Figure 2. Reconstruction of a multi-scale lobule image.
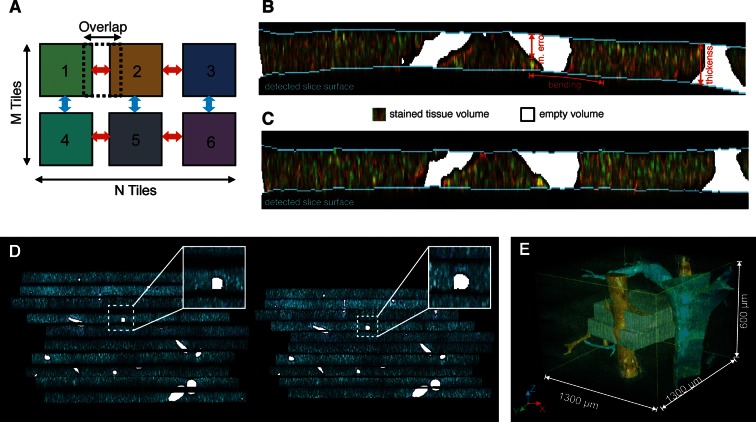
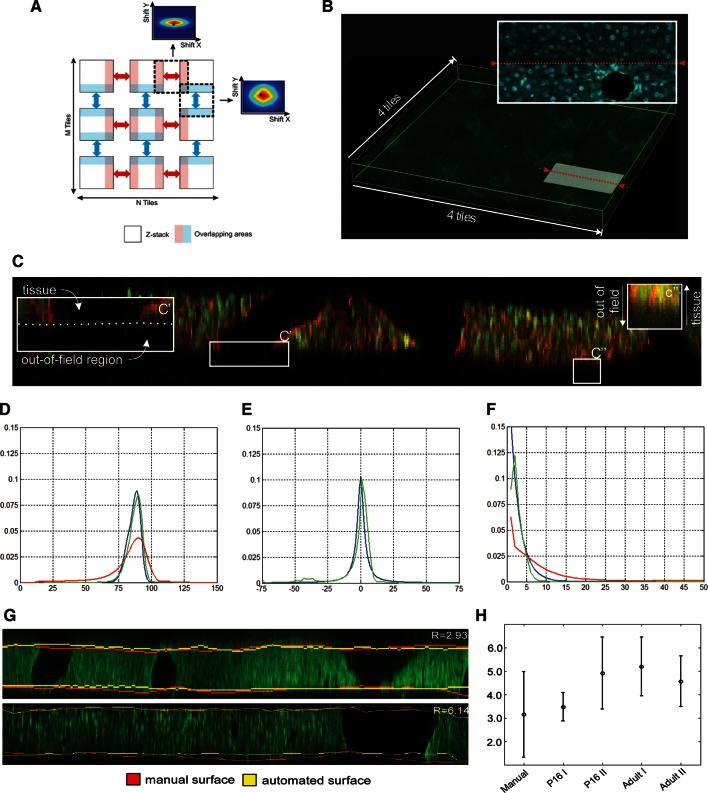
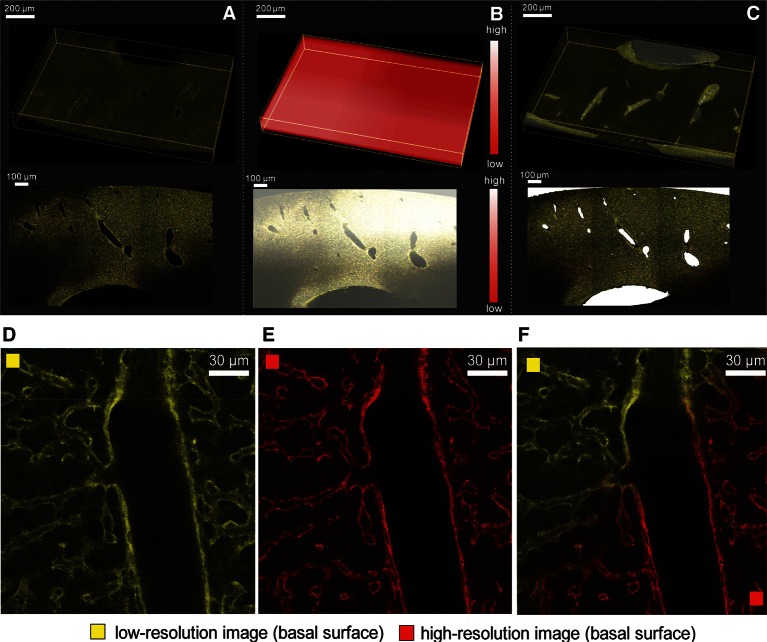
(A) Schematic representing a single serial section obtained from a grid of M × N partially overlapping 3D images (tiles). The cross-correlation between two neighbouring tiles in the grid provides a local metric, which describes the value of their relative shifts. The reconstruction of each section was performed by maximizing the sum correlations of each tile to all adjacent tiles (see ‘Methods’ for details). (B, C) Correction of tissue deformations (introduced during the sample preparation process) using a surface detection algorithm and β-spline transformation. (B) Output of the surface detection algorithm. The proposed Bayesian approach uses prior information about expected bending of the section, its thickness and measurement error (see ‘Methods’ for details) to determine the volume of the image belonging to the tissue and to the out-of-field region. (C) The tissue section after correcting its bending by using quadratic β-splines. (D) Tissue section before (left) and after (right) the correction of the mechanical distortions and the tissue damage. (E) Full lobule-level reconstruction established by the alignment of six low-resolution sections (1 μm × 1 μm × 1 μm per voxel) and the interpolation of blood vessels. Two high-resolution images (0.3 μm × 0.3 μm × 0.3 μm per voxel) were registered in the low-resolution reconstruction and are shown in grey (see Video 1).