Abstract
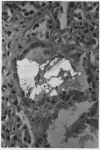
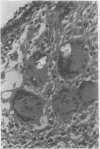
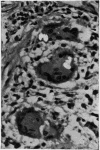
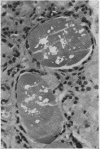
Oxalosis is the histological manifestation of a number of diverse clinicopathological states involving abnormalities of both endogenous and exogenous oxalate. Crystalline deposits of calcium oxalate, usually first detected by their birefringence, may be characterised by a combination of their physical and tinctorial properties.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHER H. E., DORMER A. E., SCOWEN E. F., WATTS R. W. The aetiology of primary hyperoxaluria. Br Med J. 1958 Jan 25;1(5064):175–181. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5064.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen A. C. Acute lobular (membranoproliferative) glomerulonephritis with hyperuricemia and obstructive uric acid nephropathy. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976 Jan;65(1):109–120. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/65.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbus G. S., Sniderman S. Oxalosis with peripheral gangrene. Arch Pathol. 1974 Feb;97(2):107–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aufderheide A. C. Renal tubular calcium oxalate crystal deposition. Its possible relation to methoxyflurane anesthesia. Arch Pathol. 1971 Sep;92(3):162–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNINGTON J. L., HABER S. L., SMITH J. V., WARNER N. E. CRYSTALS OF CALCIUM OXALATE IN THE HUMAN KIDNEY. STUDIES BY MEANS OF ELECTRON MICROPROBE AND X-RAY DIFFRACTION. Am J Clin Pathol. 1964 Jan;41:8–14. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/41.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beppu T., Mori S., Omoto R., Nishi T., Oya G. [Secondary oxalosis after ileocecal resection-report of two autopsy cases and review of the literature (author's transl)]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1975 May;72(5):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrand A., Collste L. G., Franksson C., Glas J. E., Löfström B., Magnusson G., Nordenstam H., Werner B. Oxalosis in renal transplants following methoxyflurane anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 1972 Jun;44(6):569–574. doi: 10.1093/bja/44.6.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisaillon S., Tawashi R. Growth of calcium oxalate in gel systems. J Pharm Sci. 1975 Mar;64(3):458–460. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600640325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquist L., Lindqvist B., Ostberg Y., Steen L. Primary oxalosis. Am J Med. 1973 May;54(5):673–681. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourke E., Costello J. The clinical importance of oxalic acid. Ir Med J. 1975 Feb 22;68(4):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bove K. E. Ethylene glycol toxicity. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jan;45(1):46–50. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/45.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. Letter: Vitamin-C-induced hyperoxaluria. Lancet. 1976 Jan 17;1(7951):154–154. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)93207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock J. D., Albert D. M., Skinner H. C., Miller W. H., Galla J. H. Calcium oxalate retinopathy associated with generalized oxalosis: x-ray diffraction and electron microscopic studies of crystal deposits. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Apr;13(4):256–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COGAN D. G., KUWABARA T., SILBERT J., KERN H., McMURRAY V., HURLBUT C. Calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate crystals in detached retinas. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1958 Sep;60(3):366–371. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1958.00940080382004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin A. J. Calcium pyrophosphate. Histological characterization of crystals in pseudogout. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Jan;100(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin A. J., Grace S. R. An evaluation of some complexing methods for the histochemistry of calcium. Histochemistry. 1976 Jun 28;47(3):263–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00489968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin A. J., Grace S. R. Calcium oxalate and the von Kossa method with reference to the influence of citric acid. Histochem J. 1975 Sep;7(5):451–458. doi: 10.1007/BF01003882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin A. J. Some observations on the demonstration of calcium oxalate in tissue sections. Stain Technol. 1974 May;49(3):165–173. doi: 10.3109/10520297409116970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M., Hofhkinson A., Zarembski P. M., Anderson C. K. Hyperoxaluria in adults. Br J Surg. 1968 Feb;55(2):121–128. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800550213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltart D. J., Hudson R. E. Primary oxalosis of the heart: a cause of heart block. Br Heart J. 1971 Mar;33(2):315–319. doi: 10.1136/hrt.33.