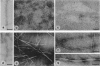
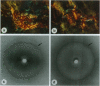
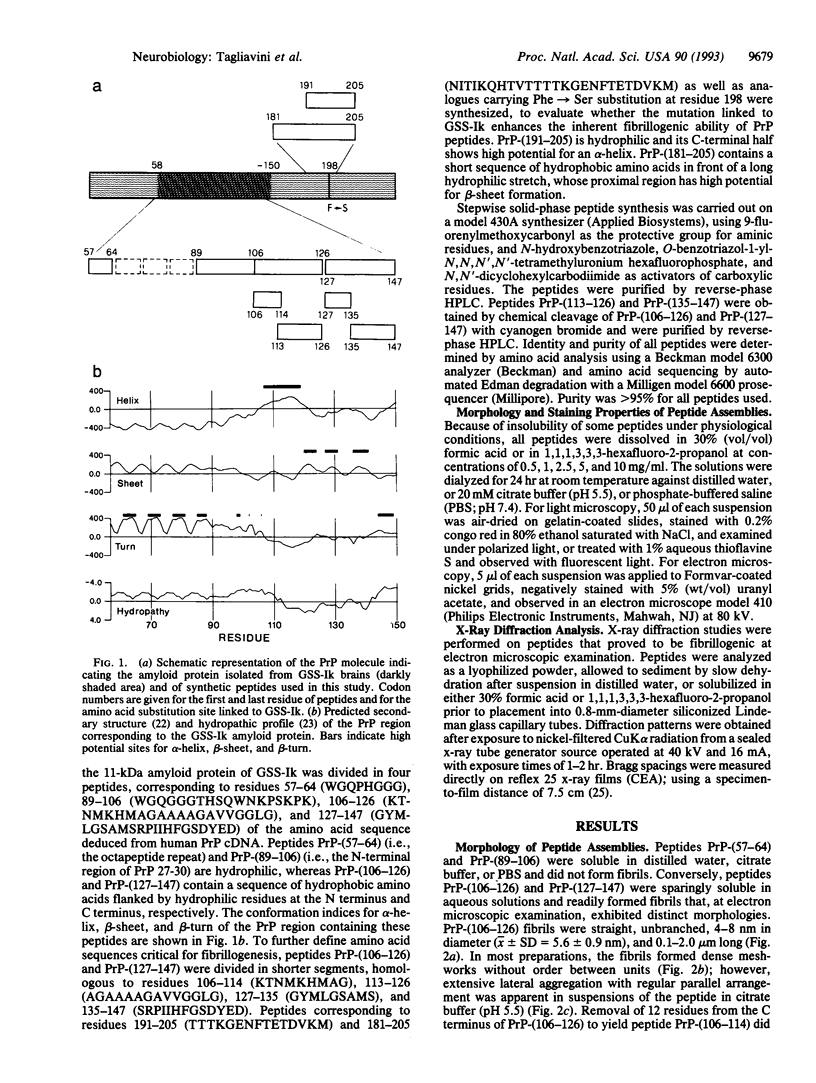
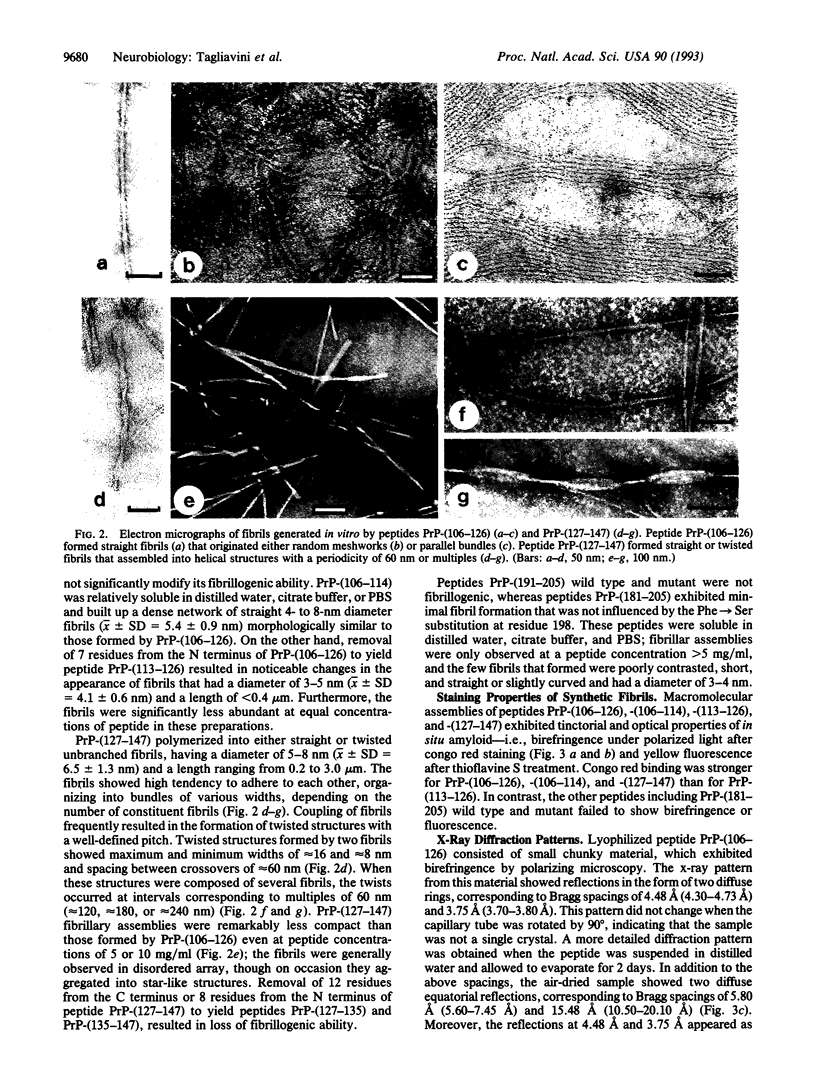
Abstract
Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease (GSS) is a prion-related encephalopathy pathologically characterized by massive deposition of prion protein (PrP) amyloid in the central nervous system. The major component of amyloid fibrils isolated from patients of the Indiana kindred of GSS (GSS-Ik) is an 11-kDa fragment of PrP spanning residues 58 to approximately 150. These patients carry a missense mutation of the PRNP gene, causing a Phe-->Ser substitution at codon 198. We investigated fibrillogenesis in vitro by using synthetic peptides homologous to consecutive segments of GSS-Ik amyloid protein (residues 57-64, 89-106, 106-126, and 127-147) as well as peptides from the PrP region with the GSS-Ik mutation (residues 191-205 and 181-205, both wild type and mutant). Peptide PrP-(106-126) formed straight fibrils similar to those extracted from GSS brains, whereas peptide PrP-(127-147) formed twisted fibrils resembling scrapie-associated fibrils isolated from subjects with transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Congo red staining and x-ray fibril diffraction showed that both straight and twisted fibrils had tinctorial and conformational properties of native amyloid. Conversely, the other peptides did not form amyloid-like fibrils under similar conditions. These findings suggest that the sequence spanning residues 106-147 of PrP is central to amyloid fibril formation in GSS and related encephalopathies.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño E. M., Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Inherited amyloids of the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Oct;1(3):448–454. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(91)90068-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Race R., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Bloom M., Lechner D., Bergstrom S., Robbins K., Mayer L., Keith J. M. Identification of scrapie prion protein-specific mRNA in scrapie-infected and uninfected brain. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):331–333. doi: 10.1038/315331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Gelderblom H., Hilmert H., Ozel M., Edelbluth C., Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie infectivity, fibrils and low molecular weight protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):476–478. doi: 10.1038/306476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dlouhy S. R., Hsiao K., Farlow M. R., Foroud T., Conneally P. M., Johnson P., Prusiner S. B., Hodes M. E., Ghetti B. Linkage of the Indiana kindred of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease to the prion protein gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):64–67. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doh-ura K., Tateishi J., Sasaki H., Kitamoto T., Sakaki Y. Pro----leu change at position 102 of prion protein is the most common but not the sole mutation related to Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):974–979. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forloni G., Angeretti N., Chiesa R., Monzani E., Salmona M., Bugiani O., Tagliavini F. Neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature. 1993 Apr 8;362(6420):543–546. doi: 10.1038/362543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P. E., Nguyen J. T., Inouye H., Surewicz W. K., Selkoe D. J., Podlisny M. B., Kirschner D. A. Fibril formation by primate, rodent, and Dutch-hemorrhagic analogues of Alzheimer amyloid beta-protein. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 10;31(44):10716–10723. doi: 10.1021/bi00159a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P. E., Nguyen J. T., Surewicz W. K., Kirschner D. A. pH-dependent structural transitions of Alzheimer amyloid peptides. Biophys J. 1991 Nov;60(5):1190–1201. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82154-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasset M., Baldwin M. A., Fletterick R. J., Prusiner S. B. Perturbation of the secondary structure of the scrapie prion protein under conditions that alter infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasset M., Baldwin M. A., Lloyd D. H., Gabriel J. M., Holtzman D. M., Cohen F., Fletterick R., Prusiner S. B. Predicted alpha-helical regions of the prion protein when synthesized as peptides form amyloid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10940–10944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghetti B., Tagliavini F., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K., Giaccone G., Verga L., Farlow M. R., Conneally P. M., Dlouhy S. R., Azzarelli B. Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. II. Neurofibrillary tangles and plaques with PrP-amyloid coexist in an affected family. Neurology. 1989 Nov;39(11):1453–1461. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.11.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone G., Tagliavini F., Verga L., Frangione B., Farlow M. R., Bugiani O., Ghetti B. Neurofibrillary tangles of the Indiana kindred of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease share antigenic determinants with those of Alzheimer disease. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 22;530(2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91304-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone G., Verga L., Bugiani O., Frangione B., Serban D., Prusiner S. B., Farlow M. R., Ghetti B., Tagliavini F. Prion protein preamyloid and amyloid deposits in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease, Indiana kindred. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9349–9353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Eanes E. D., Bladen H. A., Linke R. P., Termine J. D. Beta-pleated sheet fibrils. A comparison of native amyloid with synthetic protein fibrils. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1141–1158. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Eanes E. D., Wiley C. A. Amyloid fibrils formed from a segment of the pancreatic islet amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):608–614. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80538-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb L. G., Brown P., Haltia M., Ghiso J., Frangione B., Gajdusek D. C. Synthetic peptides corresponding to different mutated regions of the amyloid gene in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease show enhanced in vitro formation of morphologically different amyloid fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4451–4454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb L. G., Petersen R. B., Tabaton M., Brown P., LeBlanc A. C., Montagna P., Cortelli P., Julien J., Vital C., Pendelbury W. W. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: disease phenotype determined by a DNA polymorphism. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):806–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1439789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorevic P. D., Castano E. M., Sarma R., Frangione B. Ten to fourteen residue peptides of Alzheimer's disease protein are sufficient for amyloid fibril formation and its characteristic x-ray diffraction pattern. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):854–862. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K., Dlouhy S. R., Farlow M. R., Cass C., Da Costa M., Conneally P. M., Hodes M. E., Ghetti B., Prusiner S. B. Mutant prion proteins in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease with neurofibrillary tangles. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):68–71. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner D. A., Abraham C., Selkoe D. J. X-ray diffraction from intraneuronal paired helical filaments and extraneuronal amyloid fibers in Alzheimer disease indicates cross-beta conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):503–507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner D. A., Inouye H., Duffy L. K., Sinclair A., Lind M., Selkoe D. J. Synthetic peptide homologous to beta protein from Alzheimer disease forms amyloid-like fibrils in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6953–6957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar H. A., Prusiner S. B., Stowring L. E., DeArmond S. J. Scrapie prion proteins are synthesized in neurons. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jan;122(1):1–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Carman M. D., Fernandez-Madrid I. J., Power M. D., Lieberburg I., van Duinen S. G., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Mutation of the Alzheimer's disease amyloid gene in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage, Dutch type. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1124–1126. doi: 10.1126/science.2111584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Haltia M., Fernandez-Madrid I., Koivunen O., Ghiso J., Prelli F., Frangione B. Mutation in gelsolin gene in Finnish hereditary amyloidosis. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1865–1867. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury C. P. Gelsolin-related amyloidosis. Identification of the amyloid protein in Finnish hereditary amyloidosis as a fragment of variant gelsolin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1195–1199. doi: 10.1172/JCI115118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury C. P., Nurmiaho-Lassila E. L. Creation of amyloid fibrils from mutant Asn187 gelsolin peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91632-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Bolton D. C., Prusiner S. B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Rohwer R. G., Kascsak R., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):437–440. doi: 10.1126/science.6377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelli F., Levy E., van Duinen S. G., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Expression of a normal and variant Alzheimer's beta-protein gene in amyloid of hereditary cerebral hemorrhage, Dutch type: DNA and protein diagnostic assays. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91274-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Bolton D. C., Groth D. F., Bowman K. A., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P. Further purification and characterization of scrapie prions. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6942–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Chemistry and biology of prions. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12277–12288. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Bolton D. C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Purification and structural studies of a major scrapie prion protein. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90533-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Borchelt D. R., Hsiao K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie prion protein contains a phosphatidylinositol glycolipid. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Giaccone G., Prelli F., Verga L., Porro M., Trojanowski J. Q., Farlow M. R., Frangione B., Ghetti B., Bugiani O. A68 is a component of paired helical filaments of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease, Indiana kindred. Brain Res. 1993 Jul 9;616(1-2):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90226-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Prelli F., Ghiso J., Bugiani O., Serban D., Prusiner S. B., Farlow M. R., Ghetti B., Frangione B. Amyloid protein of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease (Indiana kindred) is an 11 kd fragment of prion protein with an N-terminal glycine at codon 58. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):513–519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Prelli F., Porro M., Salmona M., Bugiani O., Frangione B. A soluble form of prion protein in human cerebrospinal fluid: implications for prion-related encephalopathies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1398–1404. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Ghiso J., Frangione B. Peptides homologous to the amyloid protein of Alzheimer's disease containing a glutamine for glutamic acid substitution have accelerated amyloid fibril formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1247–1254. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91706-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]