Figure 1.
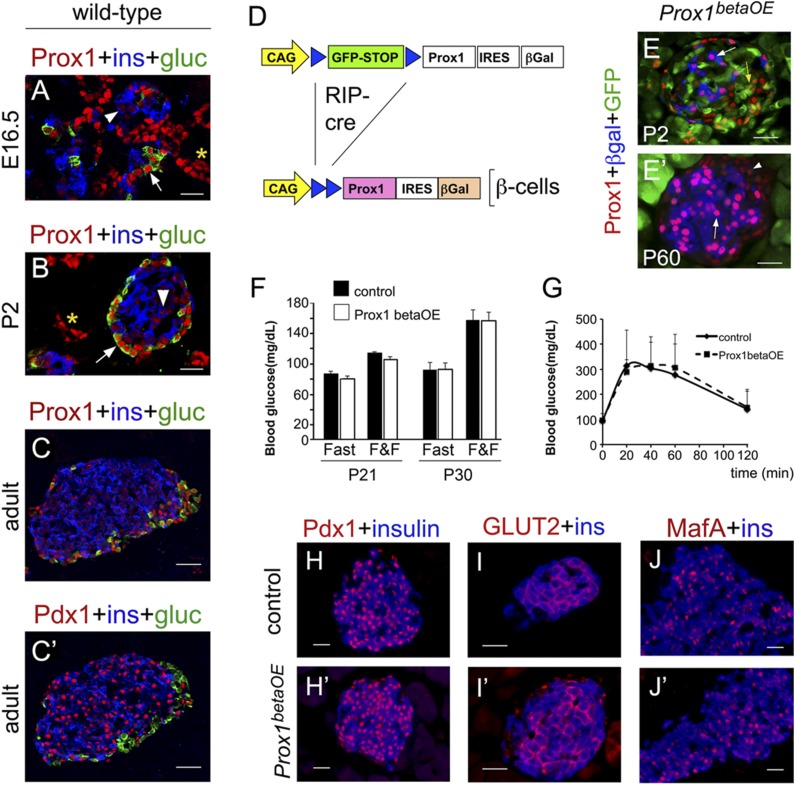
Prox1 upregulation does not affect mature β-cell function. Prox1 (red) was expressed at very low levels in insulin+ cells (blue, arrowheads) and at high levels in glucagon+ cells (green, arrows) in the pancreata of wild-type mouse embryos (A), newborns (B), and adults (C). Asterisks indicate Prox1 expression in the pancreatic ducts. C′: Compared with Prox1, Pdx1 (red) levels were noticeably higher in insulin+ pancreatic cells (blue). C and C′ are consecutive sections. D: RIP-Cre–mediated excision of a GFP-STOP cassette in the Jojo-Prox1 transgene activated the expression of exogenous Prox1 and the β-gal reporter in β-cells of Prox1betaOE mice. E: Very few cells expressed the β-gal reporter (blue, arrow) and high Prox1 (red) in Prox1betaOE pancreata at P2. GFP expression (green) denoting lack of Cre activity was very extensive in the islet core (yellow arrow) at this stage. E′: Numerous cells expressed high Prox1 (red, arrow) and β-gal (blue) throughout the islet core in Prox1betaOE adult pancreata. The arrowhead indicates Prox1 normal expression in peripheral islet cells. Both the blood glucose levels under fed (fast and fed [F&F]) and fasting (Fast) conditions (F) and the glucose clearance response (G) were comparable between Prox1betaOE and control mice (RIP-Cre). The expression of Pdx1 (red [H and H′]), GLUT2 (red [I and I′]), and MafA (red [J and J′]) in insulin+ cells (blue) was indistinguishable between control (RIP-Cre [H–J]) and Prox1betaOE (H′–J′) adult pancreata. A–C and C′ are confocal images. G: Error bars represent +SEM values; n = 5–6 mice per genotype. Scale bars: 25 μm.