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton J. R., Jr, Schwartz M. M., Lindley J. D., Hunsicker L. G. Acute renal failure following halothane anesthesia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Dec;100(12):628–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crampton R. F., Charlesworth F. A. Occurrence of natural toxins in food. Br Med Bull. 1975 Sep;31(3):209–213. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Garber A. J., Hoffsten P., Lucas B., Wise L. Renal failure after small intestinal bypass for obesity. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Dec;135(12):1610–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIELS R. A., MICHELS R., AISEN P., GOLDSTEIN G. Familial hyperoxaluria. Report of a family, review of the literature. Am J Med. 1960 Nov;29:820–831. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMPSEY E. F., FORBES A. P., MELICK R. A., HENNEMAN P. H. Urinary oxalate excretion. Metabolism. 1960 Jan;9:52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deodhar S. D., Tung K. S., Zühlke V., Nakamoto S. Renal homotransplantation in a patient with primary familial oxalosis. Arch Pathol. 1969 Jan;87(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling R. H., Rose G. A., Sutor D. J. Hyperoxaluria and renal calculi in ileal disease. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1103–1106. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91840-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle W. F., Brahman H. D., Burgess J. H. The nature of yellow-brown bodies in peritoneal lymph nodes. Arch Pathol. 1973 Nov;96(5):320–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyke P. C., Hajdu S. I., Strong E. W., Erlandson R. A., Fleisher M. Mixed tumor of parotid containing calcium oxalate crystals. Arch Pathol. 1971 Jan;91(1):89–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnest D. L., Johnson G., Williams H. E., Admirand W. H. Hyperoxaluria in patients with ileal resection: an abnormality in dietary oxalate absorption. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jun;66(6):1114–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. W., Phillips G., Mukherjee T. M., Snow M. R., Lawrence J. R., Thomas D. W. Identification of crystals deposited in brain and kidney after xylitol administration by biochemical, histochemical, and electron diffraction methods. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Jan;26(1):32–36. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FANGER H., ESPARZA A. CRYSTALS OF CALCIUM OXALATE IN KIDNEYS IN UREMIA. Am J Clin Pathol. 1964 Jun;41:597–603. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/41.6.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOCKS M., LITTWIN C. S., ZIMMERMAN L. E. Phacolytic glaucoma; a clinicopathologic study of one hundred thirty-eight cases of glaucoma associated with hypermature cataract. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1955 Jul;54(1):37–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN E. A., GREENBERG J. B., MERRILL J. P., DAMMIN G. J. Consequences of ethylene glycol poisoning. Report of four cases and review of the literature. Am J Med. 1962 Jun;32:891–902. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco V., Krinitz B. Determination of oxalic acid in foods. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1973 Jan;56(1):164–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. H., Charles N. C. Retinal oxalosis in two diabetic patients. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 Aug;78(2):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(74)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERSHOFF S. N., FARAGALLA F. F., NELSON D. A., ANDRUS S. B. Vitamin B6 deficiency and oxalate nephrocalcinosis in the cat. Am J Med. 1959 Jul;27(1):72–80. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GESSNER P. K., PARKE D. V., WILLIAMS R. T. Studies in detoxication. 86. The metabolism of 14C-labelled ethylene glycol. Biochem J. 1961 Jun;79:482–489. doi: 10.1042/bj0790482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS S. Granulomatous thyroiditis with anisotropic crystalline material. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Apr;59(4):412–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner A. Retinal oxalosis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1974 Jun;58(6):613–619. doi: 10.1136/bjo.58.6.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand S. G., Taranto A. I. Letter: Hyperoxaluria and Meckel's diverticulum. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):748–749. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-748_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCKADAY T. D., CLAYTON J. E., FREDERICK E. W., SMITH L. H., Jr PRIMARY HYPEROXALURIA. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 May;43:315–345. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196405000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES D. T. The clinical and pathological background of two cases of oxalosis. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Nov;12:498–509. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.6.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. B. Letter: Vitamin-C-induced hyperoxaluria. Lancet. 1976 Feb 14;1(7955):366–366. