Abstract
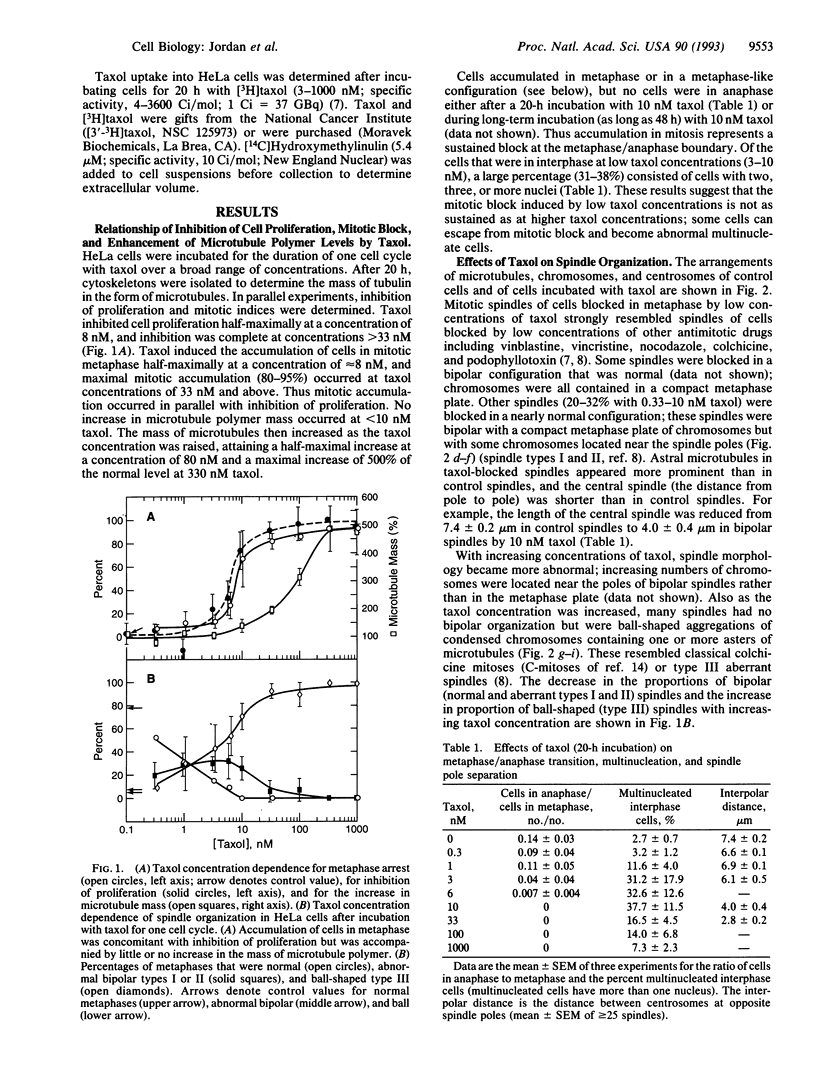
Taxol inhibited HeLa cell proliferation by inducing a sustained mitotic block at the metaphase/anaphase boundary. Half-maximal inhibition of cell proliferation occurred at 8 nM taxol, and mitosis was half-maximally blocked at 8 nM taxol. Inhibition of mitosis was associated with formation of an incomplete metaphase plate of chromosomes and an altered arrangement of spindle microtubules that strongly resembled the abnormal organization that occurs with low concentrations of vinblastine and other antimitotic compounds. No increase in microtubule polymer mass occurred below 10 nM taxol. The mass of microtubules increased half-maximally at 80 nM taxol and attained maximal levels (5 times normal) at 330 nM taxol. At submicromolar concentrations, taxol suppressed growing and shortening at the ends of microtubules reassembled in vitro from bovine brain tubulin in a manner that resembled suppression by vinblastine. Taxol was concentrated in HeLa cells several hundredfold to levels that were similar to those which suppressed dynamic instability in vitro. The results indicate that taxol shares a common antiproliferative mechanism with vinblastine. At its lowest effective concentrations, taxol appears to block mitosis by kinetically stabilizing spindle microtubules and not by changing the mass of polymerized microtubules.
