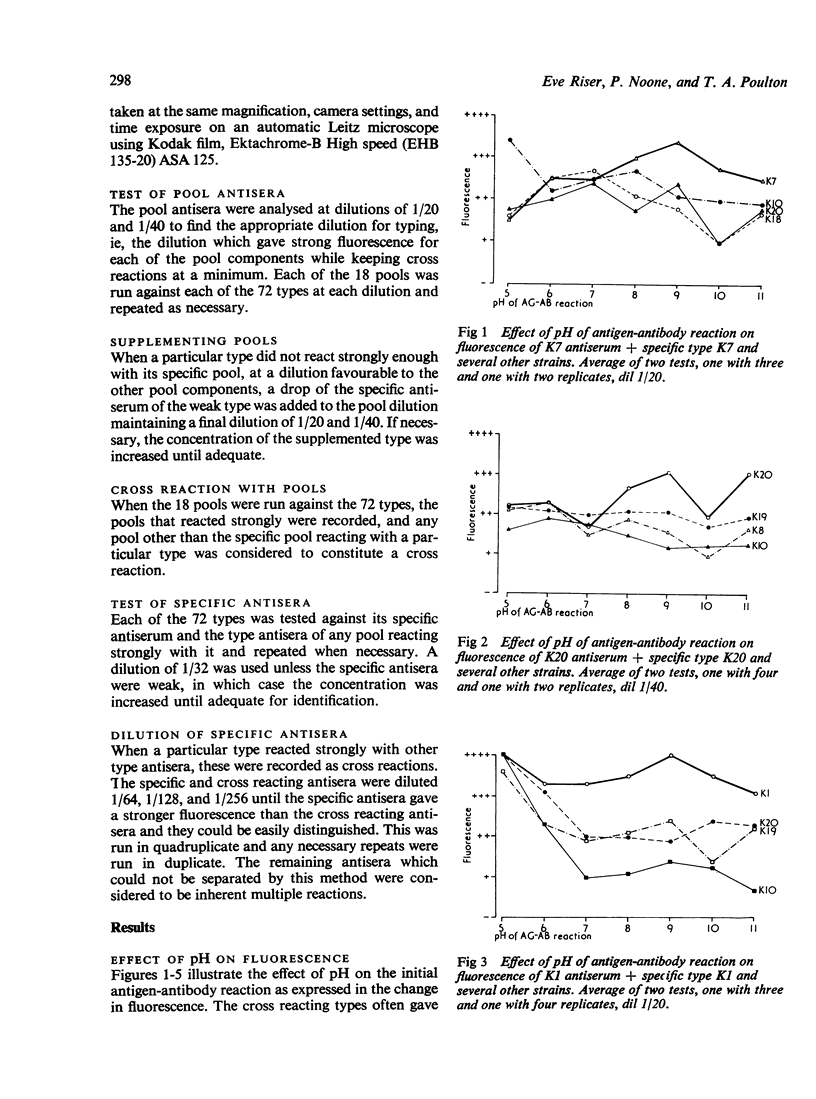
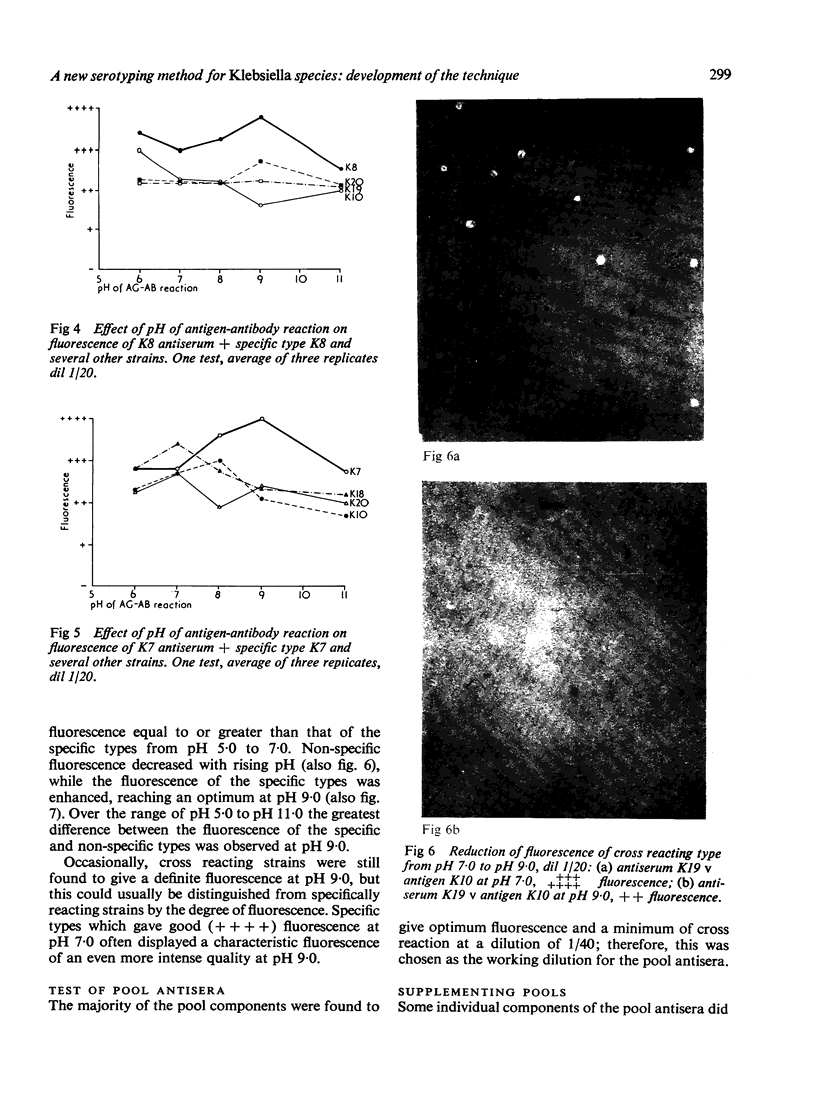
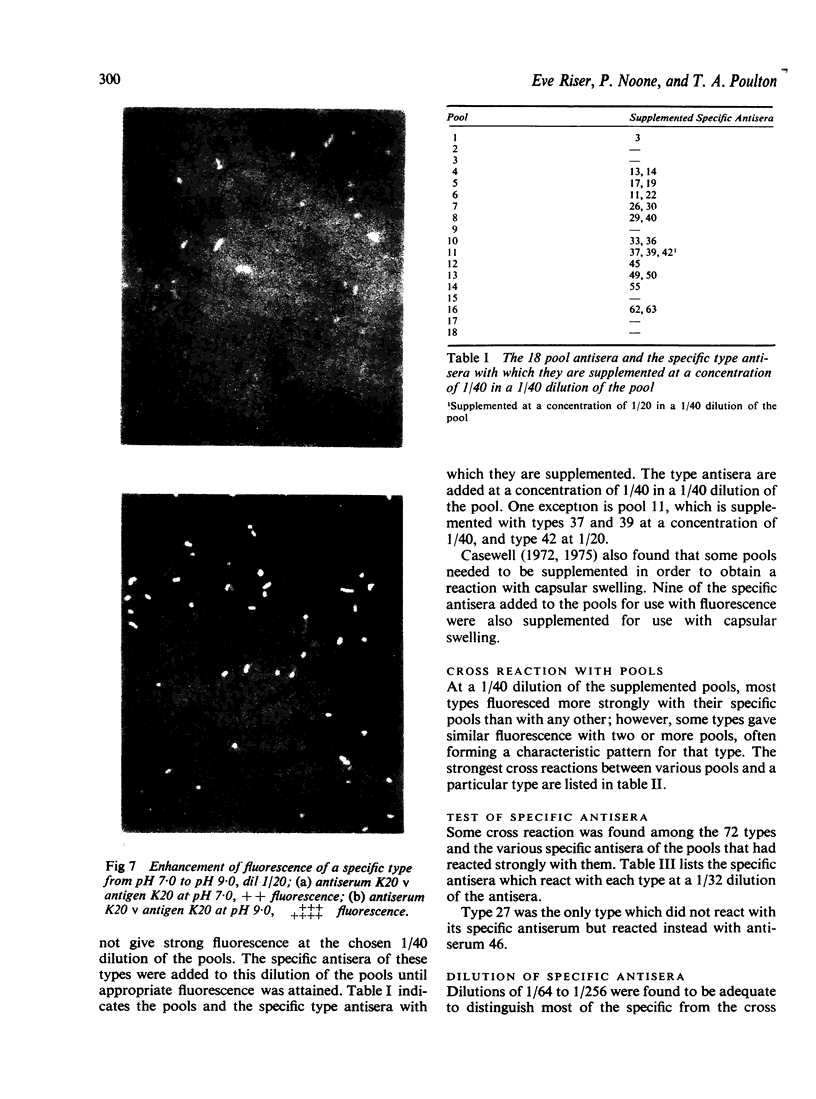
A new serotyping method for Klebsiella species using indirect immunofluorescence is described. Nonspecific fluorescence has been minimized by carrying out the capsular antigen-antibody reaction at pH 9.0. Commercial antisera have been tested with the 72 antigenic types of Klebsiella, and appropriate dilutions of each pool and specific antisera have been proposed for use in routine typing. Dilutions were chosen to allow strong fluorescence with each type and its specific antiserum and minimal fluorescence with cross reacting antisera. Where the pool antisera gave a weak reaction for one or more of the component types, it is recommended that the specific antisera for these types be added to the pool dilution. The few remaining cross reactions, with the pool and specific antisera in test dilution, are listed in a table. The unique cross reacting patterns of particular types have been found to be useful in identification. Typing Klebsiella by the fluorescent antibody technique is easy to perform and interpret; the results are reproducible, and it is less expensive than the existing capsular swelling method as it is more sensitive and requires less concentrated antisera. This new method of typing should facilitate detailed epidemiological studies of the mode of transmission of Klebsiella species in hospitals and thus allow more effective infection control measures to be instituted.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casewell M. W. Experiences in the use of commercial antisera for the capsular typing of klebsiella species. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Aug;25(8):734–737. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.8.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casewell M. W. Titres and cross reactions of commercial antisera for the capsular typing of Klebsiella species. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jan;28(1):33–36. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessum B. S. Examination of sera for toxoplasmosis antibody using immunofluorescence. J Med Lab Technol. 1970 Jan;27(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy Y. M., Dutton G. G. Occurrence of 3-O-( -D-glucopyranosyluronic acid)-D-galactose in the capsular polysaccharide of Klebsiella K-type 20. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):635–636. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.635-636.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS P. R., FIFE M. A. Studies on the Klebsiella-Aerobacter group of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(4):382–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.4.382-390.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen J. Immunochemical studies on some serological cross-reactions in the Klebsiella group. 13. Serological investigation of the cross-reaction of Klebsiella type 3(c), Klebsiella aerogenes strain b.1076/48 and "Enterobacter" strain 349. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64(4):527–533. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall F. A. Bacteriocine typing of Klebsiella spp. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Nov;24(8):712–716. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.8.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer G. V., Taylor C. E. Improved immunofluorescence obtained with a tungsten halogen lamp in a modified inverted microscope. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):88–93. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomerie J. Z., Doak P. B., Taylor D. E., North J. D., Martin W. J. Klebsiella in faecal flora of renal-transplant patients. Lancet. 1970 Oct 17;2(7677):787–792. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91458-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. J., Sleigh J. D. Control of infection due to Klebsiella aerogenes in a neurosurgical unit by withdrawal of all antibiotics. Lancet. 1970 Dec 12;2(7685):1213–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Variables of the rubella hemagglutination-inhibition test system and their effect on antigen and antibody titers. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Mar;19(3):491–504. doi: 10.1128/am.19.3.491-504.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R., Lee S., Wang W. L., Bennett J. V., Eickhoff T. C. Nosocomial klebsiella infections: intestinal colonization as a reservoir. Ann Intern Med. 1971 May;74(5):657–664. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-5-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ØRSKOV I. Serological investigations in the Klebsiella group. III. Occurrence of Klebsiella strains in the faeces of normal infants. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;36(5):461–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]