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Chalmers R. A., Lawson A. M., Schultis K., Watts R. W. Metabolic investigations after xylitol infusion in human subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Mar;29(3):258–273. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschildt S., Watts R. W. Studies on the effect of xylitol on oxalate formation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Jan;25(1):27–29. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkinson A., Zarembski P. M. Oxalic acid metabolism in man: a review. Calcif Tissue Res. 1968 Oct 21;2(2):115–132. doi: 10.1007/BF02279201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen L. H., Groeneveld J. L., Van Der Meer J. B. Deposition of calcium oxalate in the skin in two patients suffering from oxalosis caused by primary hyperoxaluria. Arch Dermatol Forsch. 1974;250(4):323–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00558193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen O. A. Calcium oxalate crystals localized in the eye. Subretinal and retinal deposits, including deposits in the pigment epithelium. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1975 Mar;53(2):187–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1975.tb01153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOTEN J. W., VAN GASTEL, MEES E. J., HOLLEMAN L. W., SCHUILING R. D. TWO CASES OF PRIMARY OXALOSIS. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Mar;18:223–229. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnett J. G., Bullough P. G. Identification of calcium oxalate deposits in bone by electron diffraction. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Dec;100(12):656–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klauwers J., Wolf P. L., Cohn R. Failure of renal transplantation in primary oxalosis. JAMA. 1969 Jul 28;209(4):551–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurrein F., Green G. H., Rowles S. L. Localized deposition of calcium oxalate around a pulmonary Aspergillus niger fungus ball. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Oct;64(4):556–563. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/64.4.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzucu E. Y. Methoxyflurane, tetracycline, and renal failure. JAMA. 1970 Feb 16;211(7):1162–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. D., Lowenstam H. A., Rossman G. R. Oxalate nephrosis and crystalline myocarditis. Case report with postmortem and crystallographic studies. Arch Pathol. 1974 Sep;98(3):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm J. Intra-vitam diagnosis of oxalosis. Acta Med Scand. 1965 Aug;178(2):155–159. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1965.tb04259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACALUSO M. P., BERG N. O. Calcium oxalate crystals in kidneys in acute tubular nephrosis and other renal diseases with functional failure. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1959;46:197–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1959.tb00330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazze R. I., Trudell J. R., Cousins M. J. Methoxyflurane metabolism and renal dysfunction: clinical correlation in man. Anesthesiology. 1971 Sep;35(3):247–252. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197109000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCollum J. P., Packer S., Manning J., Harries J. T. Proceedings: Hyperoxaluria in children with hepatic and intestinal dysfunction. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Sep;49(9):749–749. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.9.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGEE-RUSSELL S. M. Histochemical methods for calcium. J Histochem Cytochem. 1958 Jan;6(1):22–42. doi: 10.1177/6.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgram J. W., Salyer W. R. Secondary oxalosis of bone in chronic renal failure. A histopathological study of three cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974 Mar;56(2):387–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr W., Hey D. Endogene Oxalose mit Manifestation im Erwachsenenalter. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1969;347(2):185–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nime F. A., Hutchins G. M. Oxalosis caused by aspergilus infection. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1973 Oct;133(4):183–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON B. J., KUHN R. J. OPTICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF CRYSTALS IN TISSUE: CYSTINE AND CALCIUM OXALATE MONOHYDRATE. Am J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;43:401–408. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/43.5.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIZZOLATO P. HISTOCHEMICAL RECOGNITION OF CALCIUM OXALATE. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 May;12:333–336. doi: 10.1177/12.5.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzolato P., Lillie R. D. The impregnation of bone and patholigic calcification by metal salts and their recognition by unoxidized hematoxylin. Histochemie. 