Full text
PDF



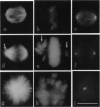
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin-Hanjani S., Wadsworth P. Inhibition of spindle elongation by taxol. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;20(2):136–144. doi: 10.1002/cm.970200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Brabander M., Geuens G., Nuydens R., Willebrords R., De Mey J. Taxol induces the assembly of free microtubules in living cells and blocks the organizing capacity of the centrosomes and kinetochores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5608–5612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díaz J. F., Andreu J. M. Assembly of purified GDP-tubulin into microtubules induced by taxol and taxotere: reversibility, ligand stoichiometry, and competition. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 23;32(11):2747–2755. doi: 10.1021/bi00062a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs D. A., Johnson R. K. Cytologic evidence that taxol, an antineoplastic agent from Taxus brevifolia, acts as a mitotic spindle poison. Cancer Treat Rep. 1978 Aug;62(8):1219–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden J. H., Bowser S. S., Rieder C. L. Kinetochores capture astral microtubules during chromosome attachment to the mitotic spindle: direct visualization in live newt lung cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Farrell K. W. Differential radiolabeling of opposite microtubule ends: methodology, equilibrium exchange-flux analysis, and drug poisoning. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 1;130(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90647-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Margolis R. L., Himes R. H., Wilson L. Identification of a distinct class of vinblastine binding sites on microtubules. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Thrower D., Wilson L. Effects of vinblastine, podophyllotoxin and nocodazole on mitotic spindles. Implications for the role of microtubule dynamics in mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jul;102(Pt 3):401–416. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.3.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Thrower D., Wilson L. Mechanism of inhibition of cell proliferation by Vinca alkaloids. Cancer Res. 1991 Apr 15;51(8):2212–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. A., Wilson L. Kinetic analysis of tubulin exchange at microtubule ends at low vinblastine concentrations. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2730–2739. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallajoki M., Weber K., Osborn M. Ability to organize microtubules in taxol-treated mitotic PtK2 cells goes with the SPN antigen and not with the centrosome. J Cell Sci. 1992 May;102(Pt 1):91–102. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi J. J., Parness J., Horwitz S. B. Taxol binds to cellular microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):688–696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Salmon E. D. Poleward kinetochore fiber movement occurs during both metaphase and anaphase-A in newt lung cell mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):569–582. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parness J., Horwitz S. B. Taxol binds to polymerized tubulin in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):479–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Alexander S. P. Kinetochores are transported poleward along a single astral microtubule during chromosome attachment to the spindle in newt lung cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):81–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowinsky E. K., Donehower R. C., Jones R. J., Tucker R. W. Microtubule changes and cytotoxicity in leukemic cell lines treated with taxol. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 15;48(14):4093–4100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowinsky E. K., Donehower R. C. The clinical pharmacology and use of antimicrotubule agents in cancer chemotherapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Oct;52(1):35–84. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Fant J., Horwitz S. B. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):665–667. doi: 10.1038/277665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1561–1565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan V. R., Speicher L. A., Tew K. D. The effects of estramustine on metaphase and anaphase in DU 145 prostatic carcinoma cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;54(2):268–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer W. D., Jordan M. A., Wilson L., Himes R. H. Binding of vinblastine to stabilized microtubules. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;36(3):366–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher L. A., Barone L., Tew K. D. Combined antimicrotubule activity of estramustine and taxol in human prostatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4433–4440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrower D., Jordan M. A., Wilson L. Quantitation of cellular tubulin in microtubules and tubulin pools by a competitive ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jan 24;136(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90248-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toso R. J., Jordan M. A., Farrell K. W., Matsumoto B., Wilson L. Kinetic stabilization of microtubule dynamic instability in vitro by vinblastine. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 9;32(5):1285–1293. doi: 10.1021/bi00056a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendell K. L., Wilson L., Jordan M. A. Mitotic block in HeLa cells by vinblastine: ultrastructural changes in kinetochore-microtubule attachment and in centrosomes. J Cell Sci. 1993 Feb;104(Pt 2):261–274. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Farrell K. W. Kinetics and steady state dynamics of tubulin addition and loss at opposite microtubule ends: the mechanism of action of colchicine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;466:690–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Miller H. P., Farrell K. W., Snyder K. B., Thompson W. C., Purich D. L. Taxol stabilization of microtubules in vitro: dynamics of tubulin addition and loss at opposite microtubule ends. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5254–5262. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]