Abstract
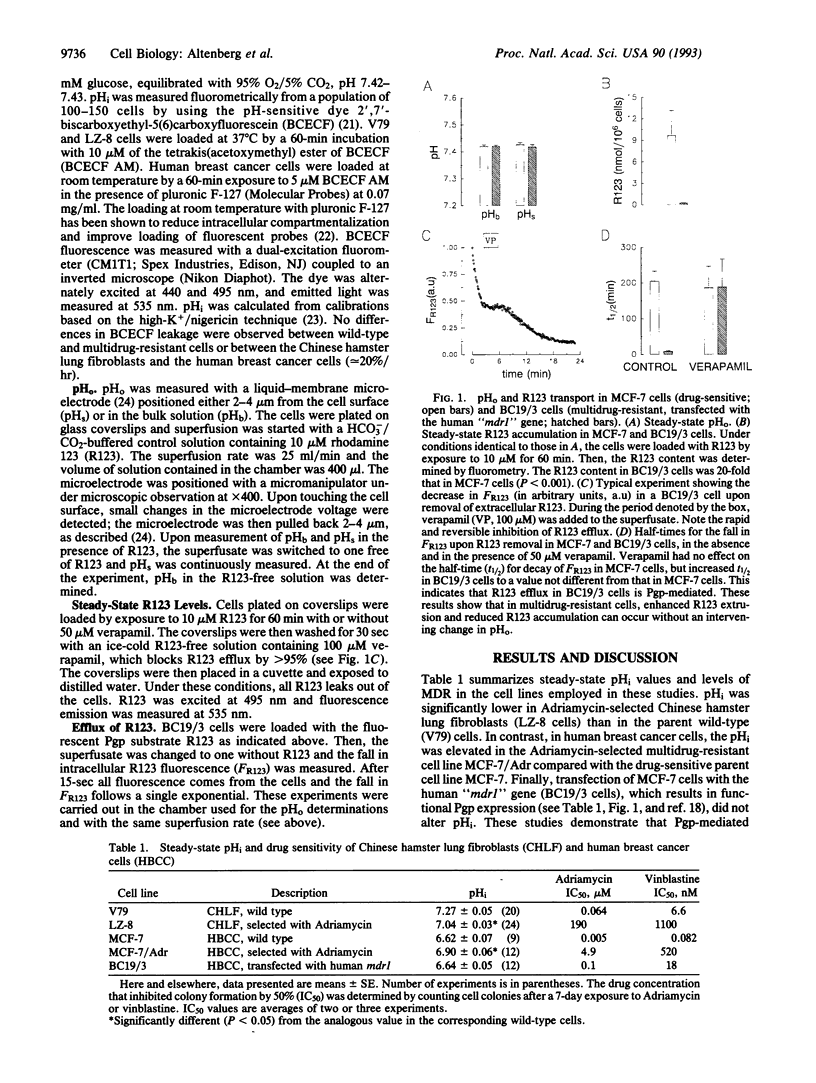
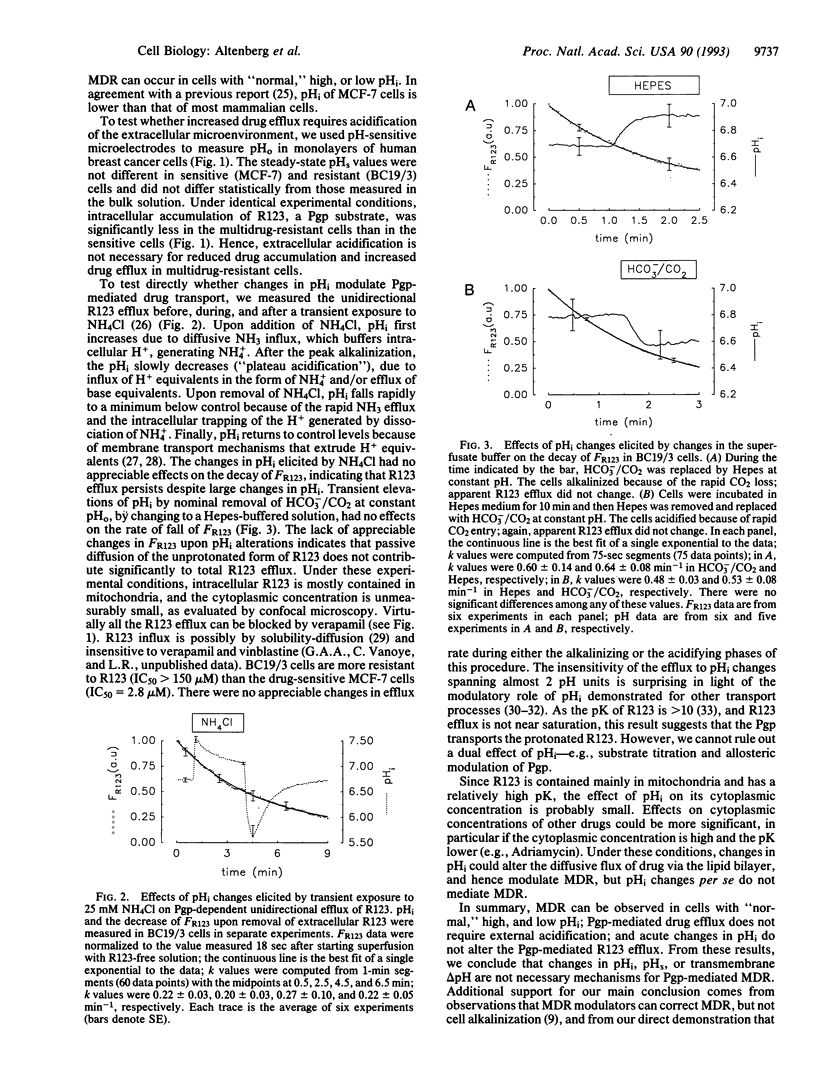
P-glycoprotein (Pgp)-mediated multidrug resistance (MDR) is thought to result from active extrusion of lipid-soluble, titratable chemotherapeutic agents. Given the lack of demonstration of coupling between ATP hydrolysis and drug transport, the resistance to chemically unrelated compounds, and findings of elevated intracellular pH (pHi), it has been proposed that reduced intracellular accumulation of drugs in MDR is due to changes in the pH difference across the plasma membrane. Elevation of pHi or decrease in local extracellular pH (pHo) could reduce the intracellular accumulation of the protonated chemotherapeutic drugs and account for Pgp-mediated MDR. Alternatively, changes in pHi or pHo could increase drug efflux by other mechanisms, such as coupled transport involving H+ or OH-, or allosteric effects on Pgp or other proteins. Both mechanisms could operate independently of the charge of the substrate. The possibility of a role of pHi in drug efflux is important to test because of the clinical significance of the phenomenon of MDR of tumors. We tested this hypothesis and found that MDR can occur in cells with low, normal, or high pHi. Further, resistant cells exhibited reduced steady-state drug accumulation and increased efflux without changes in local pHo. Finally, acute changes in pHi had no appreciable effect on Pgp-mediated drug efflux. We conclude that Pgp-mediated MDR is not a consequence of changes in pHi or pHo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenberg G., Copello J., Cotton C., Dawson K., Segal Y., Wehner F., Reuss L. Electrophysiological methods for studying ion and water transport in Necturus gall bladder epithelium. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:650–683. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92101-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambudkar S. V., Lelong I. H., Zhang J., Cardarelli C. O., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Partial purification and reconstitution of the human multidrug-resistance pump: characterization of the drug-stimulatable ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8472–8476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S., Nee J., Suhm M. A. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):161–163. doi: 10.1038/299161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., De Weer P. Intracellular pH transients in squid giant axons caused by CO2, NH3, and metabolic inhibitors. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jan;67(1):91–112. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boscoboinik D., Gupta R. S., Epand R. M. Investigation of the relationship between altered intracellular pH and multidrug resistance in mammalian cells. Br J Cancer. 1990 Apr;61(4):568–572. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B. Mitochondrial membrane potential in living cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:155–181. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalmark M., Storm H. H. A Fickian diffusion transport process with features of transport catalysis. Doxorubicin transport in human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Oct;78(4):349–364. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.4.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demant E. J., Sehested M., Jensen P. B. A model for computer simulation of P-glycoprotein and transmembrane delta pH-mediated anthracycline transport in multidrug-resistant tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 12;1055(2):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90111-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doige C. A., Yu X., Sharom F. J. ATPase activity of partially purified P-glycoprotein from multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 24;1109(2):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90078-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C., Hamilton K. L., Johnson K. E. Intracellular acidosis blocks the basolateral Na-K pump in rabbit urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 2):F946–F954. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.6.F946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild C. R., Moscow J. A., O'Brien E. E., Cowan K. H. Multidrug resistance in cells transfected with human genes encoding a variant P-glycoprotein and glutathione S-transferase-pi. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;37(6):801–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frezard F., Garnier-Suillerot A. Determination of the osmotic active drug concentration in the cytoplasm of anthracycline-resistant and -sensitive K562 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 10;1091(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90217-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., Belli T. A., Zaczkiewicz L. T., Belli J. A. High-level, unstable adriamycin resistance in a Chinese hamster mutant cell line with double minute chromosomes. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):4023–4029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer H. G., Joenje H. Increased cytosolic pH in multidrug-resistant human lung tumor cells: effect of verapamil. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 May 3;81(9):706–709. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.9.706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H. Regulation of intracellular pH in eukaryotic cells. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):1–8. doi: 10.1042/bj2500001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Zaguilán R., Gillies R. J. A plasma membrane V-type H(+)-ATPase may contribute to elevated intracellular pH (pHin) in some human tumor cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Nov 30;671:478–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb43834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micro-electrode measurement of the intracellular pH and buffering power of mouse soleus muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;267(3):791–810. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negulescu P. A., Machen T. E. Intracellular ion activities and membrane transport in parietal cells measured with fluorescent dyes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:38–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92062-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Cytoplasmic pH and free Mg2+ in lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepe P. D. Analysis of the steady-state and initial rate of doxorubicin efflux from a series of multidrug-resistant cells expressing different levels of P-glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 22;31(50):12555–12564. doi: 10.1021/bi00165a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roninson I. B., Abelson H. T., Housman D. E., Howell N., Varshavsky A. Amplification of specific DNA sequences correlates with multi-drug resistance in Chinese hamster cells. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):626–628. doi: 10.1038/309626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkadi B., Price E. M., Boucher R. C., Germann U. A., Scarborough G. A. Expression of the human multidrug resistance cDNA in insect cells generates a high activity drug-stimulated membrane ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4854–4858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoelstra E. C., Westerhoff H. V., Dekker H., Lankelma J. Kinetics of daunorubicin transport by P-glycoprotein of intact cancer cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 15;207(2):567–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiebaut F., Currier S. J., Whitaker J., Haugland R. P., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Activity of the multidrug transporter results in alkalinization of the cytosol: measurement of cytosolic pH by microinjection of a pH-sensitive dye. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 May;38(5):685–690. doi: 10.1177/38.5.1692055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Buchsbaum R. N., Zimniak A., Racker E. Intracellular pH measurements in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells utilizing spectroscopic probes generated in situ. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2210–2218. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Okamura N., Hirai M., Tanigawara Y., Saeki T., Kioka N., Komano T., Hori R. Human P-glycoprotein transports cortisol, aldosterone, and dexamethasone, but not progesterone. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24248–24252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamora J. M., Pearce H. L., Beck W. T. Physical-chemical properties shared by compounds that modulate multidrug resistance in human leukemic cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;33(4):454–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Sweet K. M., Sognier M. A., Belli J. A. An enhanced ability for transforming adriamycin into a noncytotoxic form in a multidrug-resistant cell line (LZ-8). Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Nov 3;44(9):1869–1877. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90083-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