1968;16(4):333–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00306356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzolato P. Mercurous nitrate as a histochemical reagent for calcium phosphate in bone and pathological calcification and for calcium oxalate. Histochem J. 1971 Nov;3(6):463–469. doi: 10.1007/BF01014785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHTER M. N., McCARTY K. S. Anisotropic crystals in the human thyroid gland. Am J Pathol. 1954 May-Jun;30(3):545–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscher A. A. A new histochemical method for the demonstration of calcium oxalate in tissues following ethylene glycol poisoning. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Jan;55(1):99–104. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughan P. G., Slack C. R. Simple methods for routine screening and quantitative estimation of oxalate content of tropical grasses. J Sci Food Agric. 1973 Jul;24(7):803–811. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740240708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOWEN E. F., STANSFELD A. G., WATTS R. E. Oxalosis and primary hyperoxaluria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Jan;77(1):195–205. doi: 10.1002/path.1700770119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAUFFER M. Oxalosis. Report of a case, with a review of the literature and discussion of the pathogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1960 Aug 25;263:386–390. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196008252630805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyer W. R., Hutchins G. M. Cardiac lesions in secondary oxalosis. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Aug;134(2):250–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyer W. R., Keren D. Oxalosis as a complication of chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 1973 Jul;4(1):61–66. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyer W. R., Salyer D. C. Thiamine deficiency and oxalosis. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jul;27(7):558–559. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.7.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders D. R., Sillery J., McDonald G. B. Regional differences in oxalate absorption by rat intestine: evidence for excessive absorption by the colon in steatorrhoea. Gut. 1975 Jul;16(7):543–548. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.7.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder R., De Lacroix W. F., Franzen U., Klein P. J., Müller W. Therapie-bedingte Form einer reno-cerebralen Oxalose? Acta Neuropathol. 1974 Feb 28;27(2):181–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00687169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutor D. J. Growth studies of calcium oxalate in the presence of various ions and compounds. Br J Urol. 1969 Apr;41(2):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1969.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALLQVIST H., VAANANEN I. Death of a child from oxalic acid poisoning due to eating rhubarb leaves. Ann Paediatr Fenn. 1960;6:144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Edwards J. B., Gilligan J. E., Lawrence J. R., Edwards R. G. Complications following intravenous administration of solutions containing xylitol. Med J Aust. 1972 Jun 10;1(24):1238–1246. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1972.tb116530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOIGT G. E. Der histochemische Nachweis des Calciums im Calciumoxalat bei der Athylenglykolvergiftung. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1957;41(2):89–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainder M., Kelly J. Renal tubular dysfunction secondary to jejunoileal bypass. JAMA. 1976 Mar 22;235(12):1257–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valman H. B., Oberholzer V. G., Palmer T. Hyperoxaluria after resection of ileum in childhood. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Mar;49(3):171–173. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.3.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen C. W., Lyon E. S. Mechanisms of genesis and growth of calculi. Am J Med. 1968 Nov;45(5):684–692. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. W. Oxaluria. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1973 Jan;7(2):161–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams H. E., Smith L. H., Jr Disorders of oxalate metabolism. Am J Med. 1968 Nov;45(5):715–735. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolman M. Polarized light microscopy as a tool of diagnostic pathology. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Jan;23(1):21–50. doi: 10.1177/23.1.1090645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN L. E., JOHNSON F. B. Calcium oxalate crystals within ocular tissues; a clinicopathologic and histochemical study. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1958 Sep;60(3):372–383. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1958.00940080388005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarembski P. M., Hodgkinson A., Parsons F. M. Elevation of the concentration of plasma oxalic acid in renal failure. Nature. 1966 Oct 29;212(5061):511–512. doi: 10.1038/212511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarembski P. M., Hodgkinson A. Plasma oxalic acid and calcium levels in oxalate poisoning. J Clin Pathol. 1967 May;20(3):283–285